More on Entrepreneurship/Creators

Rachel Greenberg
3 years ago
The Unsettling Fact VC-Backed Entrepreneurs Don't Want You to Know
What they'll do is scarier.

My acquaintance recently joined a VC-funded startup. Money, equity, and upside possibilities were nice, but he had a nagging dread.
They just secured a $40M round and are hiring like crazy to prepare for their IPO in two years. All signals pointed to this startup's (a B2B IT business in a stable industry) success, and its equity-holding workers wouldn't pass that up.
Five months after starting the work, my friend struggled with leaving. We might overlook the awful culture and long hours at the proper price. This price plus the company's fate and survival abilities sent my friend departing in an unpleasant unplanned resignation before jumping on yet another sinking ship.
This affects founders. This affects VC-backed companies (and all businesses). This affects anyone starting, buying, or running a business.
Here's the under-the-table approach that's draining VC capital, leaving staff terrified (or jobless), founders rattled, and investors upset. How to recognize, solve, and avoid it
The unsettling reality behind door #1
You can't raise money off just your looks, right? If "looks" means your founding team's expertise, then maybe. In my friend's case, the founding team's strong qualifications and track records won over investors before talking figures.
They're hardly the only startup to raise money without a profitable customer acquisition strategy. Another firm raised money for an expensive sleep product because it's eco-friendly. They were off to the races with a few keywords and key players.
Both companies, along with numerous others, elected to invest on product development first. Company A employed all the tech, then courted half their market (they’re a tech marketplace that connects two parties). Company B spent millions on R&D to create a palatable product, then flooded the world with marketing.
My friend is on Company B's financial team, and he's seen where they've gone wrong. It's terrible.
Company A (tech market): Growing? Not quite. To achieve the ambitious expansion they (and their investors) demand, they've poured much of their little capital into salespeople: Cold-calling commission and salary salesmen. Is it working? Considering attrition and companies' dwindling capital, I don't think so.
Company B (green sleep) has been hiring, digital marketing, and opening new stores like crazy. Growing expenses should result in growing revenues and a favorable return on investment; if you grow too rapidly, you may neglect to check that ROI.
Once Company A cut headcount and Company B declared “going concerned”, my friend realized both startups had the same ailment and didn't recognize it.
I shouldn't have to ask a friend to verify a company's cash reserves and profitability to spot a financial problem. It happened anyhow.
The frightening part isn't that investors were willing to invest millions without product-market fit, CAC, or LTV estimates. That's alarming, but not as scary as the fact that startups aren't understanding the problem until VC rounds have dried up.
When they question consultants if their company will be around in 6 months. It’s a red flag. How will they stretch $20M through a 2-year recession with a $3M/month burn rate and no profitability? Alarms go off.
Who's in danger?
In a word, everyone who raised money without a profitable client acquisition strategy or enough resources to ride out dry spells.
Money mismanagement and poor priorities affect every industry (like sinking all your capital into your product, team, or tech, at the expense of probing what customer acquisition really takes and looks like).
This isn't about tech, real estate, or recession-proof luxury products. Fast, cheap, easy money flows into flashy-looking teams with buzzwords, trending industries, and attractive credentials.
If these companies can't show progress or get a profitable CAC, they can't raise more money. They die if they can't raise more money (or slash headcount and find shoestring budget solutions until they solve the real problem).
The kiss of death (and how to avoid it)
If you're running a startup and think raising VC is the answer, pause and evaluate. Do you need the money now?
I'm not saying VC is terrible or has no role. Founders have used it as a Band-Aid for larger, pervasive problems. Venture cash isn't a crutch for recruiting consumers profitably; it's rocket fuel to get you what and who you need.
Pay-to-play isn't a way to throw money at the wall and hope for a return. Pay-to-play works until you run out of money, and if you haven't mastered client acquisition, your cash will diminish quickly.
How can you avoid this bottomless pit? Tips:
Understand your burn rate
Keep an eye on your growth or profitability.
Analyze each and every marketing channel and initiative.
Make lucrative customer acquisition strategies and satisfied customers your top two priorities. not brand-new products. not stellar hires. avoid the fundraising rollercoaster to save time. If you succeed in these two tasks, investors will approach you with their thirsty offers rather than the other way around, and your cash reserves won't diminish as a result.
Not as much as your grandfather
My family friend always justified expensive, impractical expenditures by saying it was only monopoly money. In business, startups, and especially with money from investors expecting a return, that's not true.
More founders could understand that there isn't always another round if they viewed VC money as their own limited pool. When the well runs dry, you must refill it or save the day.
Venture financing isn't your grandpa's money. A discerning investor has entrusted you with dry powder in the hope that you'll use it wisely, strategically, and thoughtfully. Use it well.
Evgenii Nelepko
3 years ago
My 3 biggest errors as a co-founder and CEO
Reflections on the closed company Hola! Dating app

I'll discuss my fuckups as an entrepreneur and CEO. All of them refer to the dating app Hola!, which I co-founded and starred in.
Spring 2021 was when we started. Two techies and two non-techies created a dating app. Pokemon Go and Tinder were combined.
Online dating is a business, and it takes two weeks from a like to a date. We questioned online dating app users if they met anyone offline last year.
75% replied yes, 50% sometimes, 25% usually.
Offline dating is popular, yet people have concerns.
Men are reluctant to make mistakes in front of others.
Women are curious about the background of everyone who approaches them.
We designed unique mechanics that let people date after a match. No endless chitchat. Women would be safe while men felt like cowboys.
I wish to emphasize three faults that lead to founders' estrangement.
This detachment ultimately led to us shutting down the company.
The wrong technology stack
Situation
Instead of generating a faster MVP and designing an app in a universal stack for iOS and Android, I argued we should pilot the app separately for iOS and Android. Technical founders' expertise made this possible.
Self-reflection
Mistaken strategy. We lost time and resources developing two apps at once. We chose iOS since it's more profitable. Apple took us out after the release, citing Guideline 4.3 Spam. After 4 months, we had nothing. We had a long way to go to get the app on Android and the Store.
I suggested creating a uniform platform for the company's growth. This makes parallel product development easier. The strategist's lack of experience and knowledge made it a piece of crap.
What would I have changed if I could?
We should have designed an Android universal stack. I expected Apple to have issues with a dating app.
Our approach should have been to launch something and subsequently improve it, but prejudice won.
The lesson
Discuss the IT stack with your CTO. It saves time and money. Choose the easiest MVP method.

2. A tardy search for investments
Situation
Though the universe and other founders encouraged me to locate investors first, I started pitching when we almost had an app.
When angels arrived, it was time to close. The app was banned, war broke out, I left the country, and the other co-founders stayed. We had no savings.
Self-reflection
I loved interviewing users. I'm proud of having done 1,000 interviews. I wanted to understand people's pain points and improve the product.
Interview results no longer affected the product. I was terrified to start pitching. I filled out accelerator applications and redid my presentation. You must go through that so you won't be terrified later.
What would I have changed if I could?
Get an external or internal mentor to help me with my first pitch as soon as possible. I'd be supported if criticized. He'd cheer with me if there was enthusiasm.
In 99% of cases, I'm comfortable jumping into the unknown, but there are exceptions. The mentor's encouragement would have prompted me to act sooner.
The lesson
Begin fundraising immediately. Months may pass. Show investors your pre-MVP project. Draw inferences from feedback.
3. Role ambiguity
Situation
My technical co-founders were also part-time lead developers, which produced communication issues. As co-founders, we communicated well and recognized the problems. Stakes, vesting, target markets, and approach were agreed upon.
We were behind schedule. Technical debt and strategic gap grew.
Bi-daily and weekly reviews didn't help. Each time, there were explanations. Inside, I was freaking out.

Self-reflection
I am a fairly easy person to talk to. I always try to stick to agreements; otherwise, my head gets stuffed with unnecessary information, interpretations, and emotions.
Sit down -> talk -> decide -> do -> evaluate the results. Repeat it.
If I don't get detailed comments, I start ruining everyone's mood. If there's a systematic violation of agreements without a good justification, I won't join the project or I'll end the collaboration.
What would I have done otherwise?
This is where it’s scariest to draw conclusions. Probably the most logical thing would have been not to start the project as we started it. But that was already a completely different project. So I would not have done anything differently and would have failed again.
But I drew conclusions for the future.
The lesson
First-time founders should find an adviser or team coach for a strategic session. It helps split the roles and responsibilities.

Thomas Tcheudjio
3 years ago
If you don't crush these 3 metrics, skip the Series A.
I recently wrote about getting VCs excited about Marketplace start-ups. SaaS founders became envious!
Understanding how people wire tens of millions is the only Series A hack I recommend.
Few people understand the intellectual process behind investing.
VC is risk management.
Series A-focused VCs must cover two risks.
1. Market risk
You need a large market to cross a threshold beyond which you can build defensibilities. Series A VCs underwrite market risk.
They must see you have reached product-market fit (PMF) in a large total addressable market (TAM).
2. Execution risk
When evaluating your growth engine's blitzscaling ability, execution risk arises.
When investors remove operational uncertainty, they profit.
Series A VCs like businesses with derisked revenue streams. Don't raise unless you have a predictable model, pipeline, and growth.
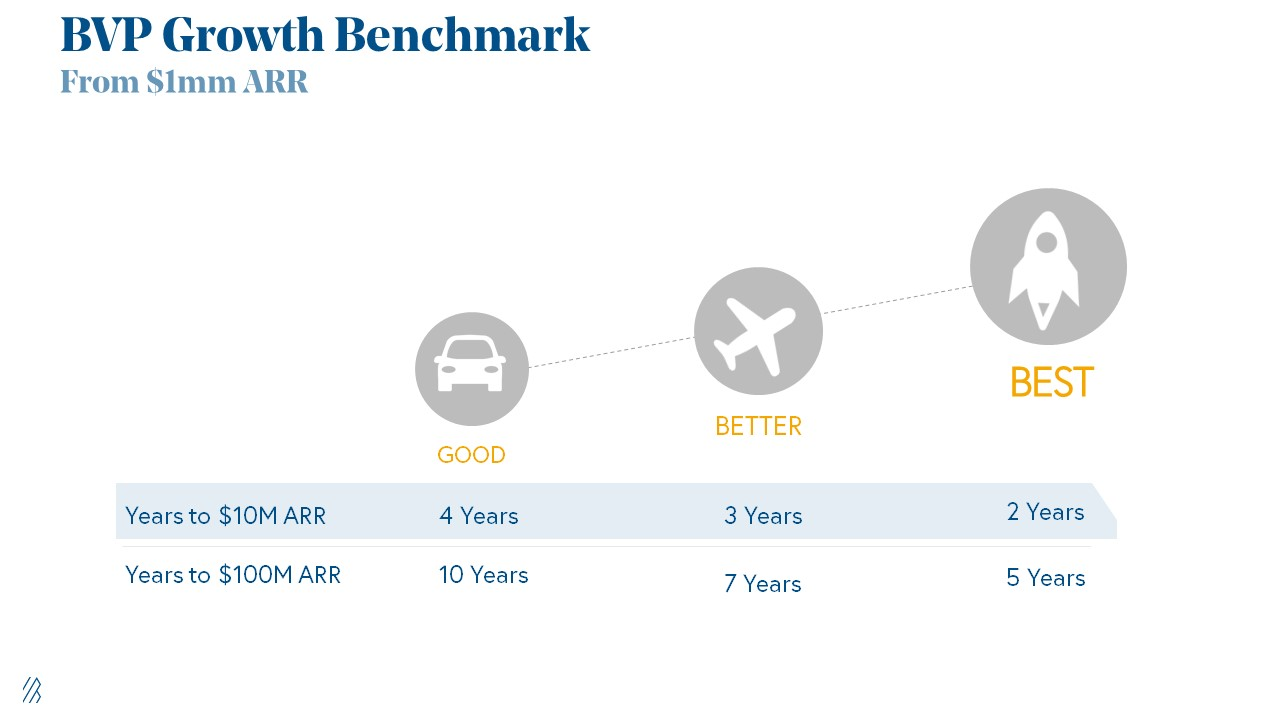
Please beat these 3 metrics before Series A:
Achieve $1.5m ARR in 12-24 months (Market risk)
Above 100% Net Dollar Retention. (Market danger)
Lead Velocity Rate supporting $10m ARR in 2–4 years (Execution risk)
Hit the 3 and you'll raise $10M in 4 months. Discussing 2/3 may take 6–7 months.
If none, don't bother raising and focus on becoming a capital-efficient business (Topics for other posts).
Let's examine these 3 metrics for the brave ones.
1. Lead Velocity Rate supporting €$10m ARR in 2 to 4 years
Last because it's the least discussed. LVR is the most reliable data when evaluating a growth engine, in my opinion.
SaaS allows you to see the future.
Monthly Sales and Sales Pipelines, two predictive KPIs, have poor data quality. Both are lagging indicators, and minor changes can cause huge modeling differences.
Analysts and Associates will trash your forecasts if they're based only on Monthly Sales and Sales Pipeline.
LVR, defined as month-over-month growth in qualified leads, is rock-solid. There's no lag. You can See The Future if you use Qualified Leads and a consistent formula and process to qualify them.
With this metric in your hand, scaling your company turns into an execution play on which VCs are able to perform calculations risk.
2. Above-100% Net Dollar Retention.
Net Dollar Retention is a better-known SaaS health metric than LVR.
Net Dollar Retention measures a SaaS company's ability to retain and upsell customers. Ask what $1 of net new customer spend will be worth in years n+1, n+2, etc.
Depending on the business model, SaaS businesses can increase their share of customers' wallets by increasing users, selling them more products in SaaS-enabled marketplaces, other add-ons, and renewing them at higher price tiers.
If a SaaS company's annualized Net Dollar Retention is less than 75%, there's a problem with the business.
Slack's ARR chart (below) shows how powerful Net Retention is. Layer chart shows how existing customer revenue grows. Slack's S1 shows 171% Net Dollar Retention for 2017–2019.

Slack S-1
3. $1.5m ARR in the last 12-24 months.
According to Point 9, $0.5m-4m in ARR is needed to raise a $5–12m Series A round.
Target at least what you raised in Pre-Seed/Seed. If you've raised $1.5m since launch, don't raise before $1.5m ARR.
Capital efficiency has returned since Covid19. After raising $2m since inception, it's harder to raise $1m in ARR.

P9's 2016-2021 SaaS Funding Napkin
In summary, less than 1% of companies VCs meet get funded. These metrics can help you win.
If there’s demand for it, I’ll do one on direct-to-consumer.
Cheers!
You might also like
James Howell
3 years ago
Which Metaverse Is Better, Decentraland or Sandbox?
The metaverse is the most commonly used term in current technology discussions. While the entire tech ecosystem awaits the metaverse's full arrival, defining it is difficult. Imagine the internet in the '80s! The metaverse is a three-dimensional virtual world where users can interact with digital solutions and each other as digital avatars.
The metaverse is a three-dimensional virtual world where users can interact with digital solutions and each other as digital avatars.
Among the metaverse hype, the Decentraland vs Sandbox debate has gained traction. Both are decentralized metaverse platforms with no central authority. So, what's the difference and which is better? Let us examine the distinctions between Decentraland and Sandbox.
2 Popular Metaverse Platforms Explained
The first step in comparing sandbox and Decentraland is to outline the definitions. Anyone keeping up with the metaverse news has heard of the two current leaders. Both have many similarities, but also many differences. Let us start with defining both platforms to see if there is a winner.
Decentraland
Decentraland, a fully immersive and engaging 3D metaverse, launched in 2017. It allows players to buy land while exploring the vast virtual universe. Decentraland offers a wide range of activities for its visitors, including games, casinos, galleries, and concerts. It is currently the longest-running metaverse project.
Decentraland began with a $24 million ICO and went public in 2020. The platform's virtual real estate parcels allow users to create a variety of experiences. MANA and LAND are two distinct tokens associated with Decentraland. MANA is the platform's native ERC-20 token, and users can burn MANA to get LAND, which is ERC-721 compliant. The MANA coin can be used to buy avatars, wearables, products, and names on Decentraland.
Sandbox
Sandbox, the next major player, began as a blockchain-based virtual world in 2011 and migrated to a 3D gaming platform in 2017. The virtual world allows users to create, play, own, and monetize their virtual experiences. Sandbox aims to empower artists, creators, and players in the blockchain community to customize the platform. Sandbox gives the ideal means for unleashing creativity in the development of the modern gaming ecosystem.
The project combines NFTs and DAOs to empower a growing community of gamers. A new play-to-earn model helps users grow as gamers and creators. The platform offers a utility token, SAND, which is required for all transactions.
What are the key points from both metaverse definitions to compare Decentraland vs sandbox?
It is ideal for individuals, businesses, and creators seeking new artistic, entertainment, and business opportunities. It is one of the rapidly growing Decentralized Autonomous Organization projects. Holders of MANA tokens also control the Decentraland domain.
Sandbox, on the other hand, is a blockchain-based virtual world that runs on the native token SAND. On the platform, users can create, sell, and buy digital assets and experiences, enabling blockchain-based gaming. Sandbox focuses on user-generated content and building an ecosystem of developers.
Sandbox vs. Decentraland
If you try to find what is better Sandbox or Decentraland, then you might struggle with only the basic definitions. Both are metaverse platforms offering immersive 3D experiences. Users can freely create, buy, sell, and trade digital assets. However, both have significant differences, especially in MANA vs SAND.
For starters, MANA has a market cap of $5,736,097,349 versus $4,528,715,461, giving Decentraland an advantage.
The MANA vs SAND pricing comparison is also noteworthy. A SAND is currently worth $3664, while a MANA is worth $2452.
The value of the native tokens and the market capitalization of the two metaverse platforms are not enough to make a choice. Let us compare Sandbox vs Decentraland based on the following factors.
Workstyle
The way Decentraland and Sandbox work is one of the main comparisons. From a distance, they both appear to work the same way. But there's a lot more to learn about both platforms' workings. Decentraland has 90,601 digital parcels of land.
Individual parcels of virtual real estate or estates with multiple parcels of land are assembled. It also has districts with similar themes and plazas, which are non-tradeable parcels owned by the community. It has three token types: MANA, LAND, and WEAR.
Sandbox has 166,464 plots of virtual land that can be grouped into estates. Estates are owned by one person, while districts are owned by two or more people. The Sandbox metaverse has four token types: SAND, GAMES, LAND, and ASSETS.
Age
The maturity of metaverse projects is also a factor in the debate. Decentraland is clearly the winner in terms of maturity. It was the first solution to create a 3D blockchain metaverse. Decentraland made the first working proof of concept public. However, Sandbox has only made an Alpha version available to the public.
Backing
The MANA vs SAND comparison would also include support for both platforms. Digital Currency Group, FBG Capital, and CoinFund are all supporters of Decentraland. It has also partnered with Polygon, the South Korean government, Cyberpunk, and Samsung.
SoftBank, a Japanese multinational conglomerate focused on investment management, is another major backer. Sandbox has the backing of one of the world's largest investment firms, as well as Slack and Uber.
Compatibility
Wallet compatibility is an important factor in comparing the two metaverse platforms. Decentraland currently has a competitive advantage. How? Both projects' marketplaces accept ERC-20 wallets. However, Decentraland has recently improved by bridging with Walletconnect. So it can let Polygon users join Decentraland.
Scalability
Because Sandbox and Decentraland use the Ethereum blockchain, scalability is an issue. Both platforms' scalability is constrained by volatile tokens and high gas fees. So, scalability issues can hinder large-scale adoption of both metaverse platforms.
Buying Land
Decentraland vs Sandbox comparisons often include virtual real estate. However, the ability to buy virtual land on both platforms defines the user experience and differentiates them. In this case, Sandbox offers better options for users to buy virtual land by combining OpenSea and Sandbox. In fact, Decentraland users can only buy from the MANA marketplace.
Innovation
The rate of development distinguishes Sandbox and Decentraland. Both platforms have been developing rapidly new features. However, Sandbox wins by adopting Polygon NFT layer 2 solutions, which consume almost 100 times less energy than Ethereum.
Collaborations
The platforms' collaborations are the key to determining "which is better Sandbox or Decentraland." Adoption of metaverse platforms like the two in question can be boosted by association with reputable brands. Among the partners are Atari, Cyberpunk, and Polygon. Rather, Sandbox has partnered with well-known brands like OpenSea, CryptoKitties, The Walking Dead, Snoop Dogg, and others.
Platform Adaptivity
Another key feature that distinguishes Sandbox and Decentraland is the ease of use. Sandbox clearly wins in terms of platform access. It allows easy access via social media, email, or a Metamask wallet. However, Decentraland requires a wallet connection.
Prospects
The future development plans also play a big role in defining Sandbox vs Decentraland. Sandbox's future development plans include bringing the platform to mobile devices. This includes consoles like PlayStation and Xbox. By the end of 2023, the platform expects to have around 5000 games.
Decentraland, on the other hand, has no set plan. In fact, the team defines the decisions that appear to have value. They plan to add celebrities, creators, and brands soon, along with NFT ads and drops.
Final Words
The comparison of Decentraland vs Sandbox provides a balanced view of both platforms. You can see how difficult it is to determine which decentralized metaverse is better now. Sandbox is still in Alpha, whereas Decentraland has a working proof of concept.
Sandbox, on the other hand, has better graphics and is backed by some big names. But both have a long way to go in the larger decentralized metaverse.

Sad NoCoiner
3 years ago
Two Key Money Principles You Should Understand But Were Never Taught

Prudence is advised. Be debt-free. Be frugal. Spend less.
This advice sounds nice, but it rarely works.
Most people never learn these two money rules. Both approaches will impact how you see personal finance.
It may safeguard you from inflation or the inability to preserve money.
Let’s dive in.
#1: Making long-term debt your ally
High-interest debt hurts consumers. Many credit cards carry 25% yearly interest (or more), so always pay on time. Otherwise, you’re losing money.
Some low-interest debt is good. Especially when buying an appreciating asset with borrowed money.
Inflation helps you.
If you borrow $800,000 at 3% interest and invest it at 7%, you'll make $32,000 (4%).
As money loses value, fixed payments get cheaper. Your assets' value and cash flow rise.
The never-in-debt crowd doesn't know this. They lose money paying off mortgages and low-interest loans early when they could have bought assets instead.
#2: How To Buy Or Build Assets To Make Inflation Irrelevant
Dozens of studies demonstrate actual wage growth is static; $2.50 in 1964 was equivalent to $22.65 now.
These reports never give solutions unless they're selling gold.
But there is one.
Assets beat inflation.
$100 invested into the S&P 500 would have an inflation-adjusted return of 17,739.30%.
Likewise, you can build assets from nothing. Doing is easy and quick. The returns can boost your income by 10% or more.
The people who obsess over inflation inadvertently make the problem worse for themselves. They wait for The Big Crash to buy assets. Or they moan about debt clocks and spending bills instead of seeking a solution.
Conclusion
Being ultra-prudent is like playing golf with a putter to avoid hitting the ball into the water. Sure, you might not slice a drive into the pond. But, you aren’t going to play well either. Or have very much fun.
Money has rules.
Avoiding debt or investment risks will limit your rewards. Long-term, being too cautious hurts your finances.
Disclaimer: This article is for entertainment purposes only. It is not financial advice, always do your own research.

Jake Prins
3 years ago
What are NFTs 2.0 and what issues are they meant to address?
New standards help NFTs reach their full potential.

NFTs lack interoperability and functionality. They have great potential but are mostly speculative. To maximize NFTs, we need flexible smart contracts.
Current requirements are too restrictive.
Most NFTs are based on ERC-721, which makes exchanging them easy. CryptoKitties, a popular online game, used the 2017 standard to demonstrate NFTs' potential.
This simple standard includes a base URI and incremental IDs for tokens. Add the tokenID to the base URI to get the token's metadata.
This let creators collect NFTs. Many NFT projects store metadata on IPFS, a distributed storage network, but others use Google Drive. NFT buyers often don't realize that if the creators delete or move the files, their NFT is just a pointer.
This isn't the standard's biggest issue. There's no way to validate NFT projects.
Creators are one of the most important aspects of art, but nothing is stored on-chain.
ERC-721 contracts only have a name and symbol.
Most of the data on OpenSea's collection pages isn't from the NFT's smart contract. It was added through a platform input field, so it's in the marketplace's database. Other websites may have different NFT information.
In five years, your NFT will be just a name, symbol, and ID.
Your NFT doesn't mention its creators. Although the smart contract has a public key, it doesn't reveal who created it.
The NFT's creators and their reputation are crucial to its value. Think digital fashion and big brands working with well-known designers when more professionals use NFTs. Don't you want them in your NFT?
Would paintings be as valuable if their artists were unknown? Would you believe it's real?
Buying directly from an on-chain artist would reduce scams. Current standards don't allow this data.
Most creator profiles live on centralized marketplaces and could disappear. Current platforms have outpaced underlying standards. The industry's standards are lagging.
For NFTs to grow beyond pointers to a monkey picture file, we may need to use new Web3-based standards.
Introducing NFTs 2.0
Fabian Vogelsteller, creator of ERC-20, developed new web3 standards. He proposed LSP7 Digital Asset and LSP8 Identifiable Digital Asset, also called NFT 2.0.
NFT and token metadata inputs are extendable. Changes to on-chain metadata inputs allow NFTs to evolve. Instead of public keys, the contract can have Universal Profile addresses attached. These profiles show creators' faces and reputations. NFTs can notify asset receivers, automating smart contracts.
LSP7 and LSP8 use ERC725Y. Using a generic data key-value store gives contracts much-needed features:
The asset can be customized and made to stand out more by allowing for unlimited data attachment.
Recognizing changes to the metadata
using a hash reference for metadata rather than a URL reference
This base will allow more metadata customization and upgradeability. These guidelines are:
Genuine and Verifiable Now, the creation of an NFT by a specific Universal Profile can be confirmed by smart contracts.
Dynamic NFTs can update Flexible & Updatable Metadata, allowing certain things to evolve over time.
Protected metadata Now, secure metadata that is readable by smart contracts can be added indefinitely.
Better NFTS prevent the locking of NFTs by only being sent to Universal Profiles or a smart contract that can interact with them.
Summary
NFTS standards lack standardization and powering features, limiting the industry.
ERC-721 is the most popular NFT standard, but it only represents incremental tokenIDs without metadata or asset representation. No standard sender-receiver interaction or security measures ensure safe asset transfers.
NFT 2.0 refers to the new LSP7-DigitalAsset and LSP8-IdentifiableDigitalAsset standards.
They have new standards for flexible metadata, secure transfers, asset representation, and interactive transfer.
With NFTs 2.0 and Universal Profiles, creators could build on-chain reputations.
NFTs 2.0 could bring the industry's needed innovation if it wants to move beyond trading profile pictures for speculation.
