More on Entrepreneurship/Creators

Pat Vieljeux
3 years ago
The three-year business plan is obsolete for startups.
If asked, run.

An entrepreneur asked me about her pitch deck. A Platform as a Service (PaaS).
She told me she hadn't done her 5-year forecasts but would soon.
I said, Don't bother. I added "time-wasting."
“I've been asked”, she said.
“Who asked?”
“a VC”
“5-year forecast?”
“Yes”
“Get another VC. If he asks, it's because he doesn't understand your solution or to waste your time.”
Some VCs are lagging. They're still using steam engines.
10-years ago, 5-year forecasts were requested.
Since then, we've adopted a 3-year plan.
But It's outdated.
Max one year.
What has happened?
Revolutionary technology. NO-CODE.
Revolution's consequences?
Product viability tests are shorter. Hugely. SaaS and PaaS.
Let me explain:
Building a minimum viable product (MVP) that works only takes a few months.
1 to 2 months for practical testing.
Your company plan can be validated or rejected in 4 months as a consequence.
After validation, you can ask for VC money. Even while a prototype can generate revenue, you may not require any.
Good VCs won't ask for a 3-year business plan in that instance.
One-year, though.
If you want, establish a three-year plan, but realize that the second year will be different.
You may have changed your business model by then.
A VC isn't interested in a three-year business plan because your solution may change.
Your ability to create revenue will be key.
But also, to pivot.
They will be interested in your value proposition.
They will want to know what differentiates you from other competitors and why people will buy your product over another.
What will interest them is your resilience, your ability to bounce back.
Not to mention your mindset. The fact that you won’t get discouraged at the slightest setback.
The grit you have when facing adversity, as challenges will surely mark your journey.
The authenticity of your approach. They’ll want to know that you’re not just in it for the money, let alone to show off.
The fact that you put your guts into it and that you are passionate about it. Because entrepreneurship is a leap of faith, a leap into the void.
They’ll want to make sure you are prepared for it because it’s not going to be a walk in the park.
They’ll want to know your background and why you got into it.
They’ll also want to know your family history.
And what you’re like in real life.
So a 5-year plan…. You can bet they won’t give a damn. Like their first pair of shoes.
Evgenii Nelepko
3 years ago
My 3 biggest errors as a co-founder and CEO
Reflections on the closed company Hola! Dating app

I'll discuss my fuckups as an entrepreneur and CEO. All of them refer to the dating app Hola!, which I co-founded and starred in.
Spring 2021 was when we started. Two techies and two non-techies created a dating app. Pokemon Go and Tinder were combined.
Online dating is a business, and it takes two weeks from a like to a date. We questioned online dating app users if they met anyone offline last year.
75% replied yes, 50% sometimes, 25% usually.
Offline dating is popular, yet people have concerns.
Men are reluctant to make mistakes in front of others.
Women are curious about the background of everyone who approaches them.
We designed unique mechanics that let people date after a match. No endless chitchat. Women would be safe while men felt like cowboys.
I wish to emphasize three faults that lead to founders' estrangement.
This detachment ultimately led to us shutting down the company.
The wrong technology stack
Situation
Instead of generating a faster MVP and designing an app in a universal stack for iOS and Android, I argued we should pilot the app separately for iOS and Android. Technical founders' expertise made this possible.
Self-reflection
Mistaken strategy. We lost time and resources developing two apps at once. We chose iOS since it's more profitable. Apple took us out after the release, citing Guideline 4.3 Spam. After 4 months, we had nothing. We had a long way to go to get the app on Android and the Store.
I suggested creating a uniform platform for the company's growth. This makes parallel product development easier. The strategist's lack of experience and knowledge made it a piece of crap.
What would I have changed if I could?
We should have designed an Android universal stack. I expected Apple to have issues with a dating app.
Our approach should have been to launch something and subsequently improve it, but prejudice won.
The lesson
Discuss the IT stack with your CTO. It saves time and money. Choose the easiest MVP method.

2. A tardy search for investments
Situation
Though the universe and other founders encouraged me to locate investors first, I started pitching when we almost had an app.
When angels arrived, it was time to close. The app was banned, war broke out, I left the country, and the other co-founders stayed. We had no savings.
Self-reflection
I loved interviewing users. I'm proud of having done 1,000 interviews. I wanted to understand people's pain points and improve the product.
Interview results no longer affected the product. I was terrified to start pitching. I filled out accelerator applications and redid my presentation. You must go through that so you won't be terrified later.
What would I have changed if I could?
Get an external or internal mentor to help me with my first pitch as soon as possible. I'd be supported if criticized. He'd cheer with me if there was enthusiasm.
In 99% of cases, I'm comfortable jumping into the unknown, but there are exceptions. The mentor's encouragement would have prompted me to act sooner.
The lesson
Begin fundraising immediately. Months may pass. Show investors your pre-MVP project. Draw inferences from feedback.
3. Role ambiguity
Situation
My technical co-founders were also part-time lead developers, which produced communication issues. As co-founders, we communicated well and recognized the problems. Stakes, vesting, target markets, and approach were agreed upon.
We were behind schedule. Technical debt and strategic gap grew.
Bi-daily and weekly reviews didn't help. Each time, there were explanations. Inside, I was freaking out.

Self-reflection
I am a fairly easy person to talk to. I always try to stick to agreements; otherwise, my head gets stuffed with unnecessary information, interpretations, and emotions.
Sit down -> talk -> decide -> do -> evaluate the results. Repeat it.
If I don't get detailed comments, I start ruining everyone's mood. If there's a systematic violation of agreements without a good justification, I won't join the project or I'll end the collaboration.
What would I have done otherwise?
This is where it’s scariest to draw conclusions. Probably the most logical thing would have been not to start the project as we started it. But that was already a completely different project. So I would not have done anything differently and would have failed again.
But I drew conclusions for the future.
The lesson
First-time founders should find an adviser or team coach for a strategic session. It helps split the roles and responsibilities.

cdixon
3 years ago
2000s Toys, Secrets, and Cycles
During the dot-com bust, I started my internet career. People used the internet intermittently to check email, plan travel, and do research. The average internet user spent 30 minutes online a day, compared to 7 today. To use the internet, you had to "log on" (most people still used dial-up), unlike today's always-on, high-speed mobile internet. In 2001, Amazon's market cap was $2.2B, 1/500th of what it is today. A study asked Americans if they'd adopt broadband, and most said no. They didn't see a need to speed up email, the most popular internet use. The National Academy of Sciences ranked the internet 13th among the 100 greatest inventions, below radio and phones. The internet was a cool invention, but it had limited uses and wasn't a good place to build a business.
A small but growing movement of developers and founders believed the internet could be more than a read-only medium, allowing anyone to create and publish. This is web 2. The runner up name was read-write web. (These terms were used in prominent publications and conferences.)
Web 2 concepts included letting users publish whatever they want ("user generated content" was a buzzword), social graphs, APIs and mashups (what we call composability today), and tagging over hierarchical navigation. Technical innovations occurred. A seemingly simple but important one was dynamically updating web pages without reloading. This is now how people expect web apps to work. Mobile devices that could access the web were niche (I was an avid Sidekick user).
The contrast between what smart founders and engineers discussed over dinner and on weekends and what the mainstream tech world took seriously during the week was striking. Enterprise security appliances, essentially preloaded servers with security software, were a popular trend. Many of the same people would talk about "serious" products at work, then talk about consumer internet products and web 2. It was tech's biggest news. Web 2 products were seen as toys, not real businesses. They were hobbies, not work-related.
There's a strong correlation between rich product design spaces and what smart people find interesting, which took me some time to learn and led to blog posts like "The next big thing will start out looking like a toy" Web 2's novel product design possibilities sparked dinner and weekend conversations. Imagine combining these features. What if you used this pattern elsewhere? What new product ideas are next? This excited people. "Serious stuff" like security appliances seemed more limited.
The small and passionate web 2 community also stood out. I attended the first New York Tech meetup in 2004. Everyone fit in Meetup's small conference room. Late at night, people demoed their software and chatted. I have old friends. Sometimes I get asked how I first met old friends like Fred Wilson and Alexis Ohanian. These topics didn't interest many people, especially on the east coast. We were friends. Real community. Alex Rampell, who now works with me at a16z, is someone I met in 2003 when a friend said, "Hey, I met someone else interested in consumer internet." Rare. People were focused and enthusiastic. Revolution seemed imminent. We knew a secret nobody else did.
My web 2 startup was called SiteAdvisor. When my co-founders and I started developing the idea in 2003, web security was out of control. Phishing and spyware were common on Internet Explorer PCs. SiteAdvisor was designed to warn users about security threats like phishing and spyware, and then, using web 2 concepts like user-generated reviews, add more subjective judgments (similar to what TrustPilot seems to do today). This staged approach was common at the time; I called it "Come for the tool, stay for the network." We built APIs, encouraged mashups, and did SEO marketing.
Yahoo's 2005 acquisitions of Flickr and Delicious boosted web 2 in 2005. By today's standards, the amounts were small, around $30M each, but it was a signal. Web 2 was assumed to be a fun hobby, a way to build cool stuff, but not a business. Yahoo was a savvy company that said it would make web 2 a priority.
As I recall, that's when web 2 started becoming mainstream tech. Early web 2 founders transitioned successfully. Other entrepreneurs built on the early enthusiasts' work. Competition shifted from ideation to execution. You had to decide if you wanted to be an idealistic indie bar band or a pragmatic stadium band.
Web 2 was booming in 2007 Facebook passed 10M users, Twitter grew and got VC funding, and Google bought YouTube. The 2008 financial crisis tested entrepreneurs' resolve. Smart people predicted another great depression as tech funding dried up.
Many people struggled during the recession. 2008-2011 was a golden age for startups. By 2009, talented founders were flooding Apple's iPhone app store. Mobile apps were booming. Uber, Venmo, Snap, and Instagram were all founded between 2009 and 2011. Social media (which had replaced web 2), cloud computing (which enabled apps to scale server side), and smartphones converged. Even if social, cloud, and mobile improve linearly, the combination could improve exponentially.
This chart shows how I view product and financial cycles. Product and financial cycles evolve separately. The Nasdaq index is a proxy for the financial sentiment. Financial sentiment wildly fluctuates.
Next row shows iconic startup or product years. Bottom-row product cycles dictate timing. Product cycles are more predictable than financial cycles because they follow internal logic. In the incubation phase, enthusiasts build products for other enthusiasts on nights and weekends. When the right mix of technology, talent, and community knowledge arrives, products go mainstream. (I show the biggest tech cycles in the chart, but smaller ones happen, like web 2 in the 2000s and fintech and SaaS in the 2010s.)
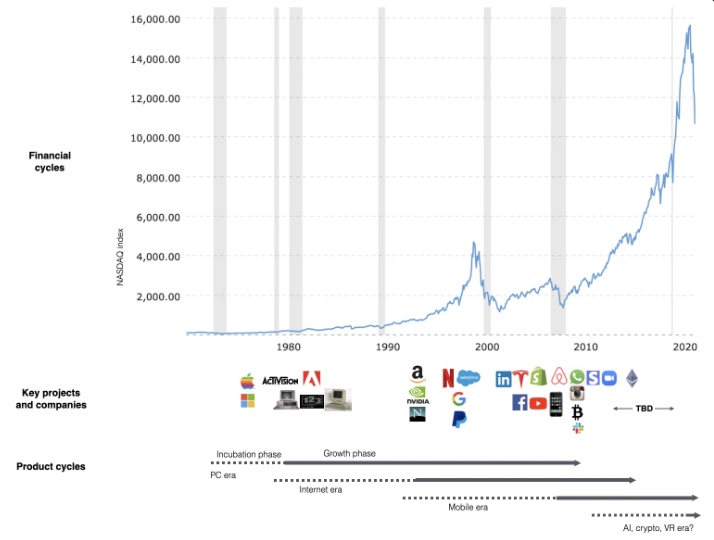
Tech has changed since the 2000s. Few tech giants dominate the internet, exerting economic and cultural influence. In the 2000s, web 2 was ignored or dismissed as trivial. Entrenched interests respond aggressively to new movements that could threaten them. Creative patterns from the 2000s continue today, driven by enthusiasts who see possibilities where others don't. Know where to look. Crypto and web 3 are where I'd start.
Today's negative financial sentiment reminds me of 2008. If we face a prolonged downturn, we can learn from 2008 by preserving capital and focusing on the long term. Keep an eye on the product cycle. Smart people are interested in things with product potential. This becomes true. Toys become necessities. Hobbies become mainstream. Optimists build the future, not cynics.
Full article is available here
You might also like

Darius Foroux
2 years ago
My financial life was changed by a single, straightforward mental model.
Prioritize big-ticket purchases

I've made several spending blunders. I get sick thinking about how much money I spent.
My financial mental model was poor back then.
Stoicism and mindfulness keep me from attaching to those feelings. It still hurts.
Until four or five years ago, I bought a new winter jacket every year.
Ten years ago, I spent twice as much. Now that I have a fantastic, warm winter parka, I don't even consider acquiring another one. No more spending. I'm not looking for jackets either.
Saving time and money by spending well is my thinking paradigm.
The philosophy is expressed in most languages. Cheap is expensive in the Netherlands. This applies beyond shopping.
In this essay, I will offer three examples of how this mental paradigm transformed my financial life.
Publishing books
In 2015, I presented and positioned my first book poorly.
I called the book Huge Life Success and made a funny Canva cover in 30 minutes. This:

That looks nothing like my present books. No logo or style. The book felt amateurish.
The book started bothering me a few weeks after publication. The advice was good, but it didn't appear professional. I studied the book business extensively.
I created a style for all my designs. Branding. Win Your Inner Wars was reissued a year later.
Title, cover, and description changed. Rearranging the chapters improved readability.
Seven years later, the book sells hundreds of copies a month. That taught me a lot.
Rushing to finish a project is enticing. Send it and move forward.
Avoid rushing everything. Relax. Develop your projects. Perform well. Perform the job well.
My first novel was underfunded and underworked. A bad book arrived. I then invested time and money in writing the greatest book I could.
That book still sells.
Traveling
I hate travel. Airports, flights, trains, and lines irritate me.
But, I enjoy traveling to beautiful areas.
I do it strangely. I make up travel rules. I never go to airports in summer. I hate being near airports on holidays. Unworthy.
No vacation packages for me. Those airline packages with a flight, shuttle, and hotel. I've had enough.
I try to avoid crowds and popular spots. July Paris? Nuts and bolts, please. Christmas in NYC? No, please keep me sane.
I fly business class behind. I accept upgrades upon check-in. I prefer driving. I drove from the Netherlands to southern Spain.
Thankfully, no lines. What if travel costs more? Thus? I enjoy it from the start. I start traveling then.
I rarely travel since I'm so difficult. One great excursion beats several average ones.
Personal effectiveness
New apps, tools, and strategies intrigue most productivity professionals.
No.
I researched years ago. I spent years investigating productivity in university.
I bought books, courses, applications, and tools. It was expensive and time-consuming.
Im finished. Productivity no longer costs me time or money. OK. I worked on it once and now follow my strategy.
I avoid new programs and systems. My stuff works. Why change winners?
Spending wisely saves time and money.
Spending wisely means spending once. Many people ignore productivity. It's understudied. No classes.
Some assume reading a few articles or a book is enough. Productivity is personal. You need a personal system.
Time invested is one-time. You can trust your system for life once you find it.
Concentrate on the expensive choices.
Life's short. Saving money quickly is enticing.
Spend less on groceries today. True. That won't fix your finances.
Adopt a lifestyle that makes you affluent over time. Consider major choices.
Are they causing long-term poverty? Are you richer?
Leasing cars comes to mind. The automobile costs a fortune today. The premium could accomplish a million nice things.
Focusing on important decisions makes life easier. Consider your future. You want to improve next year.

mbvissers.eth
3 years ago
Why does every smart contract seem to implement ERC165?

ERC165 (or EIP-165) is a standard utilized by various open-source smart contracts like Open Zeppelin or Aavegotchi.
What's it? You must implement? Why do we need it? I'll describe the standard and answer any queries.
What is ERC165
ERC165 detects and publishes smart contract interfaces. Meaning? It standardizes how interfaces are recognized, how to detect if they implement ERC165, and how a contract publishes the interfaces it implements. How does it work?
Why use ERC165? Sometimes it's useful to know which interfaces a contract implements, and which version.
Identifying interfaces
An interface function's selector. This verifies an ABI function. XORing all function selectors defines an interface in this standard. The following code demonstrates.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENCED
pragma solidity >=0.8.0 <0.9.0;
interface Solidity101 {
function hello() external pure;
function world(int) external pure;
}
contract Selector {
function calculateSelector() public pure returns (bytes4) {
Solidity101 i;
return i.hello.selector ^ i.world.selector;
// Returns 0xc6be8b58
}
function getHelloSelector() public pure returns (bytes4) {
Solidity101 i;
return i.hello.selector;
// Returns 0x19ff1d21
}
function getWorldSelector() public pure returns (bytes4) {
Solidity101 i;
return i.world.selector;
// Returns 0xdf419679
}
}This code isn't necessary to understand function selectors and how an interface's selector can be determined from the functions it implements.
Run that sample in Remix to see how interface function modifications affect contract function output.
Contracts publish their implemented interfaces.
We can identify interfaces. Now we must disclose the interfaces we're implementing. First, import IERC165 like so.
pragma solidity ^0.4.20;
interface ERC165 {
/// @notice Query if a contract implements an interface
/// @param interfaceID The interface identifier, as specified in ERC-165
/// @dev Interface identification is specified in ERC-165.
/// @return `true` if the contract implements `interfaceID` and
/// `interfaceID` is not 0xffffffff, `false` otherwise
function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceID) external view returns (bool);
}We still need to build this interface in our smart contract. ERC721 from OpenZeppelin is a good example.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
// OpenZeppelin Contracts (last updated v4.5.0) (token/ERC721/ERC721.sol)
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "./IERC721.sol";
import "./extensions/IERC721Metadata.sol";
import "../../utils/introspection/ERC165.sol";
// ...
contract ERC721 is Context, ERC165, IERC721, IERC721Metadata {
// ...
function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId) public view virtual override(ERC165, IERC165) returns (bool) {
return
interfaceId == type(IERC721).interfaceId ||
interfaceId == type(IERC721Metadata).interfaceId ||
super.supportsInterface(interfaceId);
}
// ...
}I deleted unnecessary code. The smart contract imports ERC165, IERC721 and IERC721Metadata. The is keyword at smart contract declaration implements all three.
Kind (interface).
Note that type(interface).interfaceId returns the same as the interface selector.
We override supportsInterface in the smart contract to return a boolean that checks if interfaceId is the same as one of the implemented contracts.
Super.supportsInterface() calls ERC165 code. Checks if interfaceId is IERC165.
function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId) public view virtual override returns (bool) {
return interfaceId == type(IERC165).interfaceId;
}So, if we run supportsInterface with an interfaceId, our contract function returns true if it's implemented and false otherwise. True for IERC721, IERC721Metadata, andIERC165.
Conclusion
I hope this post has helped you understand and use ERC165 and why it's employed.
Have a great day, thanks for reading!
Dmytro Spilka
3 years ago
Why NFTs Have a Bright Future Away from Collectible Art After Punks and Apes

After a crazy second half of 2021 and significant trade volumes into 2022, the market for NFT artworks like Bored Ape Yacht Club, CryptoPunks, and Pudgy Penguins has begun a sharp collapse as market downturns hit token values.
DappRadar data shows NFT monthly sales have fallen below $1 billion since June 2021. OpenSea, the world's largest NFT exchange, has seen sales volume decline 75% since May and is trading like July 2021.
Prices of popular non-fungible tokens have also decreased. Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) has witnessed volume and sales drop 63% and 15%, respectively, in the past month.

BeInCrypto analysis shows market decline. May 2022 cryptocurrency marketplace volume was $4 billion, according to a news platform. This is a sharp drop from April's $7.18 billion.
OpenSea, a big marketplace, contributed $2.6 billion, while LooksRare, Magic Eden, and Solanart also contributed.
NFT markets are digital platforms for buying and selling tokens, similar stock trading platforms. Although some of the world's largest exchanges offer NFT wallets, most users store their NFTs on their favorite marketplaces.
In January 2022, overall NFT sales volume was $16.57 billion, with LooksRare contributing $11.1 billion. May 2022's volume was $12.57 less than January, a 75% drop, and June's is expected to be considerably smaller.
A World Based on Utility
Despite declines in NFT trading volumes, not all investors are negative on NFTs. Although there are uncertainties about the sustainability of NFT-based art collections, there are fewer reservations about utility-based tokens and their significance in technology's future.
In June, business CEO Christof Straub said NFTs may help artists monetize unreleased content, resuscitate catalogs, establish deeper fan connections, and make processes more efficient through technology.
We all know NFTs can't be JPEGs. Straub noted that NFT music rights can offer more equitable rewards to musicians.
Music NFTs are here to stay if they have real value, solve real problems, are trusted and lawful, and have fair and sustainable business models.
NFTs can transform numerous industries, including music. Market opinion is shifting towards tokens with more utility than the social media artworks we're used to seeing.

While the major NFT names remain dominant in terms of volume, new utility-based initiatives are emerging as top 20 collections.
Otherdeed, Sorare, and NBA Top Shot are NFT-based games that rank above Bored Ape Yacht Club and Cryptopunks.
Users can switch video NFTs of basketball players in NBA Top Shot. Similar efforts are emerging in the non-fungible landscape.
Sorare shows how NFTs can support a new way of playing fantasy football, where participants buy and swap trading cards to create a 5-player team that wins rewards based on real-life performances.
Sorare raised 579.7 million in one of Europe's largest Series B financing deals in September 2021. Recently, the platform revealed plans to expand into Major League Baseball.
Strong growth indications suggest a promising future for NFTs. The value of art-based collections like BAYC and CryptoPunks may be questioned as markets become diluted by new limited collections, but the potential for NFTs to become intrinsically linked to tangible utility like online gaming, music and art, and even corporate reward schemes shows the industry has a bright future.
