An approximate introduction to how zk-SNARKs are possible (part 1)
You can make a proof for the statement "I know a secret number such that if you take the word ‘cow', add the number to the end, and SHA256 hash it 100 million times, the output starts with 0x57d00485aa". The verifier can verify the proof far more quickly than it would take for them to run 100 million hashes themselves, and the proof would also not reveal what the secret number is.
In the context of blockchains, this has 2 very powerful applications: Perhaps the most powerful cryptographic technology to come out of the last decade is general-purpose succinct zero knowledge proofs, usually called zk-SNARKs ("zero knowledge succinct arguments of knowledge"). A zk-SNARK allows you to generate a proof that some computation has some particular output, in such a way that the proof can be verified extremely quickly even if the underlying computation takes a very long time to run. The "ZK" part adds an additional feature: the proof can keep some of the inputs to the computation hidden.
You can make a proof for the statement "I know a secret number such that if you take the word ‘cow', add the number to the end, and SHA256 hash it 100 million times, the output starts with 0x57d00485aa". The verifier can verify the proof far more quickly than it would take for them to run 100 million hashes themselves, and the proof would also not reveal what the secret number is.
In the context of blockchains, this has two very powerful applications:
- Scalability: if a block takes a long time to verify, one person can verify it and generate a proof, and everyone else can just quickly verify the proof instead
- Privacy: you can prove that you have the right to transfer some asset (you received it, and you didn't already transfer it) without revealing the link to which asset you received. This ensures security without unduly leaking information about who is transacting with whom to the public.
But zk-SNARKs are quite complex; indeed, as recently as in 2014-17 they were still frequently called "moon math". The good news is that since then, the protocols have become simpler and our understanding of them has become much better. This post will try to explain how ZK-SNARKs work, in a way that should be understandable to someone with a medium level of understanding of mathematics.
Why ZK-SNARKs "should" be hard
Let us take the example that we started with: we have a number (we can encode "cow" followed by the secret input as an integer), we take the SHA256 hash of that number, then we do that again another 99,999,999 times, we get the output, and we check what its starting digits are. This is a huge computation.
A "succinct" proof is one where both the size of the proof and the time required to verify it grow much more slowly than the computation to be verified. If we want a "succinct" proof, we cannot require the verifier to do some work per round of hashing (because then the verification time would be proportional to the computation). Instead, the verifier must somehow check the whole computation without peeking into each individual piece of the computation.
One natural technique is random sampling: how about we just have the verifier peek into the computation in 500 different places, check that those parts are correct, and if all 500 checks pass then assume that the rest of the computation must with high probability be fine, too?
Such a procedure could even be turned into a non-interactive proof using the Fiat-Shamir heuristic: the prover computes a Merkle root of the computation, uses the Merkle root to pseudorandomly choose 500 indices, and provides the 500 corresponding Merkle branches of the data. The key idea is that the prover does not know which branches they will need to reveal until they have already "committed to" the data. If a malicious prover tries to fudge the data after learning which indices are going to be checked, that would change the Merkle root, which would result in a new set of random indices, which would require fudging the data again... trapping the malicious prover in an endless cycle.
But unfortunately there is a fatal flaw in naively applying random sampling to spot-check a computation in this way: computation is inherently fragile. If a malicious prover flips one bit somewhere in the middle of a computation, they can make it give a completely different result, and a random sampling verifier would almost never find out.
It only takes one deliberately inserted error, that a random check would almost never catch, to make a computation give a completely incorrect result.
If tasked with the problem of coming up with a zk-SNARK protocol, many people would make their way to this point and then get stuck and give up. How can a verifier possibly check every single piece of the computation, without looking at each piece of the computation individually? There is a clever solution.
see part 2
(Edited)
More on Web3 & Crypto

ANDREW SINGER
3 years ago
Crypto seen as the ‘future of money’ in inflation-mired countries
Crypto as the ‘future of money' in inflation-stricken nations
Citizens of devalued currencies “need” crypto. “Nice to have” in the developed world.
According to Gemini's 2022 Global State of Crypto report, cryptocurrencies “evolved from what many considered a niche investment into an established asset class” last year.
More than half of crypto owners in Brazil (51%), Hong Kong (51%), and India (54%), according to the report, bought cryptocurrency for the first time in 2021.
The study found that inflation and currency devaluation are powerful drivers of crypto adoption, especially in emerging market (EM) countries:
“Respondents in countries that have seen a 50% or greater devaluation of their currency against the USD over the last decade were more than 5 times as likely to plan to purchase crypto in the coming year.”
Between 2011 and 2021, the real lost 218 percent of its value against the dollar, and 45 percent of Brazilians surveyed by Gemini said they planned to buy crypto in 2019.
The rand (South Africa's currency) has fallen 103 percent in value over the last decade, second only to the Brazilian real, and 32 percent of South Africans expect to own crypto in the coming year. Mexico and India, the third and fourth highest devaluation countries, followed suit.
Compared to the US dollar, Hong Kong and the UK currencies have not devalued in the last decade. Meanwhile, only 5% and 8% of those surveyed in those countries expressed interest in buying crypto.
What can be concluded? Noah Perlman, COO of Gemini, sees various crypto use cases depending on one's location.
‘Need to have' investment in countries where the local currency has devalued against the dollar, whereas in the developed world it is still seen as a ‘nice to have'.
Crypto as money substitute
As an adjunct professor at New York University School of Law, Winston Ma distinguishes between an asset used as an inflation hedge and one used as a currency replacement.
Unlike gold, he believes Bitcoin (BTC) is not a “inflation hedge”. They acted more like growth stocks in 2022. “Bitcoin correlated more closely with the S&P 500 index — and Ether with the NASDAQ — than gold,” he told Cointelegraph. But in the developing world, things are different:
“Inflation may be a primary driver of cryptocurrency adoption in emerging markets like Brazil, India, and Mexico.”
According to Justin d'Anethan, institutional sales director at the Amber Group, a Singapore-based digital asset firm, early adoption was driven by countries where currency stability and/or access to proper banking services were issues. Simply put, he said, developing countries want alternatives to easily debased fiat currencies.
“The larger flows may still come from institutions and developed countries, but the actual users may come from places like Lebanon, Turkey, Venezuela, and Indonesia.”
“Inflation is one of the factors that has and continues to drive adoption of Bitcoin and other crypto assets globally,” said Sean Stein Smith, assistant professor of economics and business at Lehman College.
But it's only one factor, and different regions have different factors, says Stein Smith. As a “instantaneously accessible, traceable, and cost-effective transaction option,” investors and entrepreneurs increasingly recognize the benefits of crypto assets. Other places promote crypto adoption due to “potential capital gains and returns”.
According to the report, “legal uncertainty around cryptocurrency,” tax questions, and a general education deficit could hinder adoption in Asia Pacific and Latin America. In Africa, 56% of respondents said more educational resources were needed to explain cryptocurrencies.
Not only inflation, but empowering our youth to live better than their parents without fear of failure or allegiance to legacy financial markets or products, said Monica Singer, ConsenSys South Africa lead. Also, “the issue of cash and remittances is huge in Africa, as is the issue of social grants.”
Money's future?
The survey found that Brazil and Indonesia had the most cryptocurrency ownership. In each country, 41% of those polled said they owned crypto. Only 20% of Americans surveyed said they owned cryptocurrency.
These markets are more likely to see cryptocurrencies as the future of money. The survey found:
“The majority of respondents in Latin America (59%) and Africa (58%) say crypto is the future of money.”
Brazil (66%), Nigeria (63%), Indonesia (61%), and South Africa (57%). Europe and Australia had the fewest believers, with Denmark at 12%, Norway at 15%, and Australia at 17%.
Will the Ukraine conflict impact adoption?
The poll was taken before the war. Will the devastating conflict slow global crypto adoption growth?
With over $100 million in crypto donations directly requested by the Ukrainian government since the war began, Stein Smith says the war has certainly brought crypto into the mainstream conversation.
“This real-world demonstration of decentralized money's power could spur wider adoption, policy debate, and increased use of crypto as a medium of exchange.”
But the war may not affect all developing nations. “The Ukraine war has no impact on African demand for crypto,” Others loom larger. “Yes, inflation, but also a lack of trust in government in many African countries, and a young demographic very familiar with mobile phones and the internet.”
A major success story like Mpesa in Kenya has influenced the continent and may help accelerate crypto adoption. Creating a plan when everyone you trust fails you is directly related to the African spirit, she said.
On the other hand, Ma views the Ukraine conflict as a sort of crisis check for cryptocurrencies. For those in emerging markets, the Ukraine-Russia war has served as a “stress test” for the cryptocurrency payment rail, he told Cointelegraph.
“These emerging markets may see the greatest future gains in crypto adoption.”
Inflation and currency devaluation are persistent global concerns. In such places, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are now seen as the “future of money.” Not in the developed world, but that could change with better regulation and education. Inflation and its impact on cash holdings are waking up even Western nations.
Read original post here.

Elnaz Sarraf
3 years ago
Why Bitcoin's Crash Could Be Good for Investors

The crypto market crashed in June 2022. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies hit their lowest prices in over a year, causing market panic. Some believe this crash will benefit future investors.
Before I discuss how this crash might help investors, let's examine why it happened. Inflation in the U.S. reached a 30-year high in 2022 after Russia invaded Ukraine. In response, the U.S. Federal Reserve raised interest rates by 0.5%, the most in almost 20 years. This hurts cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Higher interest rates make people less likely to invest in volatile assets like crypto, so many investors sold quickly.
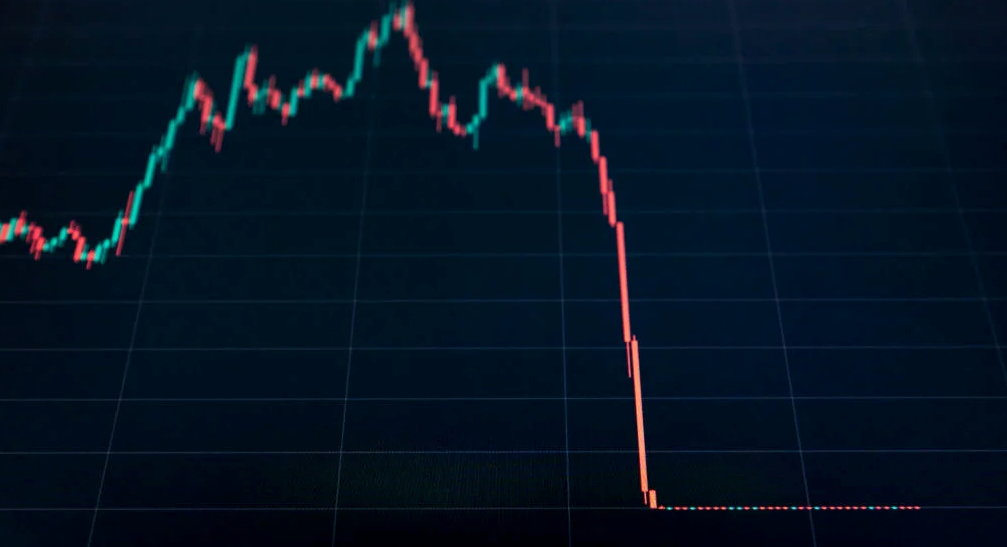
The crypto market collapsed. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Binance dropped 40%. Other cryptos crashed so hard they were delisted from almost every exchange. Bitcoin peaked in April 2022 at $41,000, but after the May interest rate hike, it crashed to $28,000. Bitcoin investors were worried. Even in bad times, this crash is unprecedented.
Bitcoin wasn't "doomed." Before the crash, LUNA was one of the top 5 cryptos by market cap. LUNA was trading around $80 at the start of May 2022, but after the rate hike?
Less than 1 cent. LUNA lost 99.99% of its value in days and was removed from every crypto exchange. Bitcoin's "crash" isn't as devastating when compared to LUNA.
Many people said Bitcoin is "due" for a LUNA-like crash and that the only reason it hasn't crashed is because it's bigger. Still false. If so, Bitcoin should be worth zero by now. We didn't. Instead, Bitcoin reached 28,000, then 29k, 30k, and 31k before falling to 18k. That's not the world's greatest recovery, but it shows Bitcoin's safety.
Bitcoin isn't falling constantly. It fell because of the initial shock of interest rates, but not further. Now, Bitcoin's value is more likely to rise than fall. Bitcoin's low price also attracts investors. They know what prices Bitcoin can reach with enough hype, and they want to capitalize on low prices before it's too late.

Bitcoin's crash was bad, but in a way it wasn't. To understand, consider 2021. In March 2021, Bitcoin surpassed $60k for the first time. Elon Musk's announcement in May that he would no longer support Bitcoin caused a massive crash in the crypto market. In May 2017, Bitcoin's price hit $29,000. Elon Musk's statement isn't worth more than the Fed raising rates. Many expected this big announcement to kill Bitcoin.

Not so. Bitcoin crashed from $58k to $31k in 2021. Bitcoin fell from $41k to $28k in 2022. This crash is smaller. Bitcoin's price held up despite tensions and stress, proving investors still believe in it. What happened after the initial crash in the past?
Bitcoin fell until mid-July. This is also something we’re not seeing today. After a week, Bitcoin began to improve daily. Bitcoin's price rose after mid-July. Bitcoin's price fluctuated throughout the rest of 2021, but it topped $67k in November. Despite no major changes, the peak occurred after the crash. Elon Musk seemed uninterested in crypto and wasn't likely to change his mind soon. What triggered this peak? Nothing, really. What really happened is that people got over the initial statement. They forgot.
Internet users have goldfish-like attention spans. People quickly forgot the crash's cause and were back investing in crypto months later. Despite the market's setbacks, more crypto investors emerged by the end of 2017. Who gained from these peaks? Bitcoin investors who bought low. Bitcoin not only recovered but also doubled its ROI. It was like a movie, and it shows us what to expect from Bitcoin in the coming months.
The current Bitcoin crash isn't as bad as the last one. LUNA is causing market panic. LUNA and Bitcoin are different cryptocurrencies. LUNA crashed because Terra wasn’t able to keep its peg with the USD. Bitcoin is unanchored. It's one of the most decentralized investments available. LUNA's distrust affected crypto prices, including Bitcoin, but it won't last forever.
This is why Bitcoin will likely rebound in the coming months. In 2022, people will get over the rise in interest rates and the crash of LUNA, just as they did with Elon Musk's crypto stance in 2021. When the world moves on to the next big controversy, Bitcoin's price will soar.
Bitcoin may recover for another reason. Like controversy, interest rates fluctuate. The Russian invasion caused this inflation. World markets will stabilize, prices will fall, and interest rates will drop.
Next, lower interest rates could boost Bitcoin's price. Eventually, it will happen. The U.S. economy can't sustain such high interest rates. Investors will put every last dollar into Bitcoin if interest rates fall again.
Bitcoin has proven to be a stable investment. This boosts its investment reputation. Even if Ethereum dethrones Bitcoin as crypto king one day (or any other crypto, for that matter). Bitcoin may stay on top of the crypto ladder for a while. We'll have to wait a few months to see if any of this is true.
This post is a summary. Read the full article here.

Shan Vernekar
3 years ago
How the Ethereum blockchain's transactions are carried out
Overview
Ethereum blockchain is a network of nodes that validate transactions. Any network node can be queried for blockchain data for free. To write data as a transition requires processing and writing to each network node's storage. Fee is paid in ether and is also called as gas.
We'll examine how user-initiated transactions flow across the network and into the blockchain.
Flow of transactions
A user wishes to move some ether from one external account to another. He utilizes a cryptocurrency wallet for this (like Metamask), which is a browser extension.
The user enters the desired transfer amount and the external account's address. He has the option to choose the transaction cost he is ready to pay.
Wallet makes use of this data, signs it with the user's private key, and writes it to an Ethereum node. Services such as Infura offer APIs that enable writing data to nodes. One of these services is used by Metamask. An example transaction is shown below. Notice the “to” address and value fields.
var rawTxn = {
nonce: web3.toHex(txnCount),
gasPrice: web3.toHex(100000000000),
gasLimit: web3.toHex(140000),
to: '0x633296baebc20f33ac2e1c1b105d7cd1f6a0718b',
value: web3.toHex(0),
data: '0xcc9ab24952616d6100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000'
};The transaction is written to the target Ethereum node's local TRANSACTION POOL. It informed surrounding nodes of the new transaction, and those nodes reciprocated. Eventually, this transaction is received by and written to each node's local TRANSACTION pool.
The miner who finds the following block first adds pending transactions (with a higher gas cost) from the nearby TRANSACTION POOL to the block.
The transactions written to the new block are verified by other network nodes.
A block is added to the main blockchain after there is consensus and it is determined to be genuine. The local blockchain is updated with the new node by additional nodes as well.
Block mining begins again next.

The image above shows how transactions go via the network and what's needed to submit them to the main block chain.
References
ethereum.org/transactions How Ethereum transactions function, their data structure, and how to send them via app. ethereum.org
You might also like

Alexandra Walker-Jones
3 years ago
These are the 15 foods you should eat daily and why.
Research on preventing disease, extending life, and caring for your body from the inside out

Grapefruit and pomegranates aren't on the list, so ignore that. Mostly, I enjoyed the visual, but those fruits are healthful, too.
15 (or 17 if you consider the photo) different foods a day sounds like a lot. If you're not used to it — it is.
These lists don't aim for perfection. Instead, use this article and the science below to eat more of these foods. If you can eat 5 foods one day and 5 the next, you're doing well. This list should be customized to your requirements and preferences.
“Every time you eat or drink, you are either feeding disease or fighting it” -Heather Morgan.
The 15 Foods That You Should Consume Daily and Why:
1. Dark/Red Berries
(blueberries, blackberries, acai, goji, cherries, strawberries, raspberries)
The 2010 Global Burden of Disease Study is the greatest definitive analysis of death and disease risk factors in history. They found the primary cause of both death, disability, and disease inside the United States was diet.
Not eating enough fruit, and specifically berries, was one of the best predictors of disease (1).
What's special about berries? It's their color! Berries have the most antioxidants of any fruit, second only to spices. The American Cancer Society found that those who ate the most berries were less likely to die of cardiovascular disease.
2. Beans
Soybeans, black beans, kidney beans, lentils, split peas, chickpeas.
Beans are one of the most important predictors of survival in older people, according to global research (2).
For every 20 grams (2 tablespoons) of beans consumed daily, the risk of death is reduced by 8%.
Soybeans and soy foods are high in phytoestrogen, which reduces breast and prostate cancer risks. Phytoestrogen blocks the receptors' access to true estrogen, mitigating the effects of weight gain, dairy (high in estrogen), and hormonal fluctuations (3).
3. Nuts
(almonds, walnuts, pecans, pistachios, Brazil nuts, cashews, hazelnuts, macadamia nuts)
Eating a handful of nuts every day reduces the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. Nuts also reduce oxidation, blood sugar, and LDL (bad) cholesterol, improving arterial function (4).
Despite their high-fat content, studies have linked daily nut consumption to a slimmer waistline and a lower risk of obesity (5).
4. Flaxseed
(milled flaxseed)
2013 research found that ground flaxseed had one of the strongest anti-hypertensive effects of any food. A few tablespoons (added to a smoothie or baked goods) lowered blood pressure and stroke risk 23 times more than daily aerobic exercise (6).
Flax shouldn't replace exercise, but its nutritional punch is worth adding to your diet.
5. Other seeds
(chia seeds, hemp seeds, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, fennel seeds)
Seeds are high in fiber and omega-3 fats and can be added to most dishes without being noticed.
When eaten with or after a meal, chia seeds moderate blood sugar and reduce inflammatory chemicals in the blood (7). Overall, a great daily addition.
6. Dates
Dates are one of the world's highest sugar foods, with 80% sugar by weight. Pure cake frosting is 60%, maple syrup is 66%, and cotton-candy jelly beans are 70%.
Despite their high sugar content, dates have a low glycemic index, meaning they don't affect blood sugar levels dramatically. They also improve triglyceride and antioxidant stress levels (8).
Dates are a great source of energy and contain high levels of dietary fiber and polyphenols, making 3-10 dates a great way to fight disease, support gut health with prebiotics, and satisfy a sweet tooth (9).
7. Cruciferous Veggies
(broccoli, Brussel sprouts, horseradish, kale, cauliflower, cabbage, boy choy, arugula, radishes, turnip greens)
Cruciferous vegetables contain an active ingredient that makes them disease-fighting powerhouses. Sulforaphane protects our brain, eyesight, against free radicals and environmental hazards, and treats and prevents cancer (10).
Unless you eat raw cruciferous vegetables daily, you won't get enough sulforaphane (and thus, its protective nutritional benefits). Cooking destroys the enzyme needed to create this super-compound.
If you chop broccoli, cauliflower, or turnip greens and let them sit for 45 minutes before cooking them, the enzyme will have had enough time to work its sulforaphane magic, allowing the vegetables to retain the same nutritional value as if eaten raw. Crazy, right? For more on this, see What Chopping Your Vegetables Has to Do with Fighting Cancer.
8. Whole grains
(barley, brown rice, quinoa, oats, millet, popcorn, whole-wheat pasta, wild rice)
Whole-grains are one of the healthiest ways to consume your daily carbs and help maintain healthy gut flora.
This happens when fibre is broken down in the colon and starts a chain reaction, releasing beneficial substances into the bloodstream and reducing the risk of Type 2 Diabetes and inflammation (11).
9. Spices
(turmeric, cumin, cinnamon, ginger, saffron, cloves, cardamom, chili powder, nutmeg, coriander)
7% of a person's cells will have DNA damage. This damage is caused by tiny breaks in our DNA caused by factors like free-radical exposure.
Free radicals cause mutations that damage lipids, proteins, and DNA, increasing the risk of disease and cancer. Free radicals are unavoidable because they result from cellular metabolism, but they can be avoided by consuming anti-oxidant and detoxifying foods.
Including spices and herbs like rosemary or ginger in our diet may cut DNA damage by 25%. Yes, this damage can be improved through diet. Turmeric worked better at a lower dose (just a pinch, daily). For maximum free-radical fighting (and anti-inflammatory) effectiveness, use 1.5 tablespoons of similar spices (12).
10. Leafy greens
(spinach, collard greens, lettuce, other salad greens, swiss chard)
Studies show that people who eat more leafy greens perform better on cognitive tests and slow brain aging by a year or two (13).
As we age, blood flow to the brain drops due to a decrease in nitric oxide, which prevents blood vessels from dilatation. Daily consumption of nitrate-rich vegetables like spinach and swiss chard may prevent dementia and Alzheimer's.
11. Fermented foods
(sauerkraut, tempeh, kombucha, plant-based kefir)
Miso, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain probiotics that support gut microbiome.
Probiotics balance the good and bad bacteria in our bodies and offer other benefits. Fermenting fruits and vegetables increases their antioxidant and vitamin content, preventing disease in multiple ways (14).
12. Sea vegetables
(seaweed, nori, dulse flakes)
A population study found that eating one sheet of nori seaweed per day may cut breast cancer risk by more than half (15).
Seaweed and sea vegetables may help moderate estrogen levels in the metabolism, reducing cancer and disease risk.
Sea vegetables make up 30% of the world's edible plants and contain unique phytonutrients. A teaspoon of these super sea-foods on your dinner will help fight disease from the inside out.
13. Water
I'm less concerned about whether you consider water food than whether you drink enough. If this list were ranked by what single item led to the best health outcomes, water would be first.
Research shows that people who drink 5 or more glasses of water per day have a 50% lower risk of dying from heart disease than those who drink 2 or less (16).
Drinking enough water boosts energy, improves skin, mental health, and digestion, and reduces the risk of various health issues, including obesity.
14. Tea
All tea consumption is linked to a lower risk of stroke, heart disease, and early death, with green tea leading for antioxidant content and immediate health benefits.
Green tea leaves may also be able to interfere with each stage of cancer formation, from the growth of the first mutated cell to the spread and progression of cancer in the body. Green tea is a quick and easy way to support your long-term and short-term health (17).
15. Supplemental B12 vitamin
B12, or cobalamin, is a vitamin responsible for cell metabolism. Not getting enough B12 can have serious consequences.
Historically, eating vegetables from untreated soil helped humans maintain their vitamin B12 levels. Due to modern sanitization, our farming soil lacks B12.
B12 is often cited as a problem only for vegetarians and vegans (as animals we eat are given B12 supplements before slaughter), but recent studies have found that plant-based eaters have lower B12 deficiency rates than any other diet (18).
Article Sources:
Yuga Labs
3 years ago
Yuga Labs (BAYC and MAYC) buys CryptoPunks and Meebits and gives them commercial rights
Yuga has acquired the CryptoPunks and Meebits NFT IP from Larva Labs. These include 423 CryptoPunks and 1711 Meebits.
We set out to create in the NFT space because we admired CryptoPunks and the founders' visionary work. A lot of their work influenced how we built BAYC and NFTs. We're proud to lead CryptoPunks and Meebits into the future as part of our broader ecosystem.
"Yuga Labs invented the modern profile picture project and are the best in the world at operating these projects. They are ideal CrytoPunk and Meebit stewards. We are confident that in their hands, these projects will thrive in the emerging decentralized web.”
–The founders of Larva Labs, CryptoPunks, and Meebits
This deal grew out of discussions between our partner Guy Oseary and the Larva Labs founders. One call led to another, and now we're here. This does not mean Matt and John will join Yuga. They'll keep running Larva Labs and creating awesome projects that help shape the future of web3.
Next steps
Here's what we plan to do with CryptoPunks and Meebits now that we own the IP. Owners of CryptoPunks and Meebits will soon receive commercial rights equal to those of BAYC and MAYC holders. Our legal teams are working on new terms and conditions for both collections, which we hope to share with the community soon. We expect a wide range of third-party developers and community creators to incorporate CryptoPunks and Meebits into their web3 projects. We'll build the brand alongside them.
We don't intend to cram these NFT collections into the BAYC club model. We see BAYC as the hub of the Yuga universe, and CryptoPunks as a historical collection. We will work to improve the CryptoPunks and Meebits collections as good stewards. We're not in a hurry. We'll consult the community before deciding what to do next.
For us, NFTs are about culture. We're deeply invested in the BAYC community, and it's inspiring to see them grow, collaborate, and innovate. We're excited to see what CryptoPunks and Meebits do with IP rights. Our goal has always been to create a community-owned brand that goes beyond NFTs, and now we can include CryptoPunks and Meebits.

Sam Warain
3 years ago
Sam Altman, CEO of Open AI, foresees the next trillion-dollar AI company
“I think if I had time to do something else, I would be so excited to go after this company right now.”

Sam Altman, CEO of Open AI, recently discussed AI's present and future.
Open AI is important. They're creating the cyberpunk and sci-fi worlds.
They use the most advanced algorithms and data sets.
GPT-3...sound familiar? Open AI built most copyrighting software. Peppertype, Jasper AI, Rytr. If you've used any, you'll be shocked by the quality.
Open AI isn't only GPT-3. They created DallE-2 and Whisper (a speech recognition software released last week).
What will they do next? What's the next great chance?
Sam Altman, CEO of Open AI, recently gave a lecture about the next trillion-dollar AI opportunity.
Who is the organization behind Open AI?
Open AI first. If you know, skip it.
Open AI is one of the earliest private AI startups. Elon Musk, Greg Brockman, and Rebekah Mercer established OpenAI in December 2015.
OpenAI has helped its citizens and AI since its birth.
They have scary-good algorithms.
Their GPT-3 natural language processing program is excellent.
The algorithm's exponential growth is astounding. GPT-2 came out in November 2019. May 2020 brought GPT-3.
Massive computation and datasets improved the technique in just a year. New York Times said GPT-3 could write like a human.
Same for Dall-E. Dall-E 2 was announced in April 2022. Dall-E 2 won a Colorado art contest.
Open AI's algorithms challenge jobs we thought required human innovation.
So what does Sam Altman think?
The Present Situation and AI's Limitations
During the interview, Sam states that we are still at the tip of the iceberg.
So I think so far, we’ve been in the realm where you can do an incredible copywriting business or you can do an education service or whatever. But I don’t think we’ve yet seen the people go after the trillion dollar take on Google.
He's right that AI can't generate net new human knowledge. It can train and synthesize vast amounts of knowledge, but it simply reproduces human work.
“It’s not going to cure cancer. It’s not going to add to the sum total of human scientific knowledge.”
But the key word is yet.
And that is what I think will turn out to be wrong that most surprises the current experts in the field.
Reinforcing his point that massive innovations are yet to come.
But where?
The Next $1 Trillion AI Company
Sam predicts a bio or genomic breakthrough.
There’s been some promising work in genomics, but stuff on a bench top hasn’t really impacted it. I think that’s going to change. And I think this is one of these areas where there will be these new $100 billion to $1 trillion companies started, and those areas are rare.
Avoid human trials since they take time. Bio-materials or simulators are suitable beginning points.
AI may have a breakthrough. DeepMind, an OpenAI competitor, has developed AlphaFold to predict protein 3D structures.
It could change how we see proteins and their function. AlphaFold could provide fresh understanding into how proteins work and diseases originate by revealing their structure. This could lead to Alzheimer's and cancer treatments. AlphaFold could speed up medication development by revealing how proteins interact with medicines.
Deep Mind offered 200 million protein structures for scientists to download (including sustainability, food insecurity, and neglected diseases).

Being in AI for 4+ years, I'm amazed at the progress. We're past the hype cycle, as evidenced by the collapse of AI startups like C3 AI, and have entered a productive phase.
We'll see innovative enterprises that could replace Google and other trillion-dollar companies.
What happens after AI adoption is scary and unpredictable. How will AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) affect us? Highly autonomous systems that exceed humans at valuable work (Open AI)
My guess is that the things that we’ll have to figure out are how we think about fairly distributing wealth, access to AGI systems, which will be the commodity of the realm, and governance, how we collectively decide what they can do, what they don’t do, things like that. And I think figuring out the answer to those questions is going to just be huge. — Sam Altman CEO
