More on Entrepreneurship/Creators

Hasan AboulHasan
3 years ago
High attachment products can help you earn money automatically.

Affiliate marketing is a popular online moneymaker. You promote others' products and get commissions. Affiliate marketing requires constant product promotion.
Affiliate marketing can be profitable even without much promotion. Yes, this is Autopilot Money.

How to Pick an Affiliate Program to Generate Income Autonomously
Autopilot moneymaking requires a recurring affiliate marketing program.
Finding the best product and testing it takes a lot of time and effort.
Here are three ways to choose the best service or product to promote:
Find a good attachment-rate product or service.
When choosing a product, ask if you can easily switch to another service. Attachment rate is how much people like a product.
Higher attachment rates mean better Autopilot products.
Consider promoting GetResponse. It's a 33% recurring commission email marketing tool. This means you get 33% of the customer's plan as long as he pays.
GetResponse has a high attachment rate because it's hard to leave and start over with another tool.
2. Pick a good or service with a lot of affiliate assets.
Check if a program has affiliate assets or creatives before joining.
Images and banners to promote the product in your business.
They save time; I look for promotional creatives. Creatives or affiliate assets are website banners or images. This reduces design time.
3. Select a service or item that consumers already adore.
New products are hard to sell. Choosing a trusted company's popular product or service is helpful.
As a beginner, let people buy a product they already love.
Online entrepreneurs and digital marketers love Systeme.io. It offers tools for creating pages, email marketing, funnels, and more. This product guarantees a high ROI.
Make the product known!
Affiliate marketers struggle to get traffic. Using affiliate marketing to make money is easier than you think if you have a solid marketing strategy.
Your plan should include:
1- Publish affiliate-related blog posts and SEO-optimize them
2- Sending new visitors product-related emails
3- Create a product resource page.
4-Review products
5-Make YouTube videos with links in the description.
6- Answering FAQs about your products and services on your blog and Quora.
7- Create an eCourse on how to use this product.
8- Adding Affiliate Banners to Your Website.
With these tips, you can promote your products and make money on autopilot.

cdixon
3 years ago
2000s Toys, Secrets, and Cycles
During the dot-com bust, I started my internet career. People used the internet intermittently to check email, plan travel, and do research. The average internet user spent 30 minutes online a day, compared to 7 today. To use the internet, you had to "log on" (most people still used dial-up), unlike today's always-on, high-speed mobile internet. In 2001, Amazon's market cap was $2.2B, 1/500th of what it is today. A study asked Americans if they'd adopt broadband, and most said no. They didn't see a need to speed up email, the most popular internet use. The National Academy of Sciences ranked the internet 13th among the 100 greatest inventions, below radio and phones. The internet was a cool invention, but it had limited uses and wasn't a good place to build a business.
A small but growing movement of developers and founders believed the internet could be more than a read-only medium, allowing anyone to create and publish. This is web 2. The runner up name was read-write web. (These terms were used in prominent publications and conferences.)
Web 2 concepts included letting users publish whatever they want ("user generated content" was a buzzword), social graphs, APIs and mashups (what we call composability today), and tagging over hierarchical navigation. Technical innovations occurred. A seemingly simple but important one was dynamically updating web pages without reloading. This is now how people expect web apps to work. Mobile devices that could access the web were niche (I was an avid Sidekick user).
The contrast between what smart founders and engineers discussed over dinner and on weekends and what the mainstream tech world took seriously during the week was striking. Enterprise security appliances, essentially preloaded servers with security software, were a popular trend. Many of the same people would talk about "serious" products at work, then talk about consumer internet products and web 2. It was tech's biggest news. Web 2 products were seen as toys, not real businesses. They were hobbies, not work-related.
There's a strong correlation between rich product design spaces and what smart people find interesting, which took me some time to learn and led to blog posts like "The next big thing will start out looking like a toy" Web 2's novel product design possibilities sparked dinner and weekend conversations. Imagine combining these features. What if you used this pattern elsewhere? What new product ideas are next? This excited people. "Serious stuff" like security appliances seemed more limited.
The small and passionate web 2 community also stood out. I attended the first New York Tech meetup in 2004. Everyone fit in Meetup's small conference room. Late at night, people demoed their software and chatted. I have old friends. Sometimes I get asked how I first met old friends like Fred Wilson and Alexis Ohanian. These topics didn't interest many people, especially on the east coast. We were friends. Real community. Alex Rampell, who now works with me at a16z, is someone I met in 2003 when a friend said, "Hey, I met someone else interested in consumer internet." Rare. People were focused and enthusiastic. Revolution seemed imminent. We knew a secret nobody else did.
My web 2 startup was called SiteAdvisor. When my co-founders and I started developing the idea in 2003, web security was out of control. Phishing and spyware were common on Internet Explorer PCs. SiteAdvisor was designed to warn users about security threats like phishing and spyware, and then, using web 2 concepts like user-generated reviews, add more subjective judgments (similar to what TrustPilot seems to do today). This staged approach was common at the time; I called it "Come for the tool, stay for the network." We built APIs, encouraged mashups, and did SEO marketing.
Yahoo's 2005 acquisitions of Flickr and Delicious boosted web 2 in 2005. By today's standards, the amounts were small, around $30M each, but it was a signal. Web 2 was assumed to be a fun hobby, a way to build cool stuff, but not a business. Yahoo was a savvy company that said it would make web 2 a priority.
As I recall, that's when web 2 started becoming mainstream tech. Early web 2 founders transitioned successfully. Other entrepreneurs built on the early enthusiasts' work. Competition shifted from ideation to execution. You had to decide if you wanted to be an idealistic indie bar band or a pragmatic stadium band.
Web 2 was booming in 2007 Facebook passed 10M users, Twitter grew and got VC funding, and Google bought YouTube. The 2008 financial crisis tested entrepreneurs' resolve. Smart people predicted another great depression as tech funding dried up.
Many people struggled during the recession. 2008-2011 was a golden age for startups. By 2009, talented founders were flooding Apple's iPhone app store. Mobile apps were booming. Uber, Venmo, Snap, and Instagram were all founded between 2009 and 2011. Social media (which had replaced web 2), cloud computing (which enabled apps to scale server side), and smartphones converged. Even if social, cloud, and mobile improve linearly, the combination could improve exponentially.
This chart shows how I view product and financial cycles. Product and financial cycles evolve separately. The Nasdaq index is a proxy for the financial sentiment. Financial sentiment wildly fluctuates.
Next row shows iconic startup or product years. Bottom-row product cycles dictate timing. Product cycles are more predictable than financial cycles because they follow internal logic. In the incubation phase, enthusiasts build products for other enthusiasts on nights and weekends. When the right mix of technology, talent, and community knowledge arrives, products go mainstream. (I show the biggest tech cycles in the chart, but smaller ones happen, like web 2 in the 2000s and fintech and SaaS in the 2010s.)
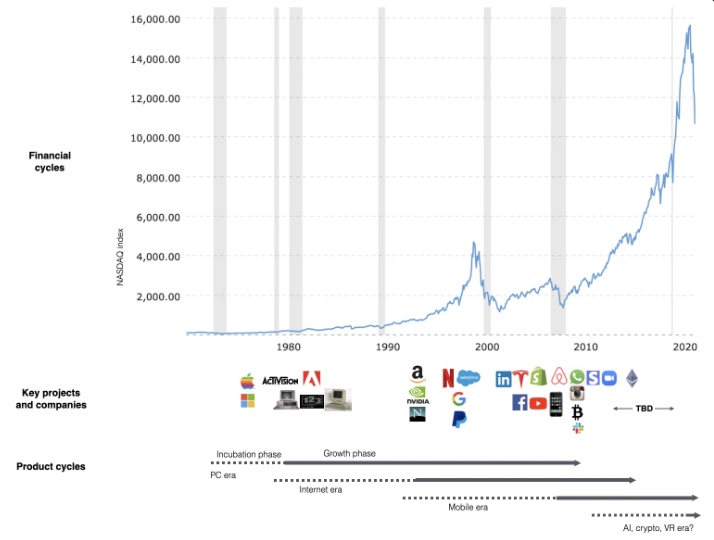
Tech has changed since the 2000s. Few tech giants dominate the internet, exerting economic and cultural influence. In the 2000s, web 2 was ignored or dismissed as trivial. Entrenched interests respond aggressively to new movements that could threaten them. Creative patterns from the 2000s continue today, driven by enthusiasts who see possibilities where others don't. Know where to look. Crypto and web 3 are where I'd start.
Today's negative financial sentiment reminds me of 2008. If we face a prolonged downturn, we can learn from 2008 by preserving capital and focusing on the long term. Keep an eye on the product cycle. Smart people are interested in things with product potential. This becomes true. Toys become necessities. Hobbies become mainstream. Optimists build the future, not cynics.
Full article is available here

Rachel Greenberg
3 years ago
The Unsettling Fact VC-Backed Entrepreneurs Don't Want You to Know
What they'll do is scarier.

My acquaintance recently joined a VC-funded startup. Money, equity, and upside possibilities were nice, but he had a nagging dread.
They just secured a $40M round and are hiring like crazy to prepare for their IPO in two years. All signals pointed to this startup's (a B2B IT business in a stable industry) success, and its equity-holding workers wouldn't pass that up.
Five months after starting the work, my friend struggled with leaving. We might overlook the awful culture and long hours at the proper price. This price plus the company's fate and survival abilities sent my friend departing in an unpleasant unplanned resignation before jumping on yet another sinking ship.
This affects founders. This affects VC-backed companies (and all businesses). This affects anyone starting, buying, or running a business.
Here's the under-the-table approach that's draining VC capital, leaving staff terrified (or jobless), founders rattled, and investors upset. How to recognize, solve, and avoid it
The unsettling reality behind door #1
You can't raise money off just your looks, right? If "looks" means your founding team's expertise, then maybe. In my friend's case, the founding team's strong qualifications and track records won over investors before talking figures.
They're hardly the only startup to raise money without a profitable customer acquisition strategy. Another firm raised money for an expensive sleep product because it's eco-friendly. They were off to the races with a few keywords and key players.
Both companies, along with numerous others, elected to invest on product development first. Company A employed all the tech, then courted half their market (they’re a tech marketplace that connects two parties). Company B spent millions on R&D to create a palatable product, then flooded the world with marketing.
My friend is on Company B's financial team, and he's seen where they've gone wrong. It's terrible.
Company A (tech market): Growing? Not quite. To achieve the ambitious expansion they (and their investors) demand, they've poured much of their little capital into salespeople: Cold-calling commission and salary salesmen. Is it working? Considering attrition and companies' dwindling capital, I don't think so.
Company B (green sleep) has been hiring, digital marketing, and opening new stores like crazy. Growing expenses should result in growing revenues and a favorable return on investment; if you grow too rapidly, you may neglect to check that ROI.
Once Company A cut headcount and Company B declared “going concerned”, my friend realized both startups had the same ailment and didn't recognize it.
I shouldn't have to ask a friend to verify a company's cash reserves and profitability to spot a financial problem. It happened anyhow.
The frightening part isn't that investors were willing to invest millions without product-market fit, CAC, or LTV estimates. That's alarming, but not as scary as the fact that startups aren't understanding the problem until VC rounds have dried up.
When they question consultants if their company will be around in 6 months. It’s a red flag. How will they stretch $20M through a 2-year recession with a $3M/month burn rate and no profitability? Alarms go off.
Who's in danger?
In a word, everyone who raised money without a profitable client acquisition strategy or enough resources to ride out dry spells.
Money mismanagement and poor priorities affect every industry (like sinking all your capital into your product, team, or tech, at the expense of probing what customer acquisition really takes and looks like).
This isn't about tech, real estate, or recession-proof luxury products. Fast, cheap, easy money flows into flashy-looking teams with buzzwords, trending industries, and attractive credentials.
If these companies can't show progress or get a profitable CAC, they can't raise more money. They die if they can't raise more money (or slash headcount and find shoestring budget solutions until they solve the real problem).
The kiss of death (and how to avoid it)
If you're running a startup and think raising VC is the answer, pause and evaluate. Do you need the money now?
I'm not saying VC is terrible or has no role. Founders have used it as a Band-Aid for larger, pervasive problems. Venture cash isn't a crutch for recruiting consumers profitably; it's rocket fuel to get you what and who you need.
Pay-to-play isn't a way to throw money at the wall and hope for a return. Pay-to-play works until you run out of money, and if you haven't mastered client acquisition, your cash will diminish quickly.
How can you avoid this bottomless pit? Tips:
Understand your burn rate
Keep an eye on your growth or profitability.
Analyze each and every marketing channel and initiative.
Make lucrative customer acquisition strategies and satisfied customers your top two priorities. not brand-new products. not stellar hires. avoid the fundraising rollercoaster to save time. If you succeed in these two tasks, investors will approach you with their thirsty offers rather than the other way around, and your cash reserves won't diminish as a result.
Not as much as your grandfather
My family friend always justified expensive, impractical expenditures by saying it was only monopoly money. In business, startups, and especially with money from investors expecting a return, that's not true.
More founders could understand that there isn't always another round if they viewed VC money as their own limited pool. When the well runs dry, you must refill it or save the day.
Venture financing isn't your grandpa's money. A discerning investor has entrusted you with dry powder in the hope that you'll use it wisely, strategically, and thoughtfully. Use it well.
You might also like

Jayden Levitt
3 years ago
Starbucks' NFT Project recently defeated its rivals.
The same way Amazon killed bookstores. You just can’t see it yet.

Shultz globalized coffee. Before Starbucks, coffee sucked.
All accounts say 1970s coffee was awful.
Starbucks had three stores selling ground Indonesian coffee in the 1980s.
What a show!
A year after joining the company at 29, Shultz traveled to Italy for R&D.
He noticed the coffee shops' sense of theater and community and realized Starbucks was in the wrong business.
Integrating coffee and destination created a sense of community in the store.
Brilliant!
He told Starbucks' founders about his experience.
They disapproved.
For two years.
Shultz left and opened an Italian coffee shop chain like any good entrepreneur.
Starbucks ran into financial trouble, so the founders offered to sell to Shultz.
Shultz bought Starbucks in 1987 for $3.8 million, including six stores and a payment plan.
Starbucks is worth $100.79Billion, per Google Finance.
26,500 times Shultz's initial investment

Starbucks is releasing its own NFT Platform under Shultz and his early Vision.
This year, Starbucks Odyssey launches. The new digital experience combines a Loyalty Rewards program with NFT.
The side chain Polygon-based platform doesn't require a Crypto Wallet. Customers can earn and buy digital assets to unlock incentives and experiences.
They've removed all friction, making it more immersive and convenient than a coffee shop.
Brilliant!
NFTs are the access coupon to their digital community, but they don't highlight the technology.
They prioritize consumer experience by adding non-technical users to Web3. Their collectables are called journey stamps, not NFTs.
No mention of bundled gas fees.
Brady Brewer, Starbucks' CMO, said;
“It happens to be built on blockchain and web3 technologies, but the customer — to be honest — may very well not even know that what they’re doing is interacting with blockchain technology. It’s just the enabler,”
Rewards members will log into a web app using their loyalty program credentials to access Starbucks Odyssey. They won't know about blockchain transactions.
Starbucks has just dealt its rivals a devastating blow.
It generates more than ten times the revenue of its closest competitor Costa Coffee.
The coffee giant is booming.

Starbucks is ahead of its competitors. No wonder.
They have an innovative, adaptable leadership team.
Starbucks' DNA challenges the narrative, especially when others reject their ideas.
I’m off for a cappuccino.

Koji Mochizuki
4 years ago
How to Launch an NFT Project by Yourself
Creating 10,000 auto-generated artworks, deploying a smart contract to the Ethereum / Polygon blockchain, setting up some tools, etc.
There is so much to do from launching to running an NFT project. Creating parts for artworks, generating 10,000 unique artworks and metadata, creating a smart contract and deploying it to a blockchain network, creating a website, creating a Twitter account, setting up a Discord server, setting up an OpenSea collection. In addition, you need to have MetaMask installed in your browser and have some ETH / MATIC. Did you get tired of doing all this? Don’t worry, once you know what you need to do, all you have to do is do it one by one.
To be honest, it’s best to run an NFT project in a team of three or more, including artists, developers, and marketers. However, depending on your motivation, you can do it by yourself. Some people might come later to offer help with your project. The most important thing is to take a step as soon as possible.
Creating Parts for Artworks
There are lots of free/paid software for drawing, but after all, I think Adobe Illustrator or Photoshop is the best. The images of Skulls In Love are a composite of 48x48 pixel parts created using Photoshop.
The most important thing in creating parts for generative art is to repeatedly test what your artworks will look like after each layer has been combined. The generated artworks should not be too unnatural.
How Many Parts Should You Create?
Are you wondering how many parts you should create to avoid duplication as much as possible when generating your artworks? My friend Stephane, a developer, has created a great tool to help with that.
Generating 10,000 Unique Artworks and Metadata
I highly recommend using the HashLips Art Engine to generate your artworks and metadata. Perhaps there is no better artworks generation tool at the moment.
GitHub: https://github.com/HashLips/hashlips_art_engine
YouTube:
Storing Artworks and Metadata
Ideally, the generated artworks and metadata should be stored on-chain, but if you want to store them off-chain, you should use IPFS. Do not store in centralized storage. This is because data will be lost if the server goes down or if the company goes down. On the other hand, IPFS is a more secure way to find data because it utilizes a distributed, decentralized system.
Storing to IPFS is easy with Pinata, NFT.Storage, and so on. The Skulls In Love uses Pinata. It’s very easy to use, just upload the folder containing your artworks.
Creating and Deploying a Smart Contract
You don’t have to create a smart contract from scratch. There are many great NFT projects, many of which publish their contract source code on Etherscan / PolygonScan. You can choose the contract you like and reuse it. Of course, that requires some knowledge of Solidity, but it depends on your efforts. If you don’t know which contract to choose, use the HashLips smart contract. It’s very simple, but it has almost all the functions you need.
GitHub: https://github.com/HashLips/hashlips_nft_contract
Note: Later on, you may want to change the cost value. You can change it on Remix or Etherscan / PolygonScan. But in this case, enter the Wei value instead of the Ether value. For example, if you want to sell for 1 MATIC, you have to enter “1000000000000000000”. If you set this value to “1”, you will have a nightmare. I recommend using Simple Unit Converter as a tool to calculate the Wei value.
Creating a Website
The website here is not just a static site to showcase your project, it’s a so-called dApp that allows you to access your smart contract and mint NFTs. In fact, this level of dApp is not too difficult for anyone who has ever created a website. Because the ethers.js / web3.js libraries make it easy to interact with your smart contract. There’s also no problem connecting wallets, as MetaMask has great documentation.
The Skulls In Love uses a simple, fast, and modern dApp that I built from scratch using Next.js. It is published on GitHub, so feel free to use it.
Why do people mint NFTs on a website?
Ethereum’s gas fees are high, so if you mint all your NFTs, there will be a huge initial cost. So it makes sense to get the buyers to help with the gas fees for minting.
What about Polygon? Polygon’s gas fees are super cheap, so even if you mint 10,000 NFTs, it’s not a big deal. But we don’t do that. Since NFT projects are a kind of game, it involves the fun of not knowing what will come out after minting.
Creating a Twitter Account
I highly recommend creating a Twitter account. Twitter is an indispensable tool for announcing giveaways and reaching more people. It’s better to announce your project and your artworks little by little, 1–2 weeks before launching your project.
Creating and Setting Up a Discord Server
I highly recommend creating a Discord server as well as a Twitter account. The Discord server is a community and its home. Fans of your NFT project will want to join your community and interact with many other members. So, carefully create each channel on your Discord server to make it a cozy place for your community members.
If you are unfamiliar with Discord, you may be particularly confused by the following:
What bots should I use?
How should I set roles and permissions?
But don’t worry. There are lots of great YouTube videos and blog posts about these.
It’s also a good idea to join the Discord servers of some NFT projects and see how they’re made. Our Discord server is so simple that even beginners will find it easy to understand. Please join us and see it!
Note: First, create a test account and a test server to make sure your bots and permissions work properly. It is better to verify the behavior on the test server before setting up your production server.
UPDATED: As your Discord server grows, you cannot manage it on your own. In this case, you will be hiring several moderators, but choose carefully before hiring. And don’t give them important role permissions right after hiring. Initially, the same permissions as other members are sufficient. After a while, you can add permissions as needed, such as kicking/banning, using the “@every” tag, and adding roles. Again, don’t immediately give significant permissions to your Mod role. Your server can be messed up by fake moderators.
Setting Up Your OpenSea Collection
Before you start selling your NFTs, you need to reserve some for airdrops, giveaways, staff, and more. It’s up to you whether it’s 100, 500, or how many.
After minting some of your NFTs, your account and collection should have been created in OpenSea. Go to OpenSea, connect to your wallet, and set up your collection. Just set your logo, banner image, description, links, royalties, and more. It’s not that difficult.
Promoting Your Project
After all, promotion is the most important thing. In fact, almost every successful NFT project spends a lot of time and effort on it.
In addition to Twitter and Discord, it’s even better to use Instagram, Reddit, and Medium. Also, register your project in NFTCalendar and DISBOARD
DISBOARD is the public Discord server listing community.
About Promoters
You’ll probably get lots of contacts from promoters on your Discord, Twitter, Instagram, and more. But most of them are scams, so don’t pay right away. If you have a promoter that looks attractive to you, be sure to check the promoter’s social media accounts or website to see who he/she is. They basically charge in dollars. The amount they charge isn’t cheap, but promoters with lots of followers may have some temporary effect on your project. Some promoters accept 50% prepaid and 50% postpaid. If you can afford it, it might be worth a try. I never ask them, though.
When Should the Promotion Activities Start?
You may be worried that if you promote your project before it starts, someone will copy your project (artworks). It is true that some projects have actually suffered such damage. I don’t have a clear answer to this question right now, but:
- Do not publish all the information about your project too early
- The information should be released little by little
- Creating artworks that no one can easily copy
I think these are important.
If anyone has a good idea, please share it!
About Giveaways
When hosting giveaways, you’ll probably use multiple social media platforms. You may want to grow your Discord server faster. But if joining the Discord server is included in the giveaway requirements, some people hate it. I recommend holding giveaways for each platform. On Twitter and Reddit, you should just add the words “Discord members-only giveaway is being held now! Please join us if you like!”.
If you want to easily pick a giveaway winner in your browser, I recommend Twitter Picker.
Precautions for Distributing Free NFTs
If you want to increase your Twitter followers and Discord members, you can actually get a lot of people by holding events such as giveaways and invite contests. However, distributing many free NFTs at once can be dangerous. Some people who want free NFTs, as soon as they get a free one, sell it at a very low price on marketplaces such as OpenSea. They don’t care about your project and are only thinking about replacing their own “free” NFTs with Ethereum. The lower the floor price of your NFTs, the lower the value of your NFTs (project). Try to think of ways to get people to “buy” your NFTs as much as possible.
Ethereum vs. Polygon
Even though Ethereum has high gas fees, NFT projects on the Ethereum network are still mainstream and popular. On the other hand, Polygon has very low gas fees and fast transaction processing, but NFT projects on the Polygon network are not very popular.
Why? There are several reasons, but the biggest one is that it’s a lot of work to get MATIC (on Polygon blockchain, use MATIC instead of ETH) ready to use. Simply put, you need to bridge your tokens to the Polygon chain. So people need to do this first before minting your NFTs on your website. It may not be a big deal for those who are familiar with crypto and blockchain, but it may be complicated for those who are not. I hope that the tedious work will be simplified in the near future.
If you are confident that your NFTs will be purchased even if they are expensive, or if the total supply of your NFTs is low, you may choose Ethereum. If you just want to save money, you should choose Polygon. Keep in mind that gas fees are incurred not only when minting, but also when performing some of your smart contract functions and when transferring your NFTs.
If I were to launch a new NFT project, I would probably choose Ethereum or Solana.
Conclusion
Some people may want to start an NFT project to make money, but don’t forget to enjoy your own project. Several months ago, I was playing with creating generative art by imitating the CryptoPunks. I found out that auto-generated artworks would be more interesting than I had imagined, and since then I’ve been completely absorbed in generative art.
This is one of the Skulls In Love artworks:
This character wears a cowboy hat, black slim sunglasses, and a kimono. If anyone looks like this, I can’t help laughing!
The Skulls In Love NFTs can be minted for a small amount of MATIC on the official website. Please give it a try to see what kind of unique characters will appear 💀💖
Thank you for reading to the end. I hope this article will be helpful to those who want to launch an NFT project in the future ✨

Vishal Chawla
3 years ago
5 Bored Apes borrowed to claim $1.1 million in APE tokens
Takeaway
Unknown user took advantage of the ApeCoin airdrop to earn $1.1 million.
He used a flash loan to borrow five BAYC NFTs, claim the airdrop, and repay the NFTs.
Yuga Labs, the creators of BAYC, airdropped ApeCoin (APE) to anyone who owns one of their NFTs yesterday.
For the Bored Ape Yacht Club and Mutant Ape Yacht Club collections, the team allocated 150 million tokens, or 15% of the total ApeCoin supply, worth over $800 million. Each BAYC holder received 10,094 tokens worth $80,000 to $200,000.
But someone managed to claim the airdrop using NFTs they didn't own. They used the airdrop's specific features to carry it out. And it worked, earning them $1.1 million in ApeCoin.
The trick was that the ApeCoin airdrop wasn't based on who owned which Bored Ape at a given time. Instead, anyone with a Bored Ape at the time of the airdrop could claim it. So if you gave someone your Bored Ape and you hadn't claimed your tokens, they could claim them.
The person only needed to get hold of some Bored Apes that hadn't had their tokens claimed to claim the airdrop. They could be returned immediately.
So, what happened?
The person found a vault with five Bored Ape NFTs that hadn't been used to claim the airdrop.
A vault tokenizes an NFT or a group of NFTs. You put a bunch of NFTs in a vault and make a token. This token can then be staked for rewards or sold (representing part of the value of the collection of NFTs). Anyone with enough tokens can exchange them for NFTs.
This vault uses the NFTX protocol. In total, it contained five Bored Apes: #7594, #8214, #9915, #8167, and #4755. Nobody had claimed the airdrop because the NFTs were locked up in the vault and not controlled by anyone.
The person wanted to unlock the NFTs to claim the airdrop but didn't want to buy them outright s o they used a flash loan, a common tool for large DeFi hacks. Flash loans are a low-cost way to borrow large amounts of crypto that are repaid in the same transaction and block (meaning that the funds are never at risk of not being repaid).
With a flash loan of under $300,000 they bought a Bored Ape on NFT marketplace OpenSea. A large amount of the vault's token was then purchased, allowing them to redeem the five NFTs. The NFTs were used to claim the airdrop, before being returned, the tokens sold back, and the loan repaid.
During this process, they claimed 60,564 ApeCoin airdrops. They then sold them on Uniswap for 399 ETH ($1.1 million). Then they returned the Bored Ape NFT used as collateral to the same NFTX vault.
Attack or arbitrage?
However, security firm BlockSecTeam disagreed with many social media commentators. A flaw in the airdrop-claiming mechanism was exploited, it said.
According to BlockSecTeam's analysis, the user took advantage of a "vulnerability" in the airdrop.
"We suspect a hack due to a flaw in the airdrop mechanism. The attacker exploited this vulnerability to profit from the airdrop claim" said BlockSecTeam.
For example, the airdrop could have taken into account how long a person owned the NFT before claiming the reward.
Because Yuga Labs didn't take a snapshot, anyone could buy the NFT in real time and claim it. This is probably why BAYC sales exploded so soon after the airdrop announcement.
