More on Marketing

Jon Brosio
3 years ago
This Landing Page is a (Legal) Money-Printing Machine
and it’s easy to build.

A landing page with good copy is a money-maker.
Let's be honest, page-builder templates are garbage.
They can help you create a nice-looking landing page, but not persuasive writing.
Over the previous 90 days, I've examined 200+ landing pages.
What's crazy?
Top digital entrepreneurs use a 7-part strategy to bring in email subscribers, generate prospects, and (passively) sell their digital courses.
Steal this 7-part landing page architecture to maximize digital product sales.
The offer
Landing pages require offers.
Newsletter, cohort, or course offer.
Your reader should see this offer first. Includind:
Headline
Imagery
Call-to-action
Clear, persuasive, and simplicity are key. Example: the Linkedin OS course home page of digital entrepreneur Justin Welsh offers:

A distinctly defined problem
Everyone needs an enemy.
You need an opponent on your landing page. Problematic.
Next, employ psychology to create a struggle in your visitor's thoughts.
Don't be clever here; label your customer's problem. The more particular you are, the bigger the situation will seem.
When you build a clear monster, you invite defeat. I appreciate Theo Ohene's Growth Roadmaps landing page.

Exacerbation of the effects
Problem identification doesn't motivate action.
What would an unresolved problem mean?
This is landing page copy. When you describe the unsolved problem's repercussions, you accomplish several things:
You write a narrative (and stories are remembered better than stats)
You cause the reader to feel something.
You help the reader relate to the issue
Important!
My favorite script is:
"Sure, you can let [problem] go untreated. But what will happen if you do? Soon, you'll begin to notice [new problem 1] will start to arise. That might bring up [problem 2], etc."
Take the copywriting course, digital writer and entrepreneur Dickie Bush illustrates below when he labels the problem (see: "poor habit") and then illustrates the repercussions.

The tale of transformation
Every landing page needs that "ah-ha!" moment.
Transformation stories do this.
Did you find a solution? Someone else made the discovery? Have you tested your theory?
Next, describe your (or your subject's) metamorphosis.
Kieran Drew nails his narrative (and revelation) here. Right before the disclosure, he introduces his "ah-ha!" moment:

Testimonials
Social proof completes any landing page.
Social proof tells the reader, "If others do it, it must be worthwhile."
This is your argument.
Positive social proof helps (obviously).
Offer "free" training in exchange for a testimonial if you need social evidence. This builds social proof.
Most social proof is testimonies (recommended). Kurtis Hanni's creative take on social proof (using a screenshot of his colleague) is entertaining.
Bravo.

Reveal your offer
Now's the moment to act.
Describe the "bundle" that provides the transformation.
Here's:
Course
Cohort
Ebook
Whatever you're selling.
Include a product or service image, what the consumer is getting ("how it works"), the price, any "free" bonuses (preferred), and a CTA ("buy now").
Clarity is key. Don't make a cunning offer. Make sure your presentation emphasizes customer change (benefits). Dan Koe's Modern Mastery landing page makes an offer. Consider:

An ultimatum
Offering isn't enough.
You must give your prospect an ultimatum.
They can buy your merchandise from you.
They may exit the webpage.
That’s it.
It's crucial to show what happens if the reader does either. Stress the consequences of not buying (again, a little consequence amplification). Remind them of the benefits of buying.
I appreciate Charles Miller's product offer ending:

The top online creators use a 7-part landing page structure:
Offer the service
Describe the problem
Amplify the consequences
Tell the transformational story
Include testimonials and social proof.
Reveal the offer (with any bonuses if applicable)
Finally, give the reader a deadline to encourage them to take action.
Sequence these sections to develop a landing page that (essentially) prints money.

Jano le Roux
3 years ago
Here's What I Learned After 30 Days Analyzing Apple's Microcopy
Move people with tiny words.

Apple fanboy here.
Macs are awesome.
Their iPhones rock.
$19 cloths are great.
$999 stands are amazing.
I love Apple's microcopy even more.
It's like the marketing goddess bit into the Apple logo and blessed the world with microcopy.
I took on a 30-day micro-stalking mission.
Every time I caught myself wasting time on YouTube, I had to visit Apple’s website to learn the secrets of the marketing goddess herself.
We've learned. Golden apples are calling.
Cut the friction
Benefit-first, not commitment-first.
Brands lose customers through friction.
Most brands don't think like customers.
Brands want sales.
Brands want newsletter signups.
Here's their microcopy:
“Buy it now.”
“Sign up for our newsletter.”
Both are difficult. They ask for big commitments.
People are simple creatures. Want pleasure without commitment.
Apple nails this.
So, instead of highlighting the commitment, they highlight the benefit of the commitment.
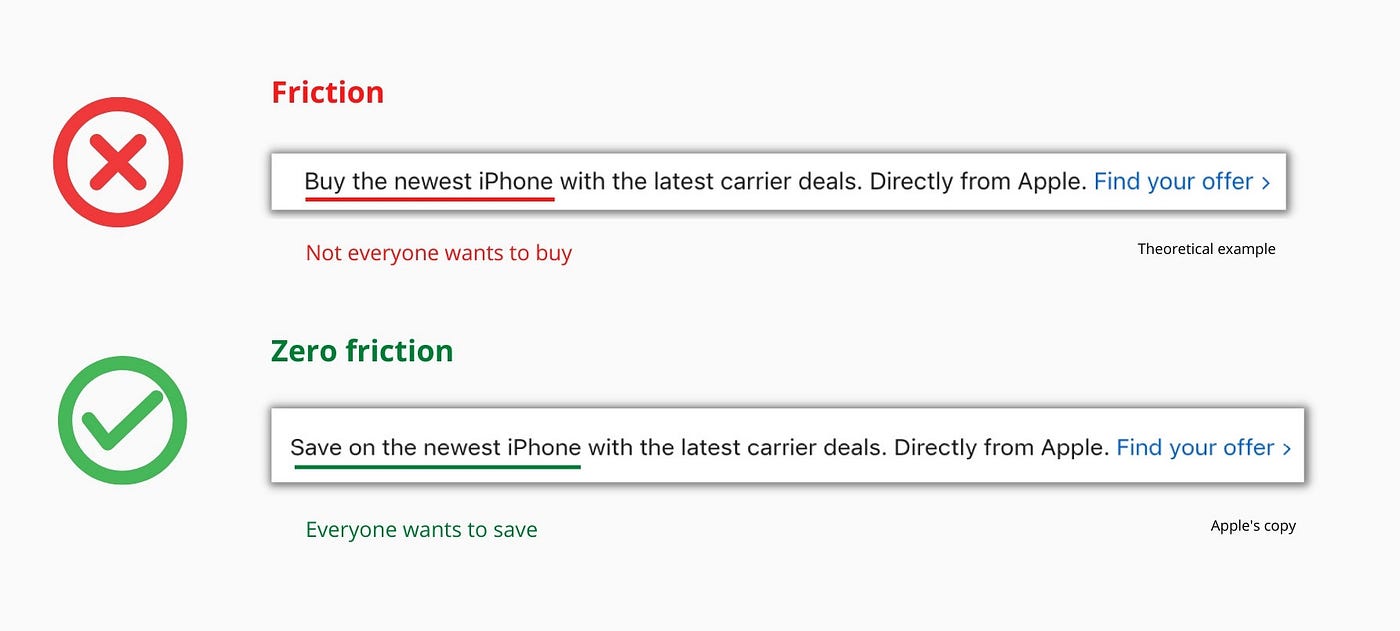
Saving on the latest iPhone sounds easier than buying it. Everyone saves, but not everyone buys.
A subtle change in framing reduces friction.
Apple eliminates customer objections to reduce friction.
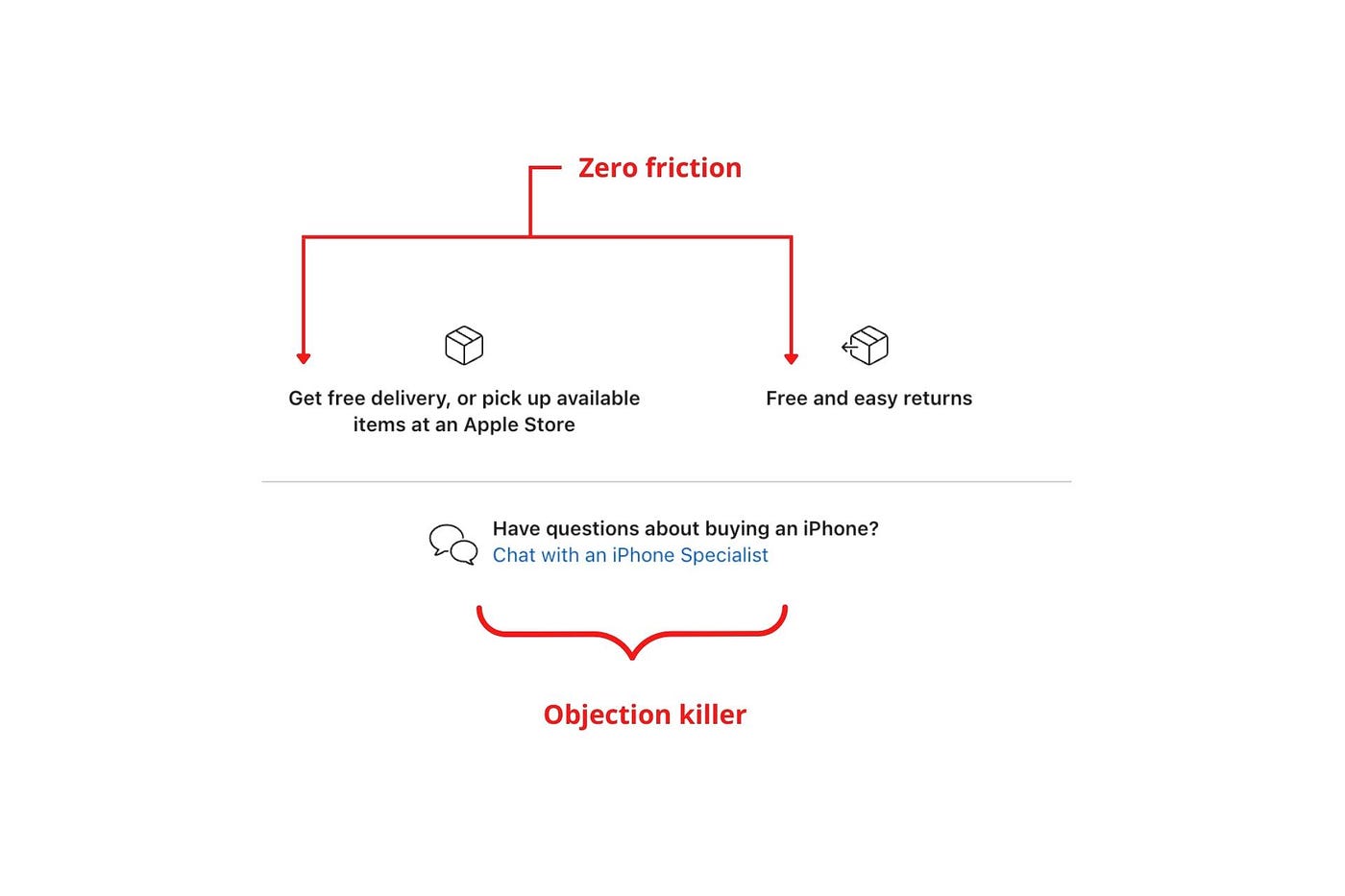
Less customer friction means simpler processes.
Apple's copy expertly reassures customers about shipping fees and not being home. Apple assures customers that returning faulty products is easy.
Apple knows that talking to a real person is the best way to reduce friction and improve their copy.
Always rhyme
Learn about fine rhyme.
Poets make things beautiful with rhyme.
Copywriters use rhyme to stand out.
Apple’s copywriters have mastered the art of corporate rhyme.
Two techniques are used.
1. Perfect rhyme
Here, rhymes are identical.

2. Imperfect rhyme
Here, rhyming sounds vary.

Apple prioritizes meaning over rhyme.
Apple never forces rhymes that don't fit.
It fits so well that the copy seems accidental.
Add alliteration
Alliteration always entertains.
Alliteration repeats initial sounds in nearby words.
Apple's copy uses alliteration like no other brand I've seen to create a rhyming effect or make the text more fun to read.
For example, in the sentence "Sam saw seven swans swimming," the initial "s" sound is repeated five times. This creates a pleasing rhythm.
Microcopy overuse is like pouring ketchup on a Michelin-star meal.
Alliteration creates a memorable phrase in copywriting. It's subtler than rhyme, and most people wouldn't notice; it simply resonates.

I love how Apple uses alliteration and contrast between "wonders" and "ease".
Assonance, or repeating vowels, isn't Apple's thing.
You ≠ Hero, Customer = Hero
Your brand shouldn't be the hero.
Because they'll be using your product or service, your customer should be the hero of your copywriting. With your help, they should feel like they can achieve their goals.
I love how Apple emphasizes what you can do with the machine in this microcopy.

It's divine how they position their tools as sidekicks to help below.

This one takes the cake:

Dialogue-style writing
Conversational copy engages.
Excellent copy Like sharing gum with a friend.
This helps build audience trust.

Apple does this by using natural connecting words like "so" and phrases like "But that's not all."
Snowclone-proof
The mother of all microcopy techniques.
A snowclone uses an existing phrase or sentence to create a new one. The new phrase or sentence uses the same structure but different words.
It’s usually a well know saying like:
To be or not to be.
This becomes a formula:
To _ or not to _.
Copywriters fill in the blanks with cause-related words. Example:
To click or not to click.

Apple turns "survival of the fittest" into "arrival of the fittest."
It's unexpected and surprises the reader.
So this was fun.
But my fun has just begun.
Microcopy is 21st-century poetry.
I came as an Apple fanboy.
I leave as an Apple fanatic.
Now I’m off to find an apple tree.
Cause you know how it goes.
(Apples, trees, etc.)
This post is a summary. Original post available here.

Jon Brosio
3 years ago
You can learn more about marketing from these 8 copywriting frameworks than from a college education.
Email, landing pages, and digital content

Today's most significant skill:
Copywriting.
Unfortunately, most people don't know how to write successful copy because they weren't taught in school.
I've been obsessed with copywriting for two years. I've read 15 books, completed 3 courses, and studied internet's best digital entrepreneurs.
Here are 8 copywriting frameworks that educate more than a four-year degree.
1. Feature — Advantage — Benefit (F.A.B)
This is the most basic copywriting foundation. Email marketing, landing page copy, and digital video ads can use it.
F.A.B says:
How it works (feature)
which is helpful (advantage)
What's at stake (benefit)
The Hustle uses this framework on their landing page to convince people to sign up:

2. P. A. S. T. O. R.
This framework is for longer-form copywriting. PASTOR uses stories to engage with prospects. It explains why people should buy this offer.
PASTOR means:
Problem
Amplify
Story
Testimonial
Offer
Response
Dan Koe's landing page is a great example. It shows PASTOR frame-by-frame.

3. Before — After — Bridge
Before-after-bridge is a copywriting framework that draws attention and shows value quickly.
This framework highlights:
where you are
where you want to be
how to get there
Works great for: Email threads/landing pages
Zain Kahn utilizes this framework to write viral threads.

4. Q.U.E.S.T
QUEST is about empathetic writing. You know their issues, obstacles, and headaches. This allows coverups.
QUEST:
Qualifies
Understands
Educates
Stimulates
Transitions
Tom Hirst's landing page uses the QUEST framework.

5. The 4P’s model
The 4P’s approach pushes your prospect to action. It educates and persuades quickly.
4Ps:
The problem the visitor is dealing with
The promise that will help them
The proof the promise works
A push towards action
Mark Manson is a bestselling author, digital creator, and pop-philosopher. He's also a great copywriter, and his membership offer uses the 4P’s framework.

6. Problem — Agitate — Solution (P.A.S)
Up-and-coming marketers should understand problem-agitate-solution copywriting. Once you understand one structure, others are easier. It drives passion and presents a clear solution.
PAS outlines:
The issue the visitor is having
It then intensifies this issue through emotion.
finally offers an answer to that issue (the offer)
The customer's story loops. Nicolas Cole and Dickie Bush use PAS to promote Ship 30 for 30.

7. Star — Story — Solution (S.S.S)
PASTOR + PAS = star-solution-story. Like PAS, it employs stories to persuade.
S.S.S. is effective storytelling:
Star: (Person had a problem)
Story: (until they had a breakthrough)
Solution: (That created a transformation)
Ali Abdaal is a YouTuber with a great S.S.S copy.

8. Attention — Interest — Desire — Action
AIDA is another classic. This copywriting framework is great for fast-paced environments (think all digital content on Linkedin, Twitter, Medium, etc.).
It works with:
Page landings
writing on thread
Email
It's a good structure since it's concise, attention-grabbing, and action-oriented.
Shane Martin, Twitter's creator, uses this approach to create viral content.

TL;DR
8 copywriting frameworks that teach marketing better than a four-year degree
Feature-advantage-benefit
Before-after-bridge
Star-story-solution
P.A.S.T.O.R
Q.U.E.S.T
A.I.D.A
P.A.S
4P’s
You might also like

The Mystique
3 years ago
Four Shocking Dark Web Incidents that Should Make You Avoid It
Dark Web activity? Is it as horrible as they say?

We peruse our phones for hours. Internet has improved our worldview.
However, the world's harshest realities remain buried on the internet and unattainable by everyone.
Browsers cannot access the Dark Web. Browse it with high-security authentication and exclusive access. There are compelling reasons to avoid the dark web at all costs.
1. The Dark Web and I

Darius wrote My Dark Web Story on reddit two years ago. The user claimed to have shared his dark web experience. DaRealEddyYT wanted to surf the dark web after hearing several stories.
He curiously downloaded Tor Browser, which provides anonymity and security.
In the Dark Room, bound
As Darius logged in, a text popped up: “Want a surprise? Click on this link.”
The link opened to a room with a chair. Only one light source illuminated the room. The chair held a female tied.
As the screen read "Let the game begin," a man entered the room and was paid in bitcoins to torment the girl.
The man dragged and tortured the woman.
A danger to safety
Leaving so soon, Darius, disgusted Darius tried to leave the stream. The anonymous user then sent Darius his personal information, including his address, which frightened him because he didn't know Tor was insecure.
After deleting the app, his phone camera was compromised.
He also stated that he left his residence and returned to find it unlocked and a letter saying, Thought we wouldn't find you? Reddit never updated the story.
The story may have been a fake, but a much scarier true story about the dark side of the internet exists.
2. The Silk Road Market

The dark web is restricted for a reason. The dark web has everything illicit imaginable. It's awful central.
The dark web has everything, from organ sales to drug trafficking to money laundering to human trafficking. Illegal drugs, pirated software, credit card, bank, and personal information can be found in seconds.
The dark web has reserved websites like Google. The Silk Road Website, which operated from 2011 to 2013, was a leading digital black market.
The FBI grew obsessed with site founder and processor Ross William Ulbricht.
The site became a criminal organization as money laundering and black enterprises increased. Bitcoin was utilized for credit card payment.
The FBI was close to arresting the site's administrator. Ross was detained after the agency closed Silk Road in 2013.
Two years later, in 2015, he was convicted and sentenced to two consecutive life terms and forty years. He appealed in 2016 but was denied, thus he is currently serving time.
The hefty sentence was for more than running a black marketing site. He was also convicted of murder-for-hire, earning about $730,000 in a short time.
3. Person-buying auctions

Bidding on individuals is another weird internet activity. After a Milan photo shoot, 20-year-old British model Chloe Ayling was kidnapped.
An ad agency in Milan made a bogus offer to shoot with the mother of a two-year-old boy. Four men gave her anesthetic and put her in a duffel bag when she arrived.
She was held captive for several days, and her images and $300,000 price were posted on the dark web. Black Death Trafficking Group kidnapped her to sell her for sex.
She was told two black death foot warriors abducted her. The captors released her when they found she was a mother because mothers were less desirable to sex slave buyers.
In July 2018, Lukasz Pawel Herba was arrested and sentenced to 16 years and nine months in prison. Being a young mother saved Chloe from creepy bidding.
However, it exceeds expectations of how many more would be in such danger daily without their knowledge.
4. Organ sales

Many are unaware of dark web organ sales. Patients who cannot acquire organs often turn to dark web brokers.
Brokers handle all transactions between donors and customers.
Bitcoins are used for dark web transactions, and the Tor server permits personal data on the web.
The WHO reports approximately 10,000 unlawful organ transplants annually. The black web sells kidneys, hearts, even eyes.
To protect our lives and privacy, we should manage our curiosity and never look up dangerous stuff.
While it's fascinating and appealing to know what's going on in the world we don't know about, it's best to prioritize our well-being because one never knows how bad it might get.
Sources

mbvissers.eth
3 years ago
Why does every smart contract seem to implement ERC165?

ERC165 (or EIP-165) is a standard utilized by various open-source smart contracts like Open Zeppelin or Aavegotchi.
What's it? You must implement? Why do we need it? I'll describe the standard and answer any queries.
What is ERC165
ERC165 detects and publishes smart contract interfaces. Meaning? It standardizes how interfaces are recognized, how to detect if they implement ERC165, and how a contract publishes the interfaces it implements. How does it work?
Why use ERC165? Sometimes it's useful to know which interfaces a contract implements, and which version.
Identifying interfaces
An interface function's selector. This verifies an ABI function. XORing all function selectors defines an interface in this standard. The following code demonstrates.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENCED
pragma solidity >=0.8.0 <0.9.0;
interface Solidity101 {
function hello() external pure;
function world(int) external pure;
}
contract Selector {
function calculateSelector() public pure returns (bytes4) {
Solidity101 i;
return i.hello.selector ^ i.world.selector;
// Returns 0xc6be8b58
}
function getHelloSelector() public pure returns (bytes4) {
Solidity101 i;
return i.hello.selector;
// Returns 0x19ff1d21
}
function getWorldSelector() public pure returns (bytes4) {
Solidity101 i;
return i.world.selector;
// Returns 0xdf419679
}
}This code isn't necessary to understand function selectors and how an interface's selector can be determined from the functions it implements.
Run that sample in Remix to see how interface function modifications affect contract function output.
Contracts publish their implemented interfaces.
We can identify interfaces. Now we must disclose the interfaces we're implementing. First, import IERC165 like so.
pragma solidity ^0.4.20;
interface ERC165 {
/// @notice Query if a contract implements an interface
/// @param interfaceID The interface identifier, as specified in ERC-165
/// @dev Interface identification is specified in ERC-165.
/// @return `true` if the contract implements `interfaceID` and
/// `interfaceID` is not 0xffffffff, `false` otherwise
function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceID) external view returns (bool);
}We still need to build this interface in our smart contract. ERC721 from OpenZeppelin is a good example.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
// OpenZeppelin Contracts (last updated v4.5.0) (token/ERC721/ERC721.sol)
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "./IERC721.sol";
import "./extensions/IERC721Metadata.sol";
import "../../utils/introspection/ERC165.sol";
// ...
contract ERC721 is Context, ERC165, IERC721, IERC721Metadata {
// ...
function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId) public view virtual override(ERC165, IERC165) returns (bool) {
return
interfaceId == type(IERC721).interfaceId ||
interfaceId == type(IERC721Metadata).interfaceId ||
super.supportsInterface(interfaceId);
}
// ...
}I deleted unnecessary code. The smart contract imports ERC165, IERC721 and IERC721Metadata. The is keyword at smart contract declaration implements all three.
Kind (interface).
Note that type(interface).interfaceId returns the same as the interface selector.
We override supportsInterface in the smart contract to return a boolean that checks if interfaceId is the same as one of the implemented contracts.
Super.supportsInterface() calls ERC165 code. Checks if interfaceId is IERC165.
function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId) public view virtual override returns (bool) {
return interfaceId == type(IERC165).interfaceId;
}So, if we run supportsInterface with an interfaceId, our contract function returns true if it's implemented and false otherwise. True for IERC721, IERC721Metadata, andIERC165.
Conclusion
I hope this post has helped you understand and use ERC165 and why it's employed.
Have a great day, thanks for reading!

Clive Thompson
3 years ago
Small Pieces of Code That Revolutionized the World
Few sentences can have global significance.

Ethan Zuckerman invented the pop-up commercial in 1997.
He was working for Tripod.com, an online service that let people make little web pages for free. Tripod offered advertising to make money. Advertisers didn't enjoy seeing their advertising next to filthy content, like a user's anal sex website.
Zuckerman's boss wanted a solution. Wasn't there a way to move the ads away from user-generated content?
When you visited a Tripod page, a pop-up ad page appeared. So, the ad isn't officially tied to any user page. It'd float onscreen.
Here’s the thing, though: Zuckerman’s bit of Javascript, that created the popup ad? It was incredibly short — a single line of code:
window.open('http://tripod.com/navbar.html'
"width=200, height=400, toolbar=no, scrollbars=no, resizable=no, target=_top");Javascript tells the browser to open a 200-by-400-pixel window on top of any other open web pages, without a scrollbar or toolbar.
Simple yet harmful! Soon, commercial websites mimicked Zuckerman's concept, infesting the Internet with pop-up advertising. In the early 2000s, a coder for a download site told me that most of their revenue came from porn pop-up ads.
Pop-up advertising are everywhere. You despise them. Hopefully, your browser blocks them.
Zuckerman wrote a single line of code that made the world worse.

I read Zuckerman's story in How 26 Lines of Code Changed the World. Torie Bosch compiled a humorous anthology of short writings about code that tipped the world.
Most of these samples are quite short. Pop-cultural preconceptions about coding say that important code is vast and expansive. Hollywood depicts programmers as blurs spouting out Niagaras of code. Google's success was formerly attributed to its 2 billion lines of code.
It's usually not true. Google's original breakthrough, the piece of code that propelled Google above its search-engine counterparts, was its PageRank algorithm, which determined a web page's value based on how many other pages connected to it and the quality of those connecting pages. People have written their own Python versions; it's only a few dozen lines.
Google's operations, like any large tech company's, comprise thousands of procedures. So their code base grows. The most impactful code can be brief.
The examples are fascinating and wide-ranging, so read the whole book (or give it to nerds as a present). Charlton McIlwain wrote a chapter on the police beat algorithm developed in the late 1960s to anticipate crime hotspots so law enforcement could dispatch more officers there. It created a racial feedback loop. Since poor Black neighborhoods were already overpoliced compared to white ones, the algorithm directed more policing there, resulting in more arrests, which convinced it to send more police; rinse and repeat.
Kelly Chudler's You Are Not Expected To Understand This depicts the police-beat algorithm.

Even shorter code changed the world: the tracking pixel.
Lily Hay Newman's chapter on monitoring pixels says you probably interact with this code every day. It's a snippet of HTML that embeds a single tiny pixel in an email. Getting an email with a tracking code spies on me. As follows: My browser requests the single-pixel image as soon as I open the mail. My email sender checks to see if Clives browser has requested that pixel. My email sender can tell when I open it.
Adding a tracking pixel to an email is easy:
<img src="URL LINKING TO THE PIXEL ONLINE" width="0" height="0">An older example: Ellen R. Stofan and Nick Partridge wrote a chapter on Apollo 11's lunar module bailout code. This bailout code operated on the lunar module's tiny on-board computer and was designed to prioritize: If the computer grew overloaded, it would discard all but the most vital work.
When the lunar module approached the moon, the computer became overloaded. The bailout code shut down anything non-essential to landing the module. It shut down certain lunar module display systems, scaring the astronauts. Module landed safely.
22-line code
POODOO INHINT
CA Q
TS ALMCADR
TC BANKCALL
CADR VAC5STOR # STORE ERASABLES FOR DEBUGGING PURPOSES.
INDEX ALMCADR
CAF 0
ABORT2 TC BORTENT
OCT77770 OCT 77770 # DONT MOVE
CA V37FLBIT # IS AVERAGE G ON
MASK FLAGWRD7
CCS A
TC WHIMPER -1 # YES. DONT DO POODOO. DO BAILOUT.
TC DOWNFLAG
ADRES STATEFLG
TC DOWNFLAG
ADRES REINTFLG
TC DOWNFLAG
ADRES NODOFLAG
TC BANKCALL
CADR MR.KLEAN
TC WHIMPERThis fun book is worth reading.
I'm a contributor to the New York Times Magazine, Wired, and Mother Jones. I've also written Coders: The Making of a New Tribe and the Remaking of the World and Smarter Than You Think: How Technology is Changing Our Minds. Twitter and Instagram: @pomeranian99; Mastodon: @clive@saturation.social.
