More on Entrepreneurship/Creators

Alana Rister, Ph.D.
3 years ago
Don't rely on lessons you learned with a small audience.
My growth-killing mistake

When you initially start developing your audience, you need guidance.
What does my audience like? What do they not like? How can I grow more?
When I started writing two years ago, I inquired daily. Taking cues from your audience to develop more valuable content is a good concept, but it's simple to let them destroy your growth.
A small audience doesn't represent the full picture.
When I had fewer than 100 YouTube subscribers, I tried several video styles and topics. I looked to my audience for what to preserve and what to change.
If my views, click-through rate, or average view % dropped, that topic or style was awful. Avoiding that style helped me grow.
Vlogs, talking head videos on writing, and long-form tutorials didn't fare well.
Since I was small, I've limited the types of films I make. I have decided to make my own videos.
Surprisingly, the videos I avoided making meet or exceed my views, CTR, and audience retention.

A limited audience can't tell you what your tribe wants. Therefore, limiting your innovation will prohibit you from reaching the right audience. Finding them may take longer.
Large Creators Experience The Same Issue
In the last two years, I've heard Vanessa Lau and Cathrin Manning say they felt pigeonholed into generating videos they didn't want to do.
Why does this happen over and over again?
Once you have a popular piece of content, your audience will grow. So when you publish inconsistent material, fewer of your new audience will view it. You interpret the drop in views as a sign that your audience doesn't want the content, so you stop making it.
Repeat this procedure a few times, and you'll create stuff you're not passionate about because you're frightened to publish it.
How to Manage Your Creativity and Audience Development
I'm not recommending you generate random content.
Instead of feeling trapped by your audience, you can cultivate a diverse audience.
Create quality material on a range of topics and styles as you improve. Be creative until you get 100 followers. Look for comments on how to improve your article.
If you observe trends in the types of content that expand your audience, focus 50-75% of your material on those trends. Allow yourself to develop 25% non-performing material.
This method can help you expand your audience faster with your primary trends and like all your stuff. Slowly, people will find 25% of your material, which will boost its performance.
How to Expand Your Audience Without Having More Limited Content
Follow these techniques to build your audience without feeling confined.
Don't think that you need restrict yourself to what your limited audience prefers.
Don't let the poor performance of your desired material demotivate you.
You shouldn't restrict the type of content you publish or the themes you cover when you have less than 100 followers.
When your audience expands, save 25% of your content for your personal interests, regardless of how well it does.

DC Palter
3 years ago
Is Venture Capital a Good Fit for Your Startup?
5 VC investment criteria

I reviewed 200 startup business concepts last week. Brainache.
The enterprises sold various goods and services. The concepts were achingly similar: give us money, we'll produce a product, then get more to expand. No different from daily plans and pitches.
Most of those 200 plans sounded plausible. But 10% looked venture-worthy. 90% of startups need alternatives to venture finance.
With the success of VC-backed businesses and the growth of venture funds, a common misperception is that investors would fund any decent company idea. Finding investors that believe in the firm and founders is the key to funding.
Incorrect. Venture capital needs investing in certain enterprises. If your startup doesn't match the model, as most early-stage startups don't, you can revise your business plan or locate another source of capital.
Before spending six months pitching angels and VCs, make sure your startup fits these criteria.
Likely to generate $100 million in sales
First, I check the income predictions in a pitch deck. If it doesn't display $100M, don't bother.
The math doesn't work for venture financing in smaller businesses.
Say a fund invests $1 million in a startup valued at $5 million that is later acquired for $20 million. That's a win everyone should celebrate. Most VCs don't care.
Consider a $100M fund. The fund must reach $360M in 7 years with a 20% return. Only 20-30 investments are possible. 90% of the investments will fail, hence the 23 winners must return $100M-$200M apiece. $15M isn't worth the work.
Angel investors and tiny funds use the same ideas as venture funds, but their smaller scale affects the calculations. If a company can support its growth through exit on less than $2M in angel financing, it must have $25M in revenues before large companies will consider acquiring it.
Aiming for Hypergrowth
A startup's size isn't enough. It must expand fast.
Developing a great business takes time. Complex technology must be constructed and tested, a nationwide expansion must be built, or production procedures must go from lab to pilot to factories. These can be enormous, world-changing corporations, but venture investment is difficult.
The normal 10-year venture fund life. Investments are made during first 3–4 years.. 610 years pass between investment and fund dissolution. Funds need their investments to exit within 5 years, 7 at the most, therefore add a safety margin.
Longer exit times reduce ROI. A 2-fold return in a year is excellent. Loss at 2x in 7 years.
Lastly, VCs must prove success to raise their next capital. The 2nd fund is raised from 1st fund portfolio increases. Third fund is raised using 1st fund's cash return. Fund managers must raise new money quickly to keep their jobs.
Branding or technology that is protected
No big firm will buy a startup at a high price if they can produce a competing product for less. Their development teams, consumer base, and sales and marketing channels are large. Who needs you?
Patents, specialist knowledge, or brand name are the only answers. The acquirer buys this, not the thing.
I've heard of several promising startups. It's not a decent investment if there's no exit strategy.
A company that installs EV charging stations in apartments and shopping areas is an example. It's profitable, repeatable, and big. A terrific company. Not a startup.
This building company's operations aren't secret. No technology to protect, no special information competitors can't figure out, no go-to brand name. Despite the immense possibilities, a large construction company would be better off starting their own.
Most venture businesses build products, not services. Services can be profitable but hard to safeguard.
Probable purchase at high multiple
Once a software business proves its value, acquiring it is easy. Pharma and medtech firms have given up on their own research and instead acquire startups after regulatory permission. Many startups, especially in specialized areas, have this weakness.
That doesn't mean any lucrative $25M-plus business won't be acquired. In many businesses, the venture model requires a high exit premium.
A startup invents a new glue. 3M, BASF, Henkel, and others may buy them. Adding more adhesive to their catalogs won't boost commerce. They won't compete to buy the business. They'll only buy a startup at a profitable price. The acquisition price represents a moderate EBITDA multiple.
The company's $100M revenue presumably yields $10m in profits (assuming they’ve reached profitability at all). A $30M-$50M transaction is likely. Not terrible, but not what venture investors want after investing $25M to create a plant and develop the business.
Private equity buys profitable companies for a moderate profit multiple. It's a good exit for entrepreneurs, but not for investors seeking 10x or more what PE firms pay. If a startup offers private equity as an exit, the conversation is over.
Constructed for purchase
The startup wants a high-multiple exit. Unless the company targets $1B in revenue and does an IPO, exit means acquisition.
If they're constructing the business for acquisition or themselves, founders must decide.
If you want an indefinitely-running business, I applaud you. We need more long-term founders. Most successful organizations are founded around consumer demands, not venture capital's urge to grow fast and exit. Not venture funding.
if you don't match the venture model, what to do
VC funds moonshots. The 10% that succeed are extraordinary. Not every firm is a rocketship, and launching the wrong startup into space, even with money, will explode.
But just because your startup won't make $100M in 5 years doesn't mean it's a bad business. Most successful companies don't follow this model. It's not venture capital-friendly.
Although venture capital gets the most attention due to a few spectacular triumphs (and disasters), it's not the only or even most typical option to fund a firm.
Other ways to support your startup:
Personal and family resources, such as credit cards, second mortgages, and lines of credit
bootstrapping off of sales
government funding and honors
Private equity & project financing
collaborating with a big business
Including a business partner
Before pitching angels and VCs, be sure your startup qualifies. If so, include them in your pitch.

cdixon
3 years ago
2000s Toys, Secrets, and Cycles
During the dot-com bust, I started my internet career. People used the internet intermittently to check email, plan travel, and do research. The average internet user spent 30 minutes online a day, compared to 7 today. To use the internet, you had to "log on" (most people still used dial-up), unlike today's always-on, high-speed mobile internet. In 2001, Amazon's market cap was $2.2B, 1/500th of what it is today. A study asked Americans if they'd adopt broadband, and most said no. They didn't see a need to speed up email, the most popular internet use. The National Academy of Sciences ranked the internet 13th among the 100 greatest inventions, below radio and phones. The internet was a cool invention, but it had limited uses and wasn't a good place to build a business.
A small but growing movement of developers and founders believed the internet could be more than a read-only medium, allowing anyone to create and publish. This is web 2. The runner up name was read-write web. (These terms were used in prominent publications and conferences.)
Web 2 concepts included letting users publish whatever they want ("user generated content" was a buzzword), social graphs, APIs and mashups (what we call composability today), and tagging over hierarchical navigation. Technical innovations occurred. A seemingly simple but important one was dynamically updating web pages without reloading. This is now how people expect web apps to work. Mobile devices that could access the web were niche (I was an avid Sidekick user).
The contrast between what smart founders and engineers discussed over dinner and on weekends and what the mainstream tech world took seriously during the week was striking. Enterprise security appliances, essentially preloaded servers with security software, were a popular trend. Many of the same people would talk about "serious" products at work, then talk about consumer internet products and web 2. It was tech's biggest news. Web 2 products were seen as toys, not real businesses. They were hobbies, not work-related.
There's a strong correlation between rich product design spaces and what smart people find interesting, which took me some time to learn and led to blog posts like "The next big thing will start out looking like a toy" Web 2's novel product design possibilities sparked dinner and weekend conversations. Imagine combining these features. What if you used this pattern elsewhere? What new product ideas are next? This excited people. "Serious stuff" like security appliances seemed more limited.
The small and passionate web 2 community also stood out. I attended the first New York Tech meetup in 2004. Everyone fit in Meetup's small conference room. Late at night, people demoed their software and chatted. I have old friends. Sometimes I get asked how I first met old friends like Fred Wilson and Alexis Ohanian. These topics didn't interest many people, especially on the east coast. We were friends. Real community. Alex Rampell, who now works with me at a16z, is someone I met in 2003 when a friend said, "Hey, I met someone else interested in consumer internet." Rare. People were focused and enthusiastic. Revolution seemed imminent. We knew a secret nobody else did.
My web 2 startup was called SiteAdvisor. When my co-founders and I started developing the idea in 2003, web security was out of control. Phishing and spyware were common on Internet Explorer PCs. SiteAdvisor was designed to warn users about security threats like phishing and spyware, and then, using web 2 concepts like user-generated reviews, add more subjective judgments (similar to what TrustPilot seems to do today). This staged approach was common at the time; I called it "Come for the tool, stay for the network." We built APIs, encouraged mashups, and did SEO marketing.
Yahoo's 2005 acquisitions of Flickr and Delicious boosted web 2 in 2005. By today's standards, the amounts were small, around $30M each, but it was a signal. Web 2 was assumed to be a fun hobby, a way to build cool stuff, but not a business. Yahoo was a savvy company that said it would make web 2 a priority.
As I recall, that's when web 2 started becoming mainstream tech. Early web 2 founders transitioned successfully. Other entrepreneurs built on the early enthusiasts' work. Competition shifted from ideation to execution. You had to decide if you wanted to be an idealistic indie bar band or a pragmatic stadium band.
Web 2 was booming in 2007 Facebook passed 10M users, Twitter grew and got VC funding, and Google bought YouTube. The 2008 financial crisis tested entrepreneurs' resolve. Smart people predicted another great depression as tech funding dried up.
Many people struggled during the recession. 2008-2011 was a golden age for startups. By 2009, talented founders were flooding Apple's iPhone app store. Mobile apps were booming. Uber, Venmo, Snap, and Instagram were all founded between 2009 and 2011. Social media (which had replaced web 2), cloud computing (which enabled apps to scale server side), and smartphones converged. Even if social, cloud, and mobile improve linearly, the combination could improve exponentially.
This chart shows how I view product and financial cycles. Product and financial cycles evolve separately. The Nasdaq index is a proxy for the financial sentiment. Financial sentiment wildly fluctuates.
Next row shows iconic startup or product years. Bottom-row product cycles dictate timing. Product cycles are more predictable than financial cycles because they follow internal logic. In the incubation phase, enthusiasts build products for other enthusiasts on nights and weekends. When the right mix of technology, talent, and community knowledge arrives, products go mainstream. (I show the biggest tech cycles in the chart, but smaller ones happen, like web 2 in the 2000s and fintech and SaaS in the 2010s.)
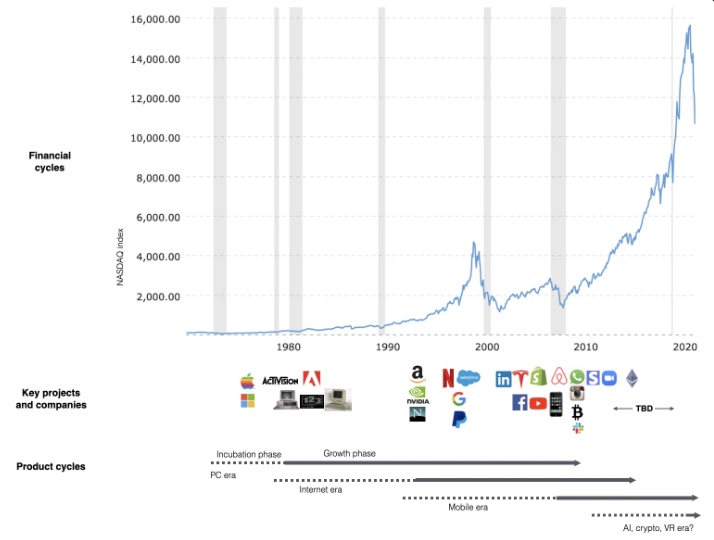
Tech has changed since the 2000s. Few tech giants dominate the internet, exerting economic and cultural influence. In the 2000s, web 2 was ignored or dismissed as trivial. Entrenched interests respond aggressively to new movements that could threaten them. Creative patterns from the 2000s continue today, driven by enthusiasts who see possibilities where others don't. Know where to look. Crypto and web 3 are where I'd start.
Today's negative financial sentiment reminds me of 2008. If we face a prolonged downturn, we can learn from 2008 by preserving capital and focusing on the long term. Keep an eye on the product cycle. Smart people are interested in things with product potential. This becomes true. Toys become necessities. Hobbies become mainstream. Optimists build the future, not cynics.
Full article is available here
You might also like

Cory Doctorow
3 years ago
The downfall of the Big Four accounting companies is just one (more) controversy away.
Economic mutual destruction.

Multibillion-dollar corporations never bothered with an independent audit, and they all lied about their balance sheets.
It's easy to forget that the Big Four accounting firms are lousy fraud enablers. Just because they sign off on your books doesn't mean you're not a hoax waiting to erupt.
This is *crazy* Capitalism depends on independent auditors. Rich folks need to know their financial advisers aren't lying. Rich folks usually succeed.
No accounting. EY, KPMG, PWC, and Deloitte make more money consulting firms than signing off on their accounts.
The Big Four sign off on phony books because failing to make friends with unscrupulous corporations may cost them consulting contracts.
The Big Four are the only firms big enough to oversee bankruptcy when they sign off on fraudulent books, as they did for Carillion in 2018. All four profited from Carillion's bankruptcy.
The Big Four are corrupt without any consequences for misconduct. Who can forget when KPMG's top management was fined millions for helping auditors cheat on ethics exams?
Consulting and auditing conflict. Consultants help a firm cover its evil activities, such as tax fraud or wage theft, whereas auditors add clarity to a company's finances. The Big Four make more money from cooking books than from uncooking them, thus they are constantly embroiled in scandals.
If a major scandal breaks, it may bring down the entire sector and substantial parts of the economy. Jim Peterson explains system risk for The Dig.
The Big Four are voluntary private partnerships where accountants invest their time, reputations, and money. If a controversy threatens the business, partners who depart may avoid scandal and financial disaster.
When disaster looms, each partner should bolt for the door, even if a disciplined stay-and-hold posture could weather the storm. This happened to Arthur Andersen during Enron's collapse, and a 2006 EU report recognized the risk to other corporations.
Each partner at a huge firm knows how much dirty laundry they've buried in the company's garden, and they have well-founded suspicions about what other partners have buried, too. When someone digs, everyone runs.
If a firm confronts substantial litigation damages or enforcement penalties, it could trigger the collapse of one of the Big Four. That would be bad news for the firm's clients, who would have trouble finding another big auditor.
Most of the world's auditing capacity is concentrated in four enormous, brittle, opaque, compromised organizations. If one of them goes bankrupt, the other three won't be able to take on its clients.
Peterson: Another collapse would strand many of the world's large public businesses, leaving them unable to obtain audit views for their securities listings and regulatory compliance.
Count Down: The Past, Present, and Uncertain Future of the Big Four Accounting Firms is in its second edition.
https://www.emerald.com/insight/publication/doi/10.1108/9781787147003

KonstantinDr
3 years ago
Early Adopters And the Fifth Reason WHY
Product management wizardry.

Early adopters buy a product even if it hasn't hit the market or has flaws.
Who are the early adopters?
Early adopters try a new technology or product first. Early adopters are interested in trying or buying new technologies and products before others. They're risk-tolerant and can provide initial cash flow and product reviews. They help a company's new product or technology gain social proof.
Early adopters are most common in the technology industry, but they're in every industry. They don't follow the crowd. They seek innovation and report product flaws before mass production. If the product works well, the first users become loyal customers, and colleagues value their opinion.
What to do with early adopters?
They can be used to collect feedback and initial product promotion, first sales, and product value validation.
How to find early followers?
Start with your immediate environment and target audience. Communicate with them to see if they're interested in your value proposition.

1) Innovators (2.5% of the population) are risk-takers seeking novelty. These people are the first to buy new and trendy items and drive social innovation. However, these people are usually elite;
Early adopters (13.5%) are inclined to accept innovations but are more cautious than innovators; they start using novelties when innovators or famous people do;
3) The early majority (34%) is conservative; they start using new products when many people have mastered them. When the early majority accepted the innovation, it became ingrained in people's minds.
4) Attracting 34% of the population later means the novelty has become a mass-market product. Innovators are using newer products;
5) Laggards (16%) are the most conservative, usually elderly people who use the same products.

Stages of new information acceptance
1. The information is strange and rejected by most. Accepted only by innovators;
2. When early adopters join, more people believe it's not so bad; when a critical mass is reached, the novelty becomes fashionable and most people use it.
3. Fascination with a novelty peaks, then declines; the majority and laggards start using it later; novelty becomes obsolete; innovators master something new.
Problems with early implementation
Early adopter sales have disadvantages.
Higher risk of defects
Selling to first-time users increases the risk of defects. Early adopters are often influential, so this can affect the brand's and its products' long-term perception.
Not what was expected
First-time buyers may be disappointed by the product. Marketing messages can mislead consumers, and if the first users believe the company misrepresented the product, this will affect future sales.
Compatibility issues
Some technological advances cause compatibility issues. Consumers may be disappointed if new technology is incompatible with their electronics.
Method 5 WHY

Let's talk about 5 why, a good tool for finding project problems' root causes. This method is also known as the five why rule, method, or questions.
The 5 why technique came from Toyota's lean manufacturing and helps quickly determine a problem's root cause.
On one, two, and three, you simply do this:
We identify and frame the issue for which a solution is sought.
We frequently ponder this question. The first 2-3 responses are frequently very dull, making you want to give up on this pointless exercise. However, after that, things get interesting. And occasionally it's so fascinating that you question whether you really needed to know.
We consider the final response, ponder it, and choose a course of action.
Always do the 5 whys with the customer or team to have a reasonable discussion and better understand what's happening.
And the “five whys” is a wonderful and simplest tool for introspection. With the accumulated practice, it is used almost automatically in any situation like “I can’t force myself to work, the mood is bad in the morning” or “why did I decide that I have no life without this food processor for 20,000 rubles, which will take half of my rather big kitchen.”
An illustration of the five whys
A simple, but real example from my work practice that I think is very indicative, given the participants' low IT skills. Anonymized, of course.
Users spend too long looking for tender documents.
Why? Because they must search through many company tender documents.
Why? Because the system can't filter department-specific bids.
Why? Because our contract management system requirements didn't include a department-tender link. That's it, right? We'll add a filter and be happy. but still…
why? Because we based the system's requirements on regulations for working with paper tender documents (when they still had envelopes and autopsies), not electronic ones, and there was no search mechanism.
Why? We didn't consider how our work would change when switching from paper to electronic tenders when drafting the requirements.
Now I know what to do in the future. We add a filter, enter department data, and teach users to use it. This is tactical, but strategically we review the same forgotten requirements to make all the necessary changes in a package, plus we include it in the checklist for the acceptance of final requirements for the future.

Errors when using 5 why
Five whys seems simple, but it can be misused.
Popular ones:
The accusation of everyone and everything is then introduced. After all, the 5 why method focuses on identifying the underlying causes rather than criticizing others. As a result, at the third step, it is not a good idea to conclude that the system is ineffective because users are stupid and that we can therefore do nothing about it.
to fight with all my might so that the outcome would be exactly 5 reasons, neither more nor less. 5 questions is a typical number (it sounds nice, yes), but there could be 3 or 7 in actuality.
Do not capture in-between responses. It is difficult to overestimate the power of the written or printed word, so the result is so-so when the focus is lost. That's it, I suppose. Simple, quick, and brilliant, like other project management tools.
Conclusion
Today we analyzed important study elements:
Early adopters and 5 WHY We've analyzed cases and live examples of how these methods help with product research and growth point identification. Next, consider the HADI cycle.


Khyati Jain
3 years ago
By Engaging in these 5 Duplicitous Daily Activities, You Rapidly Kill Your Brain Cells
No, it’s not smartphones, overeating, or sugar.

Everyday practices affect brain health. Good brain practices increase memory and cognition.
Bad behaviors increase stress, which destroys brain cells.
Bad behaviors can reverse evolution and diminish the brain. So, avoid these practices for brain health.
1. The silent assassin
Introverts appreciated quarantine.
Before the pandemic, they needed excuses to remain home; thereafter, they had enough.
I am an introvert, and I didn’t hate quarantine. There are billions of people like me who avoid people.
Social relationships are important for brain health. Social anxiety harms your brain.
Antisocial behavior changes brains. It lowers IQ and increases drug abuse risk.
What you can do is as follows:
Make a daily commitment to engage in conversation with a stranger. Who knows, you might turn out to be your lone mate.
Get outside for at least 30 minutes each day.
Shop for food locally rather than online.
Make a call to a friend you haven't spoken to in a while.
2. Try not to rush things.
People love hustle culture. This economy requires a side gig to save money.
Long hours reduce brain health. A side gig is great until you burn out.
Work ages your wallet and intellect. Overworked brains age faster and lose cognitive function.
Working longer hours can help you make extra money, but it can harm your brain.
Side hustle but don't overwork.
What you can do is as follows:
Decide what hour you are not permitted to work after.
Three hours prior to night, turn off your laptop.
Put down your phone and work.
Assign due dates to each task.
3. Location is everything!
The environment may cause brain fog. High pollution can cause brain damage.
Air pollution raises Alzheimer's risk. Air pollution causes cognitive and behavioral abnormalities.
Polluted air can trigger early development of incurable brain illnesses, not simply lung harm.
Your city's air quality is uncontrollable. You may take steps to improve air quality.
In Delhi, schools and colleges are closed to protect pupils from polluted air. So I've adapted.
What you can do is as follows:
To keep your mind healthy and young, make an investment in a high-quality air purifier.
Enclose your windows during the day.
Use a N95 mask every day.
4. Don't skip this meal.
Fasting intermittently is trendy. Delaying breakfast to finish fasting is frequent.
Some skip breakfast and have a hefty lunch instead.
Skipping breakfast might affect memory and focus. Skipping breakfast causes low cognition, delayed responsiveness, and irritation.
Breakfast affects mood and productivity.
Intermittent fasting doesn't prevent healthy breakfasts.
What you can do is as follows:
Try to fast for 14 hours, then break it with a nutritious breakfast.
So that you can have breakfast in the morning, eat dinner early.
Make sure your breakfast is heavy in fiber and protein.
5. The quickest way to damage the health of your brain
Brain health requires water. 1% dehydration can reduce cognitive ability by 5%.
Cerebral fog and mental clarity might result from 2% brain dehydration. Dehydration shrinks brain cells.
Dehydration causes midday slumps and unproductivity. Water improves work performance.
Dehydration can harm your brain, so drink water throughout the day.
What you can do is as follows:
Always keep a water bottle at your desk.
Enjoy some tasty herbal teas.
With a big glass of water, begin your day.
Bring your own water bottle when you travel.
Conclusion
Bad habits can harm brain health. Low cognition reduces focus and productivity.
Unproductive work leads to procrastination, failure, and low self-esteem.
Avoid these harmful habits to optimize brain health and function.