More on Personal Growth

Jari Roomer
3 years ago
10 Alternatives to Smartphone Scrolling
"Don't let technology control you; manage your phone."
"Don't become a slave to technology," said Richard Branson. "Manage your phone, don't let it manage you."
Unfortunately, most people are addicted to smartphones.
Worrying smartphone statistics:
46% of smartphone users spend 5–6 hours daily on their device.
The average adult spends 3 hours 54 minutes per day on mobile devices.
We check our phones 150–344 times per day (every 4 minutes).
During the pandemic, children's daily smartphone use doubled.
Having a list of productive, healthy, and fulfilling replacement activities is an effective way to reduce smartphone use.
The more you practice these smartphone replacements, the less time you'll waste.
Skills Development
Most people say they 'don't have time' to learn new skills or read more. Lazy justification. The issue isn't time, but time management. Distractions and low-quality entertainment waste hours every day.
The majority of time is spent in low-quality ways, according to Richard Koch, author of The 80/20 Principle.
What if you swapped daily phone scrolling for skill-building?
There are dozens of skills to learn, from high-value skills to make more money to new languages and party tricks.
Learning a new skill will last for years, if not a lifetime, compared to scrolling through your phone.
Watch Docs
Love documentaries. It's educational and relaxing. A good documentary helps you understand the world, broadens your mind, and inspires you to change.
Recent documentaries I liked include:
14 Peaks: Nothing Is Impossible
The Social Dilemma
Jim & Andy: The Great Beyond
Fantastic Fungi
Make money online
If you've ever complained about not earning enough money, put away your phone and get to work.
Instead of passively consuming mobile content, start creating it. Create something worthwhile. Freelance.
Internet makes starting a business or earning extra money easier than ever.
(Grand)parents didn't have this. Someone made them work 40+ hours. Few alternatives existed.
Today, all you need is internet and a monetizable skill. Use the internet instead of letting it distract you. Profit from it.
Bookworm
Jack Canfield, author of Chicken Soup For The Soul, said, "Everyone spends 2–3 hours a day watching TV." If you read that much, you'll be in the top 1% of your field."
Few people have more than two hours per day to read.
If you read 15 pages daily, you'd finish 27 books a year (as the average non-fiction book is about 200 pages).
Jack Canfield's quote remains relevant even though 15 pages can be read in 20–30 minutes per day. Most spend this time watching TV or on their phones.
What if you swapped 20 minutes of mindless scrolling for reading? You'd gain knowledge and skills.
Favorite books include:
The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People — Stephen R. Covey
The War of Art — Steven Pressfield
The Psychology of Money — Morgan Housel
A New Earth — Eckart Tolle
Get Organized
All that screen time could've been spent organizing. It could have been used to clean, cook, or plan your week.
If you're always 'behind,' spend 15 minutes less on your phone to get organized.
"Give me six hours to chop down a tree, and I'll spend the first four sharpening the ax," said Abraham Lincoln. Getting organized is like sharpening an ax, making each day more efficient.
Creativity
Why not be creative instead of consuming others'? Do something creative, like:
Painting
Musically
Photography\sWriting
Do-it-yourself
Construction/repair
Creative projects boost happiness, cognitive functioning, and reduce stress and anxiety. Creative pursuits induce a flow state, a powerful mental state.
This contrasts with smartphones' effects. Heavy smartphone use correlates with stress, depression, and anxiety.
Hike
People spend 90% of their time indoors, according to research. This generation is the 'Indoor Generation'
We lack an active lifestyle, fresh air, and vitamin D3 due to our indoor lifestyle (generated through direct sunlight exposure). Mental and physical health issues result.
Put away your phone and get outside. Go on nature walks. Explore your city on foot (or by bike, as we do in Amsterdam) if you live in a city. Move around! Outdoors!
You can't spend your whole life staring at screens.
Podcasting
Okay, a smartphone is needed to listen to podcasts. When you use your phone to get smarter, you're more productive than 95% of people.
Favorite podcasts:
The Pomp Podcast (about cryptocurrencies)
The Joe Rogan Experience
Kwik Brain (by Jim Kwik)
Podcasts can be enjoyed while walking, cleaning, or doing laundry. Win-win.
Journalize
I find journaling helpful for mental clarity. Writing helps organize thoughts.
Instead of reading internet opinions, comments, and discussions, look inward. Instead of Twitter or TikTok, look inward.
“It never ceases to amaze me: we all love ourselves more than other people, but care more about their opinion than our own.” — Marcus Aurelius
Give your mind free reign with pen and paper. It will highlight important thoughts, emotions, or ideas.
Never write for another person. You want unfiltered writing. So you get the best ideas.
Find your best hobbies
List your best hobbies. I guarantee 95% of people won't list smartphone scrolling.
It's often low-quality entertainment. The dopamine spike is short-lived, and it leaves us feeling emotionally 'empty'
High-quality leisure sparks happiness. They make us happy and alive. Everyone has different interests, so these activities vary.
My favorite quality hobbies are:
Nature walks (especially the mountains)
Video game party
Watching a film with my girlfriend
Gym weightlifting
Complexity learning (such as the blockchain and the universe)
This brings me joy. They make me feel more fulfilled and 'rich' than social media scrolling.
Make a list of your best hobbies to refer to when you're spending too much time on your phone.

Khyati Jain
3 years ago
By Engaging in these 5 Duplicitous Daily Activities, You Rapidly Kill Your Brain Cells
No, it’s not smartphones, overeating, or sugar.

Everyday practices affect brain health. Good brain practices increase memory and cognition.
Bad behaviors increase stress, which destroys brain cells.
Bad behaviors can reverse evolution and diminish the brain. So, avoid these practices for brain health.
1. The silent assassin
Introverts appreciated quarantine.
Before the pandemic, they needed excuses to remain home; thereafter, they had enough.
I am an introvert, and I didn’t hate quarantine. There are billions of people like me who avoid people.
Social relationships are important for brain health. Social anxiety harms your brain.
Antisocial behavior changes brains. It lowers IQ and increases drug abuse risk.
What you can do is as follows:
Make a daily commitment to engage in conversation with a stranger. Who knows, you might turn out to be your lone mate.
Get outside for at least 30 minutes each day.
Shop for food locally rather than online.
Make a call to a friend you haven't spoken to in a while.
2. Try not to rush things.
People love hustle culture. This economy requires a side gig to save money.
Long hours reduce brain health. A side gig is great until you burn out.
Work ages your wallet and intellect. Overworked brains age faster and lose cognitive function.
Working longer hours can help you make extra money, but it can harm your brain.
Side hustle but don't overwork.
What you can do is as follows:
Decide what hour you are not permitted to work after.
Three hours prior to night, turn off your laptop.
Put down your phone and work.
Assign due dates to each task.
3. Location is everything!
The environment may cause brain fog. High pollution can cause brain damage.
Air pollution raises Alzheimer's risk. Air pollution causes cognitive and behavioral abnormalities.
Polluted air can trigger early development of incurable brain illnesses, not simply lung harm.
Your city's air quality is uncontrollable. You may take steps to improve air quality.
In Delhi, schools and colleges are closed to protect pupils from polluted air. So I've adapted.
What you can do is as follows:
To keep your mind healthy and young, make an investment in a high-quality air purifier.
Enclose your windows during the day.
Use a N95 mask every day.
4. Don't skip this meal.
Fasting intermittently is trendy. Delaying breakfast to finish fasting is frequent.
Some skip breakfast and have a hefty lunch instead.
Skipping breakfast might affect memory and focus. Skipping breakfast causes low cognition, delayed responsiveness, and irritation.
Breakfast affects mood and productivity.
Intermittent fasting doesn't prevent healthy breakfasts.
What you can do is as follows:
Try to fast for 14 hours, then break it with a nutritious breakfast.
So that you can have breakfast in the morning, eat dinner early.
Make sure your breakfast is heavy in fiber and protein.
5. The quickest way to damage the health of your brain
Brain health requires water. 1% dehydration can reduce cognitive ability by 5%.
Cerebral fog and mental clarity might result from 2% brain dehydration. Dehydration shrinks brain cells.
Dehydration causes midday slumps and unproductivity. Water improves work performance.
Dehydration can harm your brain, so drink water throughout the day.
What you can do is as follows:
Always keep a water bottle at your desk.
Enjoy some tasty herbal teas.
With a big glass of water, begin your day.
Bring your own water bottle when you travel.
Conclusion
Bad habits can harm brain health. Low cognition reduces focus and productivity.
Unproductive work leads to procrastination, failure, and low self-esteem.
Avoid these harmful habits to optimize brain health and function.
Matthew Royse
3 years ago
These 10 phrases are unprofessional at work.
Successful workers don't talk this way.

"I know it's unprofessional, but I can't stop." — Author Sandy Hall
Do you realize your unprofessionalism? Do you care? Self-awareness?
Everyone can improve their unprofessionalism. Some workplace phrases and words shouldn't be said.
People often say out loud what they're thinking. They show insecurity, incompetence, and disrespect.
"Think before you speak," goes the saying.
Some of these phrases are "okay" in certain situations, but you'll lose colleagues' respect if you use them often.
Your word choice. Your tone. Your intentions. They matter.
Choose your words carefully to build work relationships and earn peer respect. You should build positive relationships with coworkers and clients.
These 10 phrases are unprofessional.
1. That Meeting Really Sucked
Wow! Were you there? You should be responsible if you attended. You can influence every conversation.
Alternatives
Improve the meeting instead of complaining afterward. Make it more meaningful and productive.
2. Not Sure if You Saw My Last Email
Referencing a previous email irritates people. Email follow-up can be difficult. Most people get tons of emails a day, so it may have been buried, forgotten, or low priority.
Alternatives
It's okay to follow up, but be direct, short, and let the recipient "save face"
3. Any Phrase About Sex, Politics, and Religion
Discussing sex, politics, and religion at work is foolish. If you discuss these topics, you could face harassment lawsuits.
Alternatives
Keep quiet about these contentious issues. Don't touch them.
4. I Know What I’m Talking About
Adding this won't persuade others. Research, facts, and topic mastery are key to persuasion. If you're knowledgeable, you don't need to say this.
Alternatives
Please don’t say it at all. Justify your knowledge.
5. Per Our Conversation
This phrase sounds like legal language. You seem to be documenting something legally. Cold, stern, and distant. "As discussed" sounds inauthentic.
Alternatives
It was great talking with you earlier; here's what I said.
6. Curse-Word Phrases
Swearing at work is unprofessional. You never know who's listening, so be careful. A child may be at work or on a Zoom or Teams call. Workplace cursing is unacceptable.
Alternatives
Avoid adult-only words.
7. I Hope This Email Finds You Well
This is a unique way to wish someone well. This phrase isn't as sincere as the traditional one. When you talk about the email, you're impersonal.
Alternatives
Genuinely care for others.
8. I Am Really Stressed
Happy, strong, stress-managing coworkers are valued. Manage your own stress. Exercise, sleep, and eat better.
Alternatives
Everyone has stress, so manage it. Don't talk about your stress.
9. I Have Too Much to Do
You seem incompetent. People think you can't say "no" or have poor time management. If you use this phrase, you're telling others you may need to change careers.
Alternatives
Don't complain about your workload; just manage it.
10. Bad Closing Salutations
"Warmly," "best," "regards," and "warm wishes" are common email closings. This conclusion sounds impersonal. Why use "warmly" for finance's payment status?
Alternatives
Personalize the closing greeting to the message and recipient. Use "see you tomorrow" or "talk soon" as closings.
Bringing It All Together
These 10 phrases are unprofessional at work. That meeting sucked, not sure if you saw my last email, and sex, politics, and religion phrases.
Also, "I know what I'm talking about" and any curse words. Also, avoid phrases like I hope this email finds you well, I'm stressed, and I have too much to do.
Successful workers communicate positively and foster professionalism. Don't waste chances to build strong work relationships by being unprofessional.
“Unprofessionalism damages the business reputation and tarnishes the trust of society.” — Pearl Zhu, an American author
This post is a summary. Read full article here
You might also like

Dr. Linda Dahl
3 years ago
We eat corn in almost everything. Is It Important?

Corn Kid got viral on TikTok after being interviewed by Recess Therapy. Tariq, called the Corn Kid, ate a buttery ear of corn in the video. He's corn crazy. He thinks everyone just has to try it. It turns out, whether we know it or not, we already have.
Corn is a fruit, veggie, and grain. It's the second-most-grown crop. Corn makes up 36% of U.S. exports. In the U.S., it's easy to grow and provides high yields, as proven by the vast corn belt spanning the Midwest, Great Plains, and Texas panhandle. Since 1950, the corn crop has doubled to 10 billion bushels.
You say, "Fine." We shouldn't just grow because we can. Why so much corn? What's this corn for?
Why is practical and political. Michael Pollan's The Omnivore's Dilemma has the full narrative. Early 1970s food costs increased. Nixon subsidized maize to feed the public. Monsanto genetically engineered corn seeds to make them hardier, and soon there was plenty of corn. Everyone ate. Woot! Too much corn followed. The powers-that-be had to decide what to do with leftover corn-on-the-cob.
They are fortunate that corn has a wide range of uses.
First, the edible variants. I divide corn into obvious and stealth.
Obvious corn includes popcorn, canned corn, and corn on the cob. This form isn't always digested and often comes out as entire, polka-dotting poop. Cornmeal can be ground to make cornbread, polenta, and corn tortillas. Corn provides antioxidants, minerals, and vitamins in moderation. Most synthetic Vitamin C comes from GMO maize.
Corn oil, corn starch, dextrose (a sugar), and high-fructose corn syrup are often overlooked. They're stealth corn because they sneak into practically everything. Corn oil is used for frying, baking, and in potato chips, mayonnaise, margarine, and salad dressing. Baby food, bread, cakes, antibiotics, canned vegetables, beverages, and even dairy and animal products include corn starch. Dextrose appears in almost all prepared foods, excluding those with high-fructose corn syrup. HFCS isn't as easily digested as sucrose (from cane sugar). It can also cause other ailments, which we'll discuss later.
Most foods contain corn. It's fed to almost all food animals. 96% of U.S. animal feed is corn. 39% of U.S. corn is fed to livestock. But animals prefer other foods. Omnivore chickens prefer insects, worms, grains, and grasses. Captive cows are fed a total mixed ration, which contains corn. These animals' products, like eggs and milk, are also corn-fed.
There are numerous non-edible by-products of corn that are employed in the production of items like:
fuel-grade ethanol
plastics
batteries
cosmetics
meds/vitamins binder
carpets, fabrics
glutathione
crayons
Paint/glue

How does corn influence you? Consider quick food for dinner. You order a cheeseburger, fries, and big Coke at the counter (or drive-through in the suburbs). You tell yourself, "No corn." All that contains corn. Deconstruct:
Cows fed corn produce meat and cheese. Meat and cheese were bonded with corn syrup and starch (same). The bun (corn flour and dextrose) and fries were fried in maize oil. High fructose corn syrup sweetens the drink and helps make the cup and straw.
Just about everything contains corn. Then what? A cornspiracy, perhaps? Is eating too much maize an issue, or should we strive to stay away from it whenever possible?
As I've said, eating some maize can be healthy. 92% of U.S. corn is genetically modified, according to the Center for Food Safety. The adjustments are expected to boost corn yields. Some sweet corn is genetically modified to produce its own insecticide, a protein deadly to insects made by Bacillus thuringiensis. It's safe to eat in sweet corn. Concerns exist about feeding agricultural animals so much maize, modified or not.
High fructose corn syrup should be consumed in moderation. Fructose, a sugar, isn't easily metabolized. Fructose causes diabetes, fatty liver, obesity, and heart disease. It causes inflammation, which might aggravate gout. Candy, packaged sweets, soda, fast food, juice drinks, ice cream, ice cream topping syrups, sauces & condiments, jams, bread, crackers, and pancake syrup contain the most high fructose corn syrup. Everyday foods with little nutrients. Check labels and choose cane sugar or sucrose-sweetened goods. Or, eat corn like the Corn Kid.

Jim Clyde Monge
3 years ago
Can You Sell Images Created by AI?

Some AI-generated artworks sell for enormous sums of money.
But can you sell AI-Generated Artwork?
Simple answer: yes.
However, not all AI services enable allow usage and redistribution of images.
Let's check some of my favorite AI text-to-image generators:
Dall-E2 by OpenAI
The AI art generator Dall-E2 is powerful. Since it’s still in beta, you can join the waitlist here.
OpenAI DOES NOT allow the use and redistribution of any image for commercial purposes.
Here's the policy as of April 6, 2022.

Here are some images from Dall-E2’s webpage to show its art quality.

Several Reddit users reported receiving pricing surveys from OpenAI.
This suggests the company may bring out a subscription-based tier and a commercial license to sell images soon.
MidJourney
I like Midjourney's art generator. It makes great AI images. Here are some samples:

Standard Licenses are available for $10 per month.
Standard License allows you to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, and/or sell copies of the images, except for blockchain technologies.
If you utilize or distribute the Assets using blockchain technology, you must pay MidJourney 20% of revenue above $20,000 a month or engage in an alternative agreement.
Here's their copyright and trademark page.

Dream by Wombo
Dream is one of the first public AI art generators.
This AI program is free, easy to use, and Wombo gives a royalty-free license to copy or share artworks.
Users own all artworks generated by the tool. Including all related copyrights or intellectual property rights.

Here’s Wombos' intellectual property policy.

Final Reflections
AI is creating a new sort of art that's selling well. It’s becoming popular and valued, despite some skepticism.
Now that you know MidJourney and Wombo let you sell AI-generated art, you need to locate buyers. There are several ways to achieve this, but that’s for another story.

Jano le Roux
3 years ago
Here's What I Learned After 30 Days Analyzing Apple's Microcopy
Move people with tiny words.

Apple fanboy here.
Macs are awesome.
Their iPhones rock.
$19 cloths are great.
$999 stands are amazing.
I love Apple's microcopy even more.
It's like the marketing goddess bit into the Apple logo and blessed the world with microcopy.
I took on a 30-day micro-stalking mission.
Every time I caught myself wasting time on YouTube, I had to visit Apple’s website to learn the secrets of the marketing goddess herself.
We've learned. Golden apples are calling.
Cut the friction
Benefit-first, not commitment-first.
Brands lose customers through friction.
Most brands don't think like customers.
Brands want sales.
Brands want newsletter signups.
Here's their microcopy:
“Buy it now.”
“Sign up for our newsletter.”
Both are difficult. They ask for big commitments.
People are simple creatures. Want pleasure without commitment.
Apple nails this.
So, instead of highlighting the commitment, they highlight the benefit of the commitment.
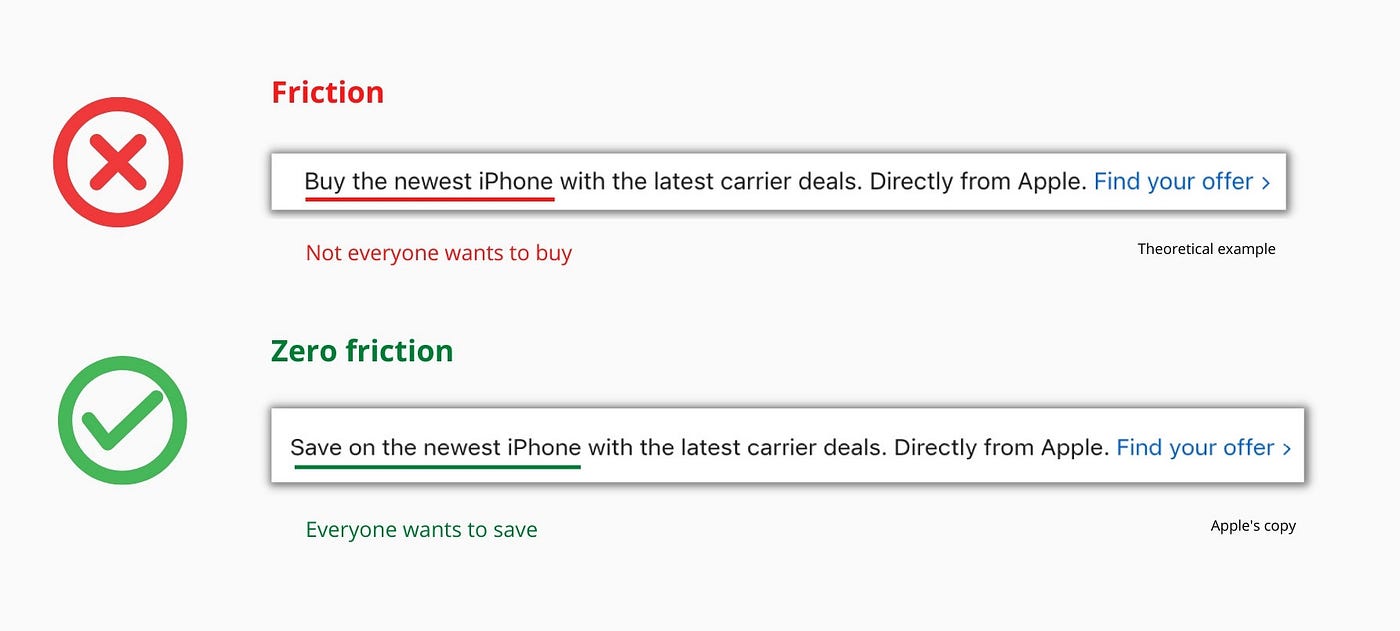
Saving on the latest iPhone sounds easier than buying it. Everyone saves, but not everyone buys.
A subtle change in framing reduces friction.
Apple eliminates customer objections to reduce friction.
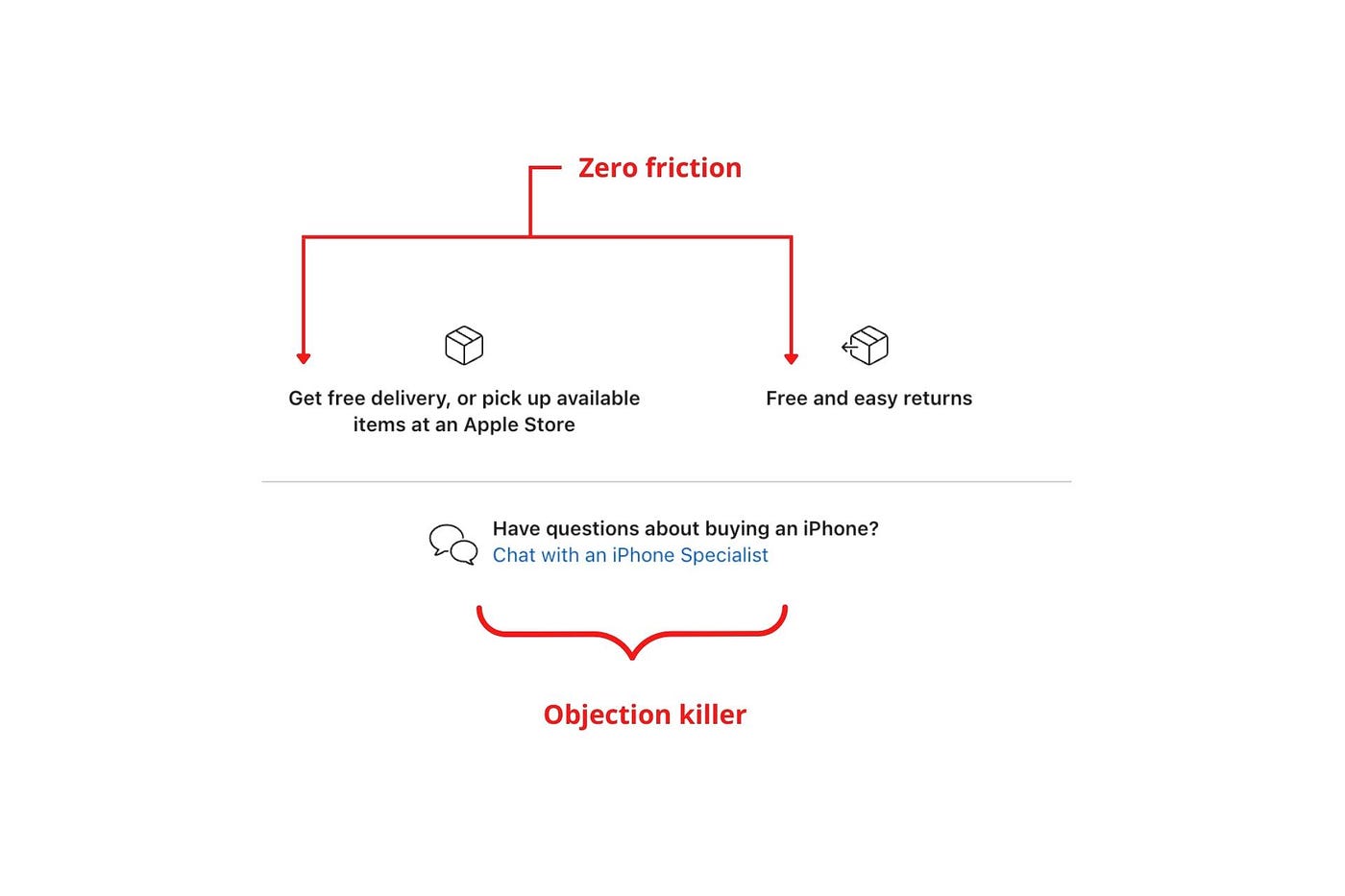
Less customer friction means simpler processes.
Apple's copy expertly reassures customers about shipping fees and not being home. Apple assures customers that returning faulty products is easy.
Apple knows that talking to a real person is the best way to reduce friction and improve their copy.
Always rhyme
Learn about fine rhyme.
Poets make things beautiful with rhyme.
Copywriters use rhyme to stand out.
Apple’s copywriters have mastered the art of corporate rhyme.
Two techniques are used.
1. Perfect rhyme
Here, rhymes are identical.

2. Imperfect rhyme
Here, rhyming sounds vary.

Apple prioritizes meaning over rhyme.
Apple never forces rhymes that don't fit.
It fits so well that the copy seems accidental.
Add alliteration
Alliteration always entertains.
Alliteration repeats initial sounds in nearby words.
Apple's copy uses alliteration like no other brand I've seen to create a rhyming effect or make the text more fun to read.
For example, in the sentence "Sam saw seven swans swimming," the initial "s" sound is repeated five times. This creates a pleasing rhythm.
Microcopy overuse is like pouring ketchup on a Michelin-star meal.
Alliteration creates a memorable phrase in copywriting. It's subtler than rhyme, and most people wouldn't notice; it simply resonates.

I love how Apple uses alliteration and contrast between "wonders" and "ease".
Assonance, or repeating vowels, isn't Apple's thing.
You ≠ Hero, Customer = Hero
Your brand shouldn't be the hero.
Because they'll be using your product or service, your customer should be the hero of your copywriting. With your help, they should feel like they can achieve their goals.
I love how Apple emphasizes what you can do with the machine in this microcopy.

It's divine how they position their tools as sidekicks to help below.

This one takes the cake:

Dialogue-style writing
Conversational copy engages.
Excellent copy Like sharing gum with a friend.
This helps build audience trust.

Apple does this by using natural connecting words like "so" and phrases like "But that's not all."
Snowclone-proof
The mother of all microcopy techniques.
A snowclone uses an existing phrase or sentence to create a new one. The new phrase or sentence uses the same structure but different words.
It’s usually a well know saying like:
To be or not to be.
This becomes a formula:
To _ or not to _.
Copywriters fill in the blanks with cause-related words. Example:
To click or not to click.

Apple turns "survival of the fittest" into "arrival of the fittest."
It's unexpected and surprises the reader.
So this was fun.
But my fun has just begun.
Microcopy is 21st-century poetry.
I came as an Apple fanboy.
I leave as an Apple fanatic.
Now I’m off to find an apple tree.
Cause you know how it goes.
(Apples, trees, etc.)
This post is a summary. Original post available here.
