More on Entrepreneurship/Creators

Antonio Neto
3 years ago
Should you skip the minimum viable product?
Are MVPs outdated and have no place in modern product culture?

Frank Robinson coined "MVP" in 2001. In the same year as the Agile Manifesto, the first Scrum experiment began. MVPs are old.
The concept was created to solve the waterfall problem at the time.
The market was still sour from the .com bubble. The tech industry needed a new approach. Product and Agile gained popularity because they weren't waterfall.
More than 20 years later, waterfall is dead as dead can be, but we are still talking about MVPs. Does that make sense?
What is an MVP?
Minimum viable product. You probably know that, so I'll be brief:
[…] The MVP fits your company and customer. It's big enough to cause adoption, satisfaction, and sales, but not bloated and risky. It's the product with the highest ROI/risk. […] — Frank Robinson, SyncDev
MVP is a complete product. It's not a prototype. It's your product's first iteration, which you'll improve. It must drive sales and be user-friendly.
At the MVP stage, you should know your product's core value, audience, and price. We are way deep into early adoption territory.
What about all the things that come before?
Modern product discovery
Eric Ries popularized the term with The Lean Startup in 2011. (Ries would work with the concept since 2008, but wide adoption came after the book was released).
Ries' definition of MVP was similar to Robinson's: "Test the market" before releasing anything. Ries never mentioned money, unlike Jobs. His MVP's goal was learning.
“Remove any feature, process, or effort that doesn't directly contribute to learning” — Eric Ries, The Lean Startup
Product has since become more about "what" to build than building it. What started as a learning tool is now a discovery discipline: fake doors, prototyping, lean inception, value proposition canvas, continuous interview, opportunity tree... These are cheap, effective learning tools.
Over time, companies realized that "maximum ROI divided by risk" started with discovery, not the MVP. MVPs are still considered discovery tools. What is the problem with that?
Time to Market vs Product Market Fit
Waterfall's Time to Market is its biggest flaw. Since projects are sliced horizontally rather than vertically, when there is nothing else to be done, it’s not because the product is ready, it’s because no one cares to buy it anymore.
MVPs were originally conceived as a way to cut corners and speed Time to Market by delivering more customer requests after they paid.

Original product development was waterfall-like.
Time to Market defines an optimal, specific window in which value should be delivered. It's impossible to predict how long or how often this window will be open.
Product Market Fit makes this window a "state." You don’t achieve Product Market Fit, you have it… and you may lose it.
Take, for example, Snapchat. They had a great time to market, but lost product-market fit later. They regained product-market fit in 2018 and have grown since.

An MVP couldn't handle this. What should Snapchat do? Launch Snapchat 2 and see what the market was expecting differently from the last time? MVPs are a snapshot in time that may be wrong in two weeks.
MVPs are mini-projects. Instead of spending a lot of time and money on waterfall, you spend less but are still unsure of the results.
MVPs aren't always wrong. When releasing your first product version, consider an MVP.
Minimum viable product became less of a thing on its own and more interchangeable with Alpha Release or V.1 release over time.
Modern discovery technics are more assertive and predictable than the MVP, but clarity comes only when you reach the market.
MVPs aren't the starting point, but they're the best way to validate your product concept.

Startup Journal
3 years ago
The Top 14 Software Business Ideas That Are Sure To Succeed in 2023
Software can change any company.

Software is becoming essential. Everyone should consider how software affects their lives and others'.
Software on your phone, tablet, or computer offers many new options. We're experts in enough ways now.
Software Business Ideas will be popular by 2023.
ERP Programs
ERP software meets rising demand.
ERP solutions automate and monitor tasks that large organizations, businesses, and even schools would struggle to do manually.
ERP software could reach $49 billion by 2024.
CRM Program
CRM software is a must-have for any customer-focused business.
Having an open mind about your business services and products allows you to change platforms.
Another company may only want your CRM service.
Medical software
Healthcare facilities need reliable, easy-to-use software.
EHRs, MDDBs, E-Prescribing, and more are software options.
The global medical software market could reach $11 billion by 2025, and mobile medical apps may follow.
Presentation Software in the Cloud
SaaS presentation tools are great.
They're easy to use, comprehensive, and full of traditional Software features.
In today's cloud-based world, these solutions make life easier for people. We don't know about you, but we like it.
Software for Project Management
People began working remotely without signs or warnings before the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic.
Many organizations found it difficult to track projects and set deadlines.
With PMP software tools, teams can manage remote units and collaborate effectively.
App for Blockchain-Based Invoicing
This advanced billing and invoicing solution is for businesses and freelancers.
These blockchain-based apps can calculate taxes, manage debts, and manage transactions.
Intelligent contracts help blockchain track transactions more efficiently. It speeds up and improves invoice generation.
Software for Business Communications
Internal business messaging is tricky.
Top business software tools for communication can share files, collaborate on documents, host video conferences, and more.
Payroll Automation System
Software development also includes developing an automated payroll system.
These software systems reduce manual tasks for timely employee payments.
These tools help enterprise clients calculate total wages quickly, simplify tax calculations, improve record-keeping, and support better financial planning.
System for Detecting Data Leaks
Both businesses and individuals value data highly. Yahoo's data breach is dangerous because of this.
This area of software development can help people protect their data.
You can design an advanced data loss prevention system.
AI-based Retail System
AI-powered shopping systems are popular. The systems analyze customers' search and purchase patterns and store history and are equipped with a keyword database.
These systems offer many customers pre-loaded products.
AI-based shopping algorithms also help users make purchases.
Software for Detecting Plagiarism
Software can help ensure your projects are original and not plagiarized.
These tools detect plagiarized content that Google, media, and educational institutions don't like.
Software for Converting Audio to Text
Machine Learning converts speech to text automatically.
These programs can quickly transcribe cloud-based files.
Software for daily horoscopes
Daily and monthly horoscopes will continue to be popular.
Software platforms that can predict forecasts, calculate birth charts, and other astrology resources are good business ideas.
E-learning Programs
Traditional study methods are losing popularity as virtual schools proliferate and physical space shrinks.
Khan Academy online courses are the best way to keep learning.
Online education portals can boost your learning. If you want to start a tech startup, consider creating an e-learning program.
Conclusion
Software is booming. There's never been a better time to start a software development business, with so many people using computers and smartphones. This article lists eight business ideas for 2023. Consider these ideas if you're just starting out or looking to expand.

Jayden Levitt
3 years ago
Billionaire who was disgraced lost his wealth more quickly than anyone in history
If you're not genuine, you'll be revealed.

Sam Bankman-Fried (SBF) was called the Cryptocurrency Warren Buffet.
No wonder.
SBF's trading expertise, Blockchain knowledge, and ability to construct FTX attracted mainstream investors.
He had a fantastic worldview, donating much of his riches to charity.
As the onion layers peel back, it's clear he wasn't the altruistic media figure he portrayed.
SBF's mistakes were disastrous.
Customer deposits were traded and borrowed by him.
With ten other employees, he shared a $40 million mansion where they all had polyamorous relationships.
Tone-deaf and wasteful marketing expenditures, such as the $200 million spent to change the name of the Miami Heat stadium to the FTX Arena
Democrats received a $40 million campaign gift.
And now there seems to be no regret.
FTX was a 32-billion-dollar cryptocurrency exchange.
It went bankrupt practically overnight.
SBF, FTX's creator, exploited client funds to leverage trade.
FTX had $1 billion in customer withdrawal reserves against $9 billion in liabilities in sister business Alameda Research.
Bloomberg Billionaire Index says it's the largest and fastest net worth loss in history.
It gets worse.
SBF's net worth is $900 Million, however he must still finalize FTX's bankruptcy.
SBF's arrest in the Bahamas and SEC inquiry followed news that his cryptocurrency exchange had crashed, losing billions in customer deposits.
A journalist contacted him on Twitter D.M., and their exchange is telling.
His ideas are revealed.
Kelsey Piper says they didn't expect him to answer because people under investigation don't comment.
Bankman-Fried wanted to communicate, and the interaction shows he has little remorse.
SBF talks honestly about FTX gaming customers' money and insults his competition.
Reporter Kelsey Piper was outraged by what he said and felt the mistakes SBF says plague him didn't evident in the messages.
Before FTX's crash, SBF was a poster child for Cryptocurrency regulation and avoided criticizing U.S. regulators.
He tells Piper that his lobbying is just excellent PR.
It shows his genuine views and supports cynics' opinions that his attempts to win over U.S. authorities were good for his image rather than Crypto.
SBF’s responses are in Grey, and Pipers are in Blue.

It's unclear if SBF cut corners for his gain. In their Twitter exchange, Piper revisits an interview question about ethics.
SBF says, "All the foolish sh*t I said"
SBF claims FTX has never invested customer monies.


Piper challenged him on Twitter.
While he insisted FTX didn't use customer deposits, he said sibling business Alameda borrowed too much from FTX's balance sheet.
He did, basically.
When consumers tried to withdraw money, FTX was short.
SBF thought Alameda had enough money to cover FTX customers' withdrawals, but life sneaks up on you.

SBF believes most exchanges have done something similar to FTX, but they haven't had a bank run (a bunch of people all wanting to get their deposits out at the same time).
SBF believes he shouldn't have consented to the bankruptcy and kept attempting to raise more money because withdrawals would be open in a month with clients whole.
If additional money came in, he needed $8 billion to bridge the creditors' deficit, and there aren't many corporations with $8 billion to spare.
Once clients feel protected, they will continue to leave their assets on the exchange, according to one idea.
Kevin OLeary, a world-renowned hedge fund manager, says not all investors will walk through the open gate once the company is safe, therefore the $8 Billion wasn't needed immediately.
SBF claims the bankruptcy was his biggest error because he could have accumulated more capital.


Final Reflections
Sam Bankman-Fried, 30, became the world's youngest billionaire in four years.
Never listen to what people say about investing; watch what they do.
SBF is a trader who gets wrecked occasionally.
Ten first-time entrepreneurs ran FTX, screwing each other with no risk management.
It prevents opposing or challenging perspectives and echo chamber highs.
Twitter D.M. conversation with a journalist is the final nail.
He lacks an experienced crew.
This event will surely speed up much-needed regulation.
It's also prompted cryptocurrency exchanges to offer proof of reserves to calm customers.
You might also like
Matthew Royse
3 years ago
7 ways to improve public speaking
How to overcome public speaking fear and give a killer presentation

"Public speaking is people's biggest fear, according to studies. Death's second. The average person is better off in the casket than delivering the eulogy." — American comedian, actor, writer, and producer Jerry Seinfeld
People fear public speaking, according to research. Public speaking can be intimidating.
Most professions require public speaking, whether to 5, 50, 500, or 5,000 people. Your career will require many presentations. In a small meeting, company update, or industry conference.
You can improve your public speaking skills. You can reduce your anxiety, improve your performance, and feel more comfortable speaking in public.
“If I returned to college, I'd focus on writing and public speaking. Effective communication is everything.” — 38th president Gerald R. Ford
You can deliver a great presentation despite your fear of public speaking. There are ways to stay calm while speaking and become a more effective public speaker.
Seven tips to improve your public speaking today. Let's help you overcome your fear (no pun intended).
Know your audience.
"You're not being judged; the audience is." — Entrepreneur, author, and speaker Seth Godin
Understand your audience before speaking publicly. Before preparing a presentation, know your audience. Learn what they care about and find useful.
Your presentation may depend on where you're speaking. A classroom is different from a company meeting.
Determine your audience before developing your main messages. Learn everything about them. Knowing your audience helps you choose the right words, information (thought leadership vs. technical), and motivational message.
2. Be Observant
Observe others' speeches to improve your own. Watching free TED Talks on education, business, science, technology, and creativity can teach you a lot about public speaking.
What worked and what didn't?
What would you change?
Their strengths
How interesting or dull was the topic?
Note their techniques to learn more. Studying the best public speakers will amaze you.
Learn how their stage presence helped them communicate and captivated their audience. Please note their pauses, humor, and pacing.
3. Practice
"A speaker should prepare based on what he wants to learn, not say." — Author, speaker, and pastor Tod Stocker
Practice makes perfect when it comes to public speaking. By repeating your presentation, you can find your comfort zone.
When you've practiced your presentation many times, you'll feel natural and confident giving it. Preparation helps overcome fear and anxiety. Review notes and important messages.
When you know the material well, you can explain it better. Your presentation preparation starts before you go on stage.
Keep a notebook or journal of ideas, quotes, and examples. More content means better audience-targeting.
4. Self-record
Videotape your speeches. Check yourself. Body language, hands, pacing, and vocabulary should be reviewed.
Best public speakers evaluate their performance to improve.
Write down what you did best, what you could improve and what you should stop doing after watching a recording of yourself. Seeing yourself can be unsettling. This is how you improve.
5. Remove text from slides
"Humans can't read and comprehend screen text while listening to a speaker. Therefore, lots of text and long, complete sentences are bad, bad, bad.” —Communications expert Garr Reynolds
Presentation slides shouldn't have too much text. 100-slide presentations bore the audience. Your slides should preview what you'll say to the audience.
Use slides to emphasize your main point visually.
If you add text, use at least 40-point font. Your slides shouldn't require squinting to read. You want people to watch you, not your slides.
6. Body language
"Body language is powerful." We had body language before speech, and 80% of a conversation is read through the body, not the words." — Dancer, writer, and broadcaster Deborah Bull
Nonverbal communication dominates. Our bodies speak louder than words. Don't fidget, rock, lean, or pace.
Relax your body to communicate clearly and without distraction through nonverbal cues. Public speaking anxiety can cause tense body language.
Maintain posture and eye contact. Don’t put your hand in your pockets, cross your arms, or stare at your notes. Make purposeful hand gestures that match what you're saying.
7. Beginning/ending Strong
Beginning and end are memorable. Your presentation must start strong and end strongly. To engage your audience, don't sound robotic.
Begin with a story, stat, or quote. Conclude with a summary of key points. Focus on how you will start and end your speech.
You should memorize your presentation's opening and closing. Memorize something naturally. Excellent presentations start and end strong because people won't remember the middle.
Bringing It All Together
Seven simple yet powerful ways to improve public speaking. Know your audience, study others, prepare and rehearse, record yourself, remove as much text as possible from slides, and start and end strong.
Follow these tips to improve your speaking and audience communication. Prepare, practice, and learn from great speakers to reduce your fear of public speaking.
"Speaking to one person or a thousand is public speaking." — Vocal coach Roger Love

Protos
3 years ago
StableGains lost $42M in Anchor Protocol.
StableGains lost millions of dollars in customer funds in Anchor Protocol without telling its users. The Anchor Protocol offered depositors 19-20% APY before its parent ecosystem, Terra LUNA, lost tens of billions of dollars in market capitalization as LUNA fell below $0.01 and its stablecoin (UST) collapsed.
A Terra Research Forum member raised the alarm. StableGains changed its homepage and Terms and Conditions to reflect how it mitigates risk, a tacit admission that it should have done so from the start.
StableGains raised $600,000 in YCombinator's W22 batch. Moonfire, Broom Ventures, and Goodwater Capital invested $3 million more.
StableGains' 15% yield product attracted $42 million in deposits. StableGains kept most of its deposits in Anchor's UST pool earning 19-20% APY, kept one-quarter of the interest as a management fee, and then gave customers their promised 15% APY. It lost almost all customer funds when UST melted down. It changed withdrawal times, hurting customers.
- StableGains said de-pegging was unlikely. According to its website, 1 UST can be bought and sold for $1 of LUNA. LUNA became worthless, and Terra shut down its blockchain.
- It promised to diversify assets across several stablecoins to reduce the risk of one losing its $1 peg, but instead kept almost all of them in one basket.
- StableGains promised withdrawals in three business days, even if a stablecoin needed time to regain its peg. StableGains uses Coinbase for deposits and withdrawals, and customers receive the exact amount of USDC requested.
StableGains scrubs its website squeaky clean
StableGains later edited its website to say it only uses the "most trusted and tested stablecoins" and extended withdrawal times from three days to indefinite time "in extreme cases."
Previously, USDC, TerraUST (UST), and Dai were used (DAI). StableGains changed UST-related website content after the meltdown. It also removed most references to DAI.
Customers noticed a new clause in the Terms and Conditions denying StableGains liability for withdrawal losses. This new clause would have required customers to agree not to sue before withdrawing funds, avoiding a class-action lawsuit.
Customers must sign a waiver to receive a refund.
Erickson Kramer & Osborne law firm has asked StableGains to preserve all internal documents on customer accounts, marketing, and TerraUSD communications. The firm has not yet filed a lawsuit.
Thousands of StableGains customers lost an estimated $42 million.
Celsius Network customers also affected
CEL used Terra LUNA's Anchor Protocol. Celsius users lost money in the crypto market crash and UST meltdown. Many held CEL and LUNA as yielding deposits.
CEO Alex Mashinsky accused "unknown malefactors" of targeting Celsius Network without evidence. Celsius has not publicly investigated this claim as of this article's publication.
CEL fell before UST de-pegged. On June 2, 2021, it reached $8.01. May 19's close: $0.82.
When some Celsius Network users threatened to leave over token losses, Mashinsky replied, "Leave if you don't think I'm sincere and working harder than you, seven days a week."
Celsius Network withdrew $500 million from Anchor Protocol, but smaller holders had trouble.
Read original article here

Joseph Mavericks
3 years ago
The world's 36th richest man uses a 5-step system to get what he wants.
Ray Dalio's super-effective roadmap

Ray Dalio's $22 billion net worth ranks him 36th globally. From 1975 to 2011, he built the world's most successful hedge fund, never losing more than 4% from 1991 to 2020. (and only doing so during 3 calendar years).
Dalio describes a 5-step process in his best-selling book Principles. It's the playbook he's used to build his hedge fund, beat the markets, and face personal challenges.
This 5-step system is so valuable and well-explained that I didn't edit or change anything; I only added my own insights in the parts I found most relevant and/or relatable as a young entrepreneur. The system's overview:
Have clear goals
Identify and don’t tolerate problems
Diagnose problems to get at their root causes
Design plans that will get you around those problems
Do what is necessary to push through the plans to get results
If you follow these 5 steps in a virtuous loop, you'll almost always see results. Repeat the process for each goal you have.
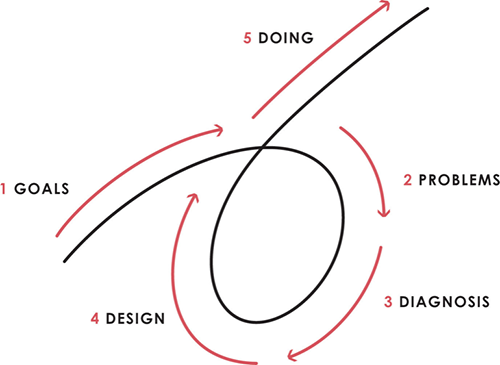
1. Have clear goals
a) Prioritize: You can have almost anything, but not everything.
I started and never launched dozens of projects for 10 years because I was scattered. I opened a t-shirt store, traded algorithms, sold art on Instagram, painted skateboards, and tinkered with electronics. I decided to try blogging for 6 months to see where it took me. Still going after 3 years.
b) Don’t confuse goals with desires.
A goal inspires you to act. Unreasonable desires prevent you from achieving your goals.
c) Reconcile your goals and desires to decide what you want.
d) Don't confuse success with its trappings.
e) Never dismiss a goal as unattainable.
Always one path is best. Your perception of what's possible depends on what you know now. I never thought I'd make money writing online so quickly, and now I see a whole new horizon of business opportunities I didn't know about before.
f) Expectations create abilities.
Don't limit your abilities. More you strive, the more you'll achieve.
g) Flexibility and self-accountability can almost guarantee success.
Flexible people accept what reality or others teach them. Self-accountability is the ability to recognize your mistakes and be more creative, flexible, and determined.
h) Handling setbacks well is as important as moving forward.
Learn when to minimize losses and when to let go and move on.
2. Don't ignore problems
a) See painful problems as improvement opportunities.
Every problem, painful situation, and challenge is an opportunity. Read The Art of Happiness for more.
b) Don't avoid problems because of harsh realities.
Recognizing your weaknesses isn't the same as giving in. It's the first step in overcoming them.
c) Specify your issues.
There is no "one-size-fits-all" solution.
d) Don’t mistake a cause of a problem with the real problem.
"I can't sleep" is a cause, not a problem. "I'm underperforming" could be a problem.
e) Separate big from small problems.
You have limited time and energy, so focus on the biggest problems.
f) Don't ignore a problem.
Identifying a problem and tolerating it is like not identifying it.
3. Identify problems' root causes
a) Decide "what to do" after assessing "what is."
"A good diagnosis takes 15 to 60 minutes, depending on its accuracy and complexity. [...] Like principles, root causes recur in different situations.
b) Separate proximate and root causes.
"You can only solve problems by removing their root causes, and to do that, you must distinguish symptoms from disease."
c) Knowing someone's (or your own) personality can help you predict their behavior.
4. Design plans that will get you around the problems
a) Retrace your steps.
Analyze your past to determine your future.
b) Consider your problem a machine's output.
Consider how to improve your machine. It's a game then.
c) There are many ways to reach your goals.
Find a solution.
d) Visualize who will do what in your plan like a movie script.
Consider your movie's actors and script's turning points, then act accordingly. The game continues.
e) Document your plan so others can judge your progress.
Accountability boosts success.
f) Know that a good plan doesn't take much time.
The execution is usually the hardest part, but most people either don't have a plan or keep changing it. Don't drive while building the car. Build it first, because it'll be bumpy.
5. Do what is necessary to push through the plans to get results
a) Great planners without execution fail.
Life is won with more than just planning. Similarly, practice without talent beats talent without practice.
b) Work ethic is undervalued.
Hyper-productivity is praised in corporate America, even if it leads nowhere. To get things done, use checklists, fewer emails, and more desk time.
c) Set clear metrics to ensure plan adherence.
I've written about the OKR strategy for organizations with multiple people here. If you're on your own, I recommend the Wheel of Life approach. Both systems start with goals and tasks to achieve them. Then start executing on a realistic timeline.
If you find solutions, weaknesses don't matter.
Everyone's weak. You, me, Gates, Dalio, even Musk. Nobody will be great at all 5 steps of the system because no one can think in all the ways required. Some are good at analyzing and diagnosing but bad at executing. Some are good planners but poor communicators. Others lack self-discipline.
Stay humble and ask for help when needed. Nobody has ever succeeded 100% on their own, without anyone else's help. That's the paradox of individual success: teamwork is the only way to get there.
Most people won't have the skills to execute even the best plan. You can get missing skills in two ways:
Self-taught (time-consuming)
Others' (requires humility) light
On knowing what to do with your life
“Some people have good mental maps and know what to do on their own. Maybe they learned them or were blessed with common sense. They have more answers than others. Others are more humble and open-minded. […] Open-mindedness and mental maps are most powerful.” — Ray Dalio
I've always known what I wanted to do, so I'm lucky. I'm almost 30 and have always had trouble executing. Good thing I never stopped experimenting, but I never committed to anything long-term. I jumped between projects. I decided 3 years ago to stick to one project for at least 6 months and haven't looked back.
Maybe you're good at staying focused and executing, but you don't know what to do. Maybe you have none of these because you haven't found your purpose. Always try new projects and talk to as many people as possible. It will give you inspiration and ideas and set you up for success.
There is almost always a way to achieve a crazy goal or idea.
Enjoy the journey, whichever path you take.
