More on Entrepreneurship/Creators

Thomas Tcheudjio
3 years ago
If you don't crush these 3 metrics, skip the Series A.
I recently wrote about getting VCs excited about Marketplace start-ups. SaaS founders became envious!
Understanding how people wire tens of millions is the only Series A hack I recommend.
Few people understand the intellectual process behind investing.
VC is risk management.
Series A-focused VCs must cover two risks.
1. Market risk
You need a large market to cross a threshold beyond which you can build defensibilities. Series A VCs underwrite market risk.
They must see you have reached product-market fit (PMF) in a large total addressable market (TAM).
2. Execution risk
When evaluating your growth engine's blitzscaling ability, execution risk arises.
When investors remove operational uncertainty, they profit.
Series A VCs like businesses with derisked revenue streams. Don't raise unless you have a predictable model, pipeline, and growth.
Please beat these 3 metrics before Series A:
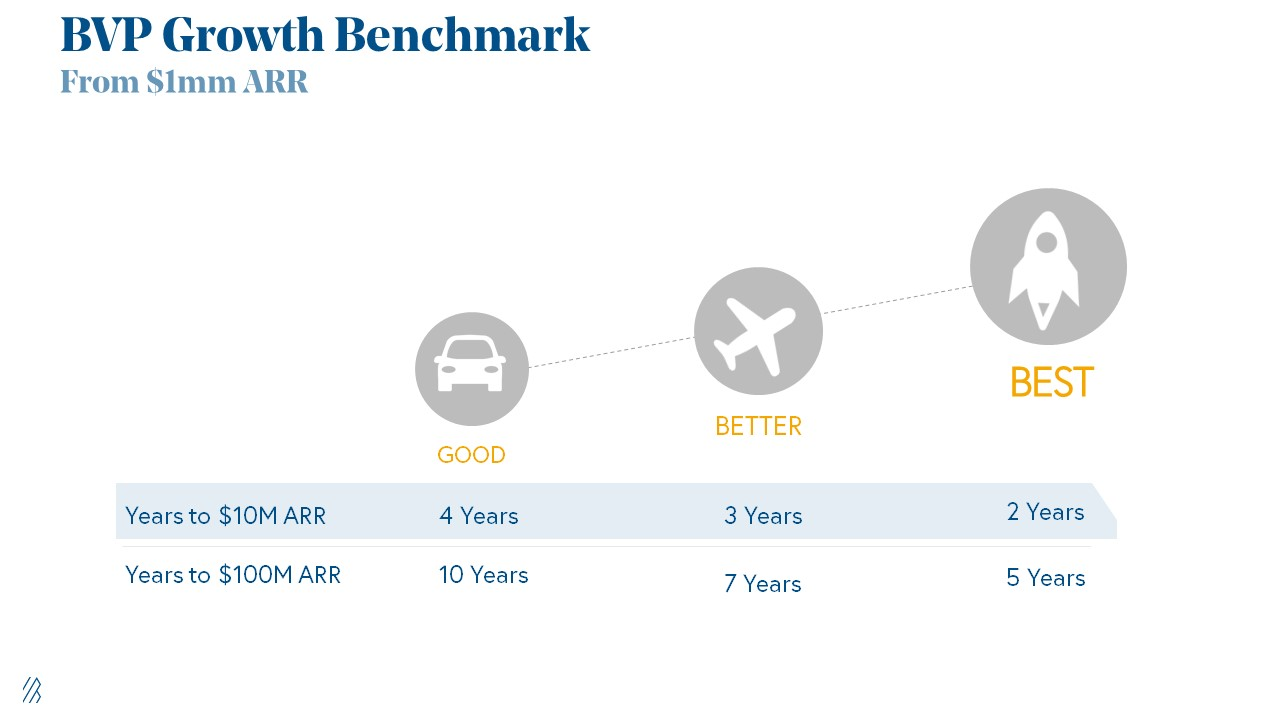
Achieve $1.5m ARR in 12-24 months (Market risk)
Above 100% Net Dollar Retention. (Market danger)
Lead Velocity Rate supporting $10m ARR in 2–4 years (Execution risk)
Hit the 3 and you'll raise $10M in 4 months. Discussing 2/3 may take 6–7 months.
If none, don't bother raising and focus on becoming a capital-efficient business (Topics for other posts).
Let's examine these 3 metrics for the brave ones.
1. Lead Velocity Rate supporting €$10m ARR in 2 to 4 years
Last because it's the least discussed. LVR is the most reliable data when evaluating a growth engine, in my opinion.
SaaS allows you to see the future.
Monthly Sales and Sales Pipelines, two predictive KPIs, have poor data quality. Both are lagging indicators, and minor changes can cause huge modeling differences.
Analysts and Associates will trash your forecasts if they're based only on Monthly Sales and Sales Pipeline.
LVR, defined as month-over-month growth in qualified leads, is rock-solid. There's no lag. You can See The Future if you use Qualified Leads and a consistent formula and process to qualify them.
With this metric in your hand, scaling your company turns into an execution play on which VCs are able to perform calculations risk.
2. Above-100% Net Dollar Retention.
Net Dollar Retention is a better-known SaaS health metric than LVR.
Net Dollar Retention measures a SaaS company's ability to retain and upsell customers. Ask what $1 of net new customer spend will be worth in years n+1, n+2, etc.
Depending on the business model, SaaS businesses can increase their share of customers' wallets by increasing users, selling them more products in SaaS-enabled marketplaces, other add-ons, and renewing them at higher price tiers.
If a SaaS company's annualized Net Dollar Retention is less than 75%, there's a problem with the business.
Slack's ARR chart (below) shows how powerful Net Retention is. Layer chart shows how existing customer revenue grows. Slack's S1 shows 171% Net Dollar Retention for 2017–2019.

Slack S-1
3. $1.5m ARR in the last 12-24 months.
According to Point 9, $0.5m-4m in ARR is needed to raise a $5–12m Series A round.
Target at least what you raised in Pre-Seed/Seed. If you've raised $1.5m since launch, don't raise before $1.5m ARR.
Capital efficiency has returned since Covid19. After raising $2m since inception, it's harder to raise $1m in ARR.

P9's 2016-2021 SaaS Funding Napkin
In summary, less than 1% of companies VCs meet get funded. These metrics can help you win.
If there’s demand for it, I’ll do one on direct-to-consumer.
Cheers!

Sanjay Priyadarshi
3 years ago
Using Ruby code, a programmer created a $48,000,000,000 product that Elon Musk admired.
Unexpected Success

Shopify CEO and co-founder Tobias Lutke. Shopify is worth $48 billion.
World-renowned entrepreneur Tobi
Tobi never expected his first online snowboard business to become a multimillion-dollar software corporation.
Tobi founded Shopify to establish a 20-person company.
The publicly traded corporation employs over 10,000 people.
Here's Tobi Lutke's incredible story.
Elon Musk tweeted his admiration for the Shopify creator.
30-October-2019.
Musk praised Shopify founder Tobi Lutke on Twitter.
Happened:

Explore this programmer's journey.
What difficulties did Tobi experience as a young child?
Germany raised Tobi.
Tobi's parents realized he was smart but had trouble learning as a toddler.
Tobi was learning disabled.
Tobi struggled with school tests.
Tobi's learning impairments were undiagnosed.
Tobi struggled to read as a dyslexic.
Tobi also found school boring.
Germany's curriculum didn't inspire Tobi's curiosity.
“The curriculum in Germany was taught like here are all the solutions you might find useful later in life, spending very little time talking about the problem…If I don’t understand the problem I’m trying to solve, it’s very hard for me to learn about a solution to a problem.”
Studying computer programming
After tenth grade, Tobi decided school wasn't for him and joined a German apprenticeship program.
This curriculum taught Tobi software engineering.
He was an apprentice in a small Siemens subsidiary team.
Tobi worked with rebellious Siemens employees.
Team members impressed Tobi.
Tobi joined the team for this reason.
Tobi was pleased to get paid to write programming all day.
His life could not have been better.
Devoted to snowboarding
Tobi loved snowboarding.
He drove 5 hours to ski at his folks' house.
His friends traveled to the US to snowboard when he was older.
However, the cheap dollar conversion rate led them to Canada.
2000.
Tobi originally decided to snowboard instead than ski.
Snowboarding captivated him in Canada.
On the trip to Canada, Tobi encounters his wife.
Tobi meets his wife Fiona McKean on his first Canadian ski trip.
They maintained in touch after the trip.
Fiona moved to Germany after graduating.
Tobi was a startup coder.
Fiona found work in Germany.
Her work included editing, writing, and academics.
“We lived together for 10 months and then she told me that she need to go back for the master's program.”
With Fiona, Tobi immigrated to Canada.
Fiona invites Tobi.
Tobi agreed to move to Canada.
Programming helped Tobi move in with his girlfriend.
Tobi was an excellent programmer, therefore what he did in Germany could be done anywhere.
He worked remotely for his German employer in Canada.
Tobi struggled with remote work.
Due to poor communication.
No slack, so he used email.
Programmers had trouble emailing.
Tobi's startup was developing a browser.
After the dot-com crash, individuals left that startup.
It ended.
Tobi didn't intend to work for any major corporations.
Tobi left his startup.
He believed he had important skills for any huge corporation.
He refused to join a huge corporation.
Because of Siemens.
Tobi learned to write professional code and about himself while working at Siemens in Germany.
Siemens culture was odd.
Employees were distrustful.
Siemens' rigorous dress code implies that the corporation doesn't trust employees' attire.
It wasn't Tobi's place.
“There was so much bad with it that it just felt wrong…20-year-old Tobi would not have a career there.”
Focused only on snowboarding
Tobi lived in Ottawa with his girlfriend.
Canada is frigid in winter.
Ottawa's winters last.
Almost half a year.
Tobi wanted to do something worthwhile now.
So he snowboarded.
Tobi began snowboarding seriously.
He sought every snowboarding knowledge.
He researched the greatest snowboarding gear first.
He created big spreadsheets for snowboard-making technologies.
Tobi grew interested in selling snowboards while researching.
He intended to sell snowboards online.
He had no choice but to start his own company.
A small local company offered Tobi a job.
Interested.
He must sign papers to join the local company.
He needed a work permit when he signed the documents.
Tobi had no work permit.
He was allowed to stay in Canada while applying for permanent residency.
“I wasn’t illegal in the country, but my state didn’t give me a work permit. I talked to a lawyer and he told me it’s going to take a while until I get a permanent residency.”
Tobi's lawyer told him he cannot get a work visa without permanent residence.
His lawyer said something else intriguing.
Tobis lawyer advised him to start a business.
Tobi declined this local company's job offer because of this.
Tobi considered opening an internet store with his technical skills.
He sold snowboards online.
“I was thinking of setting up an online store software because I figured that would exist and use it as a way to sell snowboards…make money while snowboarding and hopefully have a good life.”
What brought Tobi and his co-founder together, and how did he support Tobi?
Tobi lived with his girlfriend's parents.
In Ottawa, Tobi encounters Scott Lake.
Scott was Tobis girlfriend's family friend and worked for Tobi's future employer.
Scott and Tobi snowboarded.
Tobi pitched Scott his snowboard sales software idea.
Scott liked the idea.
They planned a business together.
“I was looking after the technology and Scott was dealing with the business side…It was Scott who ended up developing relationships with vendors and doing all the business set-up.”
Issues they ran into when attempting to launch their business online
Neither could afford a long-term lease.
That prompted their online business idea.
They would open a store.
Tobi anticipated opening an internet store in a week.
Tobi seeks open-source software.
Most existing software was pricey.
Tobi and Scott couldn't afford pricey software.
“In 2004, I was sitting in front of my computer absolutely stunned realising that we hadn’t figured out how to create software for online stores.”
They required software to:
to upload snowboard images to the website.
people to look up the types of snowboards that were offered on the website. There must be a search feature in the software.
Online users transmit payments, and the merchant must receive them.
notifying vendors of the recently received order.
No online selling software existed at the time.
Online credit card payments were difficult.
How did they advance the software while keeping expenses down?
Tobi and Scott needed money to start selling snowboards.
Tobi and Scott funded their firm with savings.
“We both put money into the company…I think the capital we had was around CAD 20,000(Canadian Dollars).”
Despite investing their savings.
They minimized costs.
They tried to conserve.
No office rental.
They worked in several coffee shops.
Tobi lived rent-free at his girlfriend's parents.
He installed software in coffee cafes.
How were the software issues handled?
Tobi found no online snowboard sales software.
Two choices remained:
Change your mind and try something else.
Use his programming expertise to produce something that will aid in the expansion of this company.
Tobi knew he was the sole programmer working on such a project from the start.
“I had this realisation that I’m going to be the only programmer who has ever worked on this, so I don’t have to choose something that lots of people know. I can choose just the best tool for the job…There is been this programming language called Ruby which I just absolutely loved ”
Ruby was open-source and only had Japanese documentation.
Latin is the source code.
Tobi used Ruby twice.
He assumed he could pick the tool this time.
Why not build with Ruby?
How did they find their first time operating a business?
Tobi writes applications in Ruby.
He wrote the initial software version in 2.5 months.
Tobi and Scott founded Snowdevil to sell snowboards.
Tobi coded for 16 hours a day.
His lifestyle was unhealthy.
He enjoyed pizza and coke.
“I would never recommend this to anyone, but at the time there was nothing more interesting to me in the world.”
Their initial purchase and encounter with it
Tobi worked in cafes then.
“I was working in a coffee shop at this time and I remember everything about that day…At some time, while I was writing the software, I had to type the email that the software would send to tell me about the order.”
Tobi recalls everything.
He checked the order on his laptop at the coffee shop.
Pennsylvanian ordered snowboard.
Tobi walked home and called Scott. Tobi told Scott their first order.
They loved the order.
How were people made aware about Snowdevil?
2004 was very different.
Tobi and Scott attempted simple website advertising.
Google AdWords was new.
Ad clicks cost 20 cents.
Online snowboard stores were scarce at the time.
Google ads propelled the snowdevil brand.
Snowdevil prospered.
They swiftly recouped their original investment in the snowboard business because to its high profit margin.
Tobi and Scott struggled with inventories.
“Snowboards had really good profit margins…Our biggest problem was keeping inventory and getting it back…We were out of stock all the time.”
Selling snowboards returned their investment and saved them money.
They did not appoint a business manager.
They accomplished everything alone.
Sales dipped in the spring, but something magical happened.
Spring sales plummeted.
They considered stocking different boards.
They naturally wanted to add boards and grow the business.
However, magic occurred.
Tobi coded and improved software while running Snowdevil.
He modified software constantly. He wanted speedier software.
He experimented to make the software more resilient.
Tobi received emails requesting the Snowdevil license.
They intended to create something similar.
“I didn’t stop programming, I was just like Ok now let me try things, let me make it faster and try different approaches…Increasingly I got people sending me emails and asking me If I would like to licence snowdevil to them. People wanted to start something similar.”
Software or skateboards, your choice
Scott and Tobi had to choose a hobby in 2005.
They might sell alternative boards or use software.
The software was a no-brainer from demand.
Daniel Weinand is invited to join Tobi's business.
Tobis German best friend is Daniel.
Tobi and Scott chose to use the software.
Tobi and Scott kept the software service.
Tobi called Daniel to invite him to Canada to collaborate.
Scott and Tobi had quit snowboarding until then.
How was Shopify launched, and whence did the name come from?
The three chose Shopify.
Named from two words.
First:
Shop
Final part:
Simplify
Shopify
Shopify's crew has always had one goal:
creating software that would make it simple and easy for people to launch online storefronts.
Launched Shopify after raising money for the first time.
Shopify began fundraising in 2005.
First, they borrowed from family and friends.
They needed roughly $200k to run the company efficiently.
$200k was a lot then.
When questioned why they require so much money. Tobi told them to trust him with their goals. The team raised seed money from family and friends.
Shopify.com has a landing page. A demo of their goal was on the landing page.
In 2006, Shopify had about 4,000 emails.
Shopify rented an Ottawa office.
“We sent a blast of emails…Some people signed up just to try it out, which was exciting.”
How things developed after Scott left the company
Shopify co-founder Scott Lake left in 2008.
Scott was CEO.
“He(Scott) realized at some point that where the software industry was going, most of the people who were the CEOs were actually the highly technical person on the founding team.”
Scott leaving the company worried Tobi.
Tobis worried about finding a new CEO.
To Tobi:
A great VC will have the network to identify the perfect CEO for your firm.
Tobi started visiting Silicon Valley to meet with venture capitalists to recruit a CEO.
Initially visiting Silicon Valley
Tobi came to Silicon Valley to start a 20-person company.
This company creates eCommerce store software.
Tobi never wanted a big corporation. He desired a fulfilling existence.
“I stayed in a hostel in the Bay Area. I had one roommate who was also a computer programmer. I bought a bicycle on Craiglist. I was there for a week, but ended up staying two and a half weeks.”
Tobi arrived unprepared.
When venture capitalists asked him business questions.
He answered few queries.
Tobi didn't comprehend VC meetings' terminology.
He wrote the terms down and looked them up.
Some were fascinated after he couldn't answer all these queries.
“I ended up getting the kind of term sheets people dream about…All the offers were conditional on moving our company to Silicon Valley.”
Canada received Tobi.
He wanted to consult his team before deciding. Shopify had five employees at the time.
2008.
A global recession greeted Tobi in Canada. The recession hurt the market.
His term sheets were useless.
The economic downturn in the world provided Shopify with a fantastic opportunity.
The global recession caused significant job losses.
Fired employees had several ideas.
They wanted online stores.
Entrepreneurship was desired. They wanted to quit work.
People took risks and tried new things during the global slump.
Shopify subscribers skyrocketed during the recession.
“In 2009, the company reached neutral cash flow for the first time…We were in a position to think about long-term investments, such as infrastructure projects.”
Then, Tobi Lutke became CEO.
How did Tobi perform as the company's CEO?
“I wasn’t good. My team was very patient with me, but I had a lot to learn…It’s a very subtle job.”
2009–2010.
Tobi limited the company's potential.
He deliberately restrained company growth.
Tobi had one costly problem:
Whether Shopify is a venture or a lifestyle business.
The company's annual revenue approached $1 million.
Tobi battled with the firm and himself despite good revenue.
His wife was supportive, but the responsibility was crushing him.
“It’s a crushing responsibility…People had families and kids…I just couldn’t believe what was going on…My father-in-law gave me money to cover the payroll and it was his life-saving.”
Throughout this trip, everyone supported Tobi.
They believed it.
$7 million in donations received
Tobi couldn't decide if this was a lifestyle or a business.
Shopify struggled with marketing then.
Later, Tobi tried 5 marketing methods.
He told himself that if any marketing method greatly increased their growth, he would call it a venture, otherwise a lifestyle.
The Shopify crew brainstormed and voted on marketing concepts.
Tested.
“Every single idea worked…We did Adwords, published a book on the concept, sponsored a podcast and all the ones we tracked worked.”
To Silicon Valley once more
Shopify marketing concepts worked once.
Tobi returned to Silicon Valley to pitch investors.
He raised $7 million, valuing Shopify at $25 million.
All investors had board seats.
“I find it very helpful…I always had a fantastic relationship with everyone who’s invested in my company…I told them straight that I am not going to pretend I know things, I want you to help me.”
Tobi developed skills via running Shopify.
Shopify had 20 employees.
Leaving his wife's parents' home
Tobi left his wife's parents in 2014.
Tobi had a child.
Shopify has 80,000 customers and 300 staff in 2013.
Public offering in 2015
Shopify investors went public in 2015.
Shopify powers 4.1 million e-Commerce sites.
Shopify stores are 65% US-based.
It is currently valued at $48 billion.

Nick
3 years ago
This Is How Much Quora Paid Me For 23 Million Content Views
You’ll be surprised; I sure was

Blogging and writing online as a side income has now been around for a significant amount of time. Nowadays, it is a continuously rising moneymaker for prospective writers, with several writing platforms existing online. At the top of the list are Medium, Vocal Media, Newsbreak, and the biggest one of them, Quora, with 300 million active users.
Quora, unlike Medium, is a question-and-answer format platform. On Medium you are permitted to write what you want, while on Quora, you answer questions on topics that you have expertise about. Quora, like Medium, now compensates its authors for the answers they provide in comparison to the previous, in which you had to be admitted to the partner program and were paid to ask questions.
Quora just recently went live with this new partner program, Quora Plus, and the way it works is that it is a subscription for $5 a month which provides you access to metered/monetized stories, in turn compensating the writers for part of that subscription for their answers.
I too on Quora have found a lot of success on the platform, gaining 23 Million Content Views, and 300,000 followers for my space, which is kind of the Quora equivalent of a Medium article. The way in which I was able to do this was entirely thanks to a hack that I uncovered to the Quora algorithm.

In this article, I plan on discussing how much money I received from 23 million content views on Quora, and I bet you’ll be shocked; I know I was.
A Brief Explanation of How I Got 23 Million Views and How You Can Do It Too
On Quora, everything in terms of obtaining views is about finding the proper question, which I only understood quite late into the game. I published my first response in 2019 but never actually wrote on Quora until the summer of 2020, and about a month into posting consistently I found out how to find the perfect question. Here’s how:
The Process
Go to your Home Page and start scrolling… While browsing, check for the following things…
Answers from people you follow or your followers.
Advertisements
These two things are the two things you want to ignore, you don’t want to answer those questions or look at the ads. You should now be left with a couple of recommended answers. To discover which recommended answer is the best to answer as well, look at these three important aspects.
Date of the answer: Was it in the past few days, preferably 2–3 days, even better, past 24 hours?
Views: Are they in the ten thousands or hundred thousands?
Upvotes: Are they in the hundreds or thousands?
Now, choose an answer to a question which you think you could answer as well that satisfies the requirements above. Once you click on it, as all answers on Quora works, it will redirect you to the page for that question, in which you will have to select once again if you should answer the question.
Amount of answers: How many responses are there to the given question? This tells you how much competition you have. My rule is beyond 25 answers, you shouldn’t answer, but you can change it anyway you’d like.
Answerers: Who did the answering for the question? If the question includes a bunch of renowned, extremely well-known people on Quora, there’s a good possibility your essay is going to get drowned out.
Views: Check for a constant quantity of high views on each answer for the question; this is what will guarantee that your answer gets a lot of views!
The Income Reveal! How Much I Made From 23 Million Content Views
DRUM ROLL, PLEASE!
8.97 USD. Yes, not even ten dollars, not even nine. Just eight dollars and ninety-seven cents.

Possible Reasons for My Low Earnings
Quora Plus and the answering partner program are newer than my Quora views.
Few people use Quora+, therefore revenues are low.
I haven't been writing much on Quora, so I'm only making money from old answers and a handful since Quora Plus launched.
Quora + pays poorly...
Should You Try Quora and Quora For Money?
My answer depends on your needs. I never got invited to Quora's question partner program due to my late start, but other writers have made hundreds. Due to Quora's new and competitive answering partner program, you may not make much money.
If you want a fun writing community, try Quora. Quora was fun when I only made money from my space. Quora +'s paywalls and new contributors eager to make money have made the platform less fun for me.
This article is a summary to save you time. You can read my full, more detailed article, here.
You might also like

Will Leitch
3 years ago
Don't treat Elon Musk like Trump.
He’s not the President. Stop treating him like one.

Elon Musk tweeted from Qatar, where he was watching the World Cup Final with Jared Kushner.
Musk's subsequent Tweets were as normal, basic, and bland as anyone's from a World Cup Final: It's depressing to see the world's richest man looking at his phone during a grand ceremony. Rich guy goes to rich guy event didn't seem important.
Before Musk posted his should-I-step-down-at-Twitter poll, CNN ran a long segment asking if it was hypocritical for him to reveal his real-time location after defending his (very dumb) suspension of several journalists for (supposedly) revealing his assassination coordinates by linking to a site that tracks Musks private jet. It was hard to ignore CNN's hypocrisy: It covered Musk as Twitter CEO like President Trump. EVERY TRUMP STORY WAS BASED ON HIM SAYING X, THEN DOING Y. Trump would do something horrific, lie about it, then pretend it was fine, then condemn a political rival who did the same thing, be called hypocritical, and so on. It lasted four years. Exhausting.
It made sense because Trump was the President of the United States. The press's main purpose is to relentlessly cover and question the president.
It's strange to say this out. Twitter isn't America. Elon Musk isn't a president. He maintains a money-losing social media service to harass and mock people he doesn't like. Treating Musk like Trump, as if he should be held accountable like Trump, shows a startling lack of perspective. Some journalists treat Twitter like a country.
The compulsive, desperate way many journalists utilize the site suggests as much. Twitter isn't the town square, despite popular belief. It's a place for obsessives to meet and converse. Journalists say they're breaking news. Their careers depend on it. They can argue it's a public service. Nope. It's a place lonely people go to speak all day. Twitter. So do journalists, Trump, and Musk. Acting as if it has a greater purpose, as if it's impossible to break news without it, or as if the republic is in peril is ludicrous. Only 23% of Americans are on Twitter, while 25% account for 97% of Tweets. I'd think a large portion of that 25% are journalists (or attention addicts) chatting to other journalists. Their loudness makes Twitter seem more important than it is. Nope. It's another stupid website. They were there before Twitter; they will be there after Twitter. It’s just a website. We can all get off it if we want. Most of us aren’t even on it in the first place.
Musk is a website-owner. No world leader. He's not as accountable as Trump was. Musk is cable news's primary character now that Trump isn't (at least for now). Becoming a TV news anchor isn't as significant as being president. Elon Musk isn't as important as we all pretend, and Twitter isn't even close. Twitter is a dumb website, Elon Musk is a rich guy going through a midlife crisis, and cable news is lazy because its leaders thought the entire world was on Twitter and are now freaking out that their playground is being disturbed.
I’ve said before that you need to leave Twitter, now. But even if you’re still on it, we need to stop pretending it matters more than it does. It’s a site for lonely attention addicts, from the man who runs it to the journalists who can’t let go of it. It’s not a town square. It’s not a country. It’s not even a successful website. Let’s stop pretending any of it’s real. It’s not.

Will Lockett
3 years ago
Thanks to a recent development, solar energy may prove to be the best energy source.

Perovskite solar cells will revolutionize everything.
Humanity is in a climatic Armageddon. Our widespread ecological crimes of the previous century are catching up with us, and planet-scale karma threatens everyone. We must adjust to new technologies and lifestyles to avoid this fate. Even solar power, a renewable energy source, has climate problems. A recent discovery could boost solar power's eco-friendliness and affordability. Perovskite solar cells are amazing.
Perovskite is a silicon-like semiconductor. Semiconductors are used to make computer chips, LEDs, camera sensors, and solar cells. Silicon makes sturdy and long-lasting solar cells, thus it's used in most modern solar panels.
Perovskite solar cells are far better. First, they're easy to make at room temperature, unlike silicon cells, which require long, intricate baking processes. This makes perovskite cells cheaper to make and reduces their carbon footprint. Perovskite cells are efficient. Most silicon panel solar farms are 18% efficient, meaning 18% of solar radiation energy is transformed into electricity. Perovskite cells are 25% efficient, making them 38% more efficient than silicon.
However, perovskite cells are nowhere near as durable. A normal silicon panel will lose efficiency after 20 years. The first perovskite cells were ineffective since they lasted barely minutes.
Recent research from Princeton shows that perovskite cells can endure 30 years. The cells kept their efficiency, therefore no sacrifices were made.
No electrical or chemical engineer here, thus I can't explain how they did it. But strangely, the team said longevity isn't the big deal. In the next years, perovskite panels will become longer-lasting. How do you test a panel if you only have a month or two? This breakthrough technique needs a uniform method to estimate perovskite life expectancy fast. The study's key milestone was establishing a standard procedure.
Lab-based advanced aging tests are their solution. Perovskite cells decay faster at higher temperatures, so scientists can extrapolate from that. The test heated the panel to 110 degrees and waited for its output to reduce by 20%. Their panel lasted 2,100 hours (87.5 days) before a 20% decline.
They did some math to extrapolate this data and figure out how long the panel would have lasted in different climates, and were shocked to find it would last 30 years in Princeton. This made perovskite panels as durable as silicon panels. This panel could theoretically be sold today.
This technology will soon allow these brilliant panels to be released into the wild. This technology could be commercially viable in ten, maybe five years.
Solar power will be the best once it does. Solar power is cheap and low-carbon. Perovskite is the cheapest renewable energy source if we switch to it. Solar panel manufacturing's carbon footprint will also drop.
Perovskites' impact goes beyond cost and carbon. Silicon panels require harmful mining and contain toxic elements (cadmium). Perovskite panels don't require intense mining or horrible materials, making their production and expiration more eco-friendly.
Solar power destroys habitat. Massive solar farms could reduce biodiversity and disrupt local ecology by destroying vital habitats. Perovskite cells are more efficient, so they can shrink a solar farm while maintaining energy output. This reduces land requirements, making perovskite solar power cheaper, and could reduce solar's environmental impact.
Perovskite solar power is scalable and environmentally friendly. Princeton scientists will speed up the development and rollout of this energy.
Why bother with fusion, fast reactors, SMRs, or traditional nuclear power? We're close to developing a nearly perfect environmentally friendly power source, and we have the tools and systems to do so quickly. It's also affordable, so we can adopt it quickly and let the developing world use it to grow. Even I struggle to justify spending billions on fusion when a great, cheap technology outperforms it. Perovskite's eco-credentials and cost advantages could save the world and power humanity's future.

MartinEdic
3 years ago
Russia Through the Windows: It's Very Bad
And why we must keep arming Ukraine

Russian expatriates write about horrific news from home.
Read this from Nadin Brzezinski. She's not a native English speaker, so there are grammar errors, but her tale smells true.
Terrible truth.
There's much more that reveals Russia's grim reality.
Non-leadership. Millions of missing supplies are presumably sold for profit, leaving untrained troops without food or gear. Missile attacks pause because they run out. Fake schemes to hold talks as a way of stalling while they scramble for solutions.
Street men were mobilized. Millions will be ground up to please a crazed despot. Fear, wrath, and hunger pull apart civilization.
It's the most dystopian story, but Ukraine is worse. Destruction of a society, country, and civilization. Only the invaders' corruption and incompetence save the Ukrainians.
Rochester, NY. My suburb had many Soviet-era Ukrainian refugees. Their kids were my classmates. Fifty years later, many are still my friends. I loved their food and culture. My town has 20,000 Ukrainians.
Grieving but determined. They don't quit. They won't quit. Russians are eternal enemies.
It's the Russian people's willingness to tolerate corruption, abuse, and stupidity by their leaders. They are paying. 65000 dead. Ruined economy. No freedom to speak. Americans do not appreciate that freedom as we should.
It lets me write/publish.
Russian friends are shocked. Many are here because their parents escaped Russian anti-semitism and authoritarian oppression. A Russian cultural legacy says a strongman's methods are admirable.
A legacy of a slavery history disguised as serfdom. Peasants and Princes.
Read Tolstoy. Then Anna Karenina. The main characters are princes and counts, whose leaders are incompetent idiots with wealth and power.
Peasants who die in their wars due to incompetence are nameless ciphers.
Sound familiar?
