DAOs are legal entities in Marshall Islands.
The Pacific island state recognizes decentralized autonomous organizations.
The Republic of the Marshall Islands has recognized decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) as legal entities, giving collectively owned and managed blockchain projects global recognition.
The Marshall Islands' amended the Non-Profit Entities Act 2021 that now recognizes DAOs, which are blockchain-based entities governed by self-organizing communities. Incorporating Admiralty LLC, the island country's first DAO, was made possible thanks to the amendement. MIDAO Directory Services Inc., a domestic organization established to assist DAOs in the Marshall Islands, assisted in the incorporation.
The new law currently allows any DAO to register and operate in the Marshall Islands.
“This is a unique moment to lead,” said Bobby Muller, former Marshall Islands chief secretary and co-founder of MIDAO. He believes DAOs will help create “more efficient and less hierarchical” organizations.
A global hub for DAOs, the Marshall Islands hopes to become a global hub for DAO registration, domicile, use cases, and mass adoption. He added:
"This includes low-cost incorporation, a supportive government with internationally recognized courts, and a technologically open environment."
According to the World Bank, the Marshall Islands is an independent island state in the Pacific Ocean near the Equator. To create a blockchain-based cryptocurrency that would be legal tender alongside the US dollar, the island state has been actively exploring use cases for digital assets since at least 2018.
In February 2018, the Marshall Islands approved the creation of a new cryptocurrency, Sovereign (SOV). As expected, the IMF has criticized the plan, citing concerns that a digital sovereign currency would jeopardize the state's financial stability. They have also criticized El Salvador, the first country to recognize Bitcoin (BTC) as legal tender.
Marshall Islands senator David Paul said the DAO legislation does not pose the same issues as a government-backed cryptocurrency. “A sovereign digital currency is financial and raises concerns about money laundering,” . This is more about giving DAOs legal recognition to make their case to regulators, investors, and consumers.
More on Web3 & Crypto
CyberPunkMetalHead
3 years ago
It's all about the ego with Terra 2.0.
UST depegs and LUNA crashes 99.999% in a fraction of the time it takes the Moon to orbit the Earth.
Fat Man, a Terra whistle-blower, promises to expose Do Kwon's dirty secrets and shady deals.

The Terra community has voted to relaunch Terra LUNA on a new blockchain. The Terra 2.0 Pheonix-1 blockchain went live on May 28, 2022, and people were airdropped the new LUNA, now called LUNA, while the old LUNA became LUNA Classic.
Does LUNA deserve another chance? To answer this, or at least start a conversation about the Terra 2.0 chain's advantages and limitations, we must assess its fundamentals, ideology, and long-term vision.
Whatever the result, our analysis must be thorough and ruthless. A failure of this magnitude cannot happen again, so we must magnify every potential breaking point by 10.
Will UST and LUNA holders be compensated in full?
The obvious. First, and arguably most important, is to restore previous UST and LUNA holders' bags.
Terra 2.0 has 1,000,000,000,000 tokens to distribute.
25% of a community pool
Holders of pre-attack LUNA: 35%
10% of aUST holders prior to attack
Holders of LUNA after an attack: 10%
UST holders as of the attack: 20%
Every LUNA and UST holder has been compensated according to the above proposal.
According to self-reported data, the new chain has 210.000.000 tokens and a $1.3bn marketcap. LUNC and UST alone lost $40bn. The new token must fill this gap. Since launch:

LUNA holders collectively own $1b worth of LUNA if we subtract the 25% community pool airdrop from the current market cap and assume airdropped LUNA was never sold.
At the current supply, the chain must grow 40 times to compensate holders. At the current supply, LUNA must reach $240.
LUNA needs a full-on Bull Market to make LUNC and UST holders whole.
Who knows if you'll be whole? From the time you bought to the amount and price, there are too many variables to determine if Terra can cover individual losses.
The above distribution doesn't consider individual cases. Terra didn't solve individual cases. It would have been huge.
What does LUNA offer in terms of value?
UST's marketcap peaked at $18bn, while LUNC's was $41bn. LUNC and UST drove the Terra chain's value.

After it was confirmed (again) that algorithmic stablecoins are bad, Terra 2.0 will no longer support them.
Algorithmic stablecoins contributed greatly to Terra's growth and value proposition. Terra 2.0 has no product without algorithmic stablecoins.
Terra 2.0 has an identity crisis because it has no actual product. It's like Volkswagen faking carbon emission results and then stopping car production.
A project that has already lost the trust of its users and nearly all of its value cannot survive without a clear and in-demand use case.
Do Kwon, how about him?
Oh, the Twitter-caller-poor? Who challenges crypto billionaires to break his LUNA chain? Who dissolved Terra Labs South Korea before depeg? Arrogant guy?
That's not a good image for LUNA, especially when making amends. I think he should step down and let a nicer person be Terra 2.0's frontman.
The verdict
Terra has a terrific community with an arrogant, unlikeable leader. The new LUNA chain must grow 40 times before it can start making up its losses, and even then, not everyone's losses will be covered.
I won't invest in Terra 2.0 or other algorithmic stablecoins in the near future. I won't be near any Do Kwon-related project within 100 miles. My opinion.
Can Terra 2.0 be saved? Comment below.

Percy Bolmér
3 years ago
Ethereum No Longer Consumes A Medium-Sized Country's Electricity To Run
The Merge cut Ethereum's energy use by 99.5%.

The Crypto community celebrated on September 15, 2022. This day, Ethereum Merged. The entire blockchain successfully merged with the Beacon chain, and it was so smooth you barely noticed.
Many have waited, dreaded, and longed for this day.
Some investors feared the network would break down, while others envisioned a seamless merging.
Speculators predict a successful Merge will lead investors to Ethereum. This could boost Ethereum's popularity.
What Has Changed Since The Merge
The merging transitions Ethereum mainnet from PoW to PoS.
PoW sends a mathematical riddle to computers worldwide (miners). First miner to solve puzzle updates blockchain and is rewarded.
The puzzles sent are power-intensive to solve, so mining requires a lot of electricity. It's sent to every miner competing to solve it, requiring duplicate computation.
PoS allows investors to stake their coins to validate a new transaction. Instead of validating a whole block, you validate a transaction and get the fees.
You can validate instead of mine. A validator stakes 32 Ethereum. After staking, the validator can validate future blocks.
Once a validator validates a block, it's sent to a randomly selected group of other validators. This group verifies that a validator is not malicious and doesn't validate fake blocks.
This way, only one computer needs to solve or validate the transaction, instead of all miners. The validated block must be approved by a small group of validators, causing duplicate computation.
PoS is more secure because validating fake blocks results in slashing. You lose your bet tokens. If a validator signs a bad block or double-signs conflicting blocks, their ETH is burned.
Theoretically, Ethereum has one block every 12 seconds, so a validator forging a block risks burning 1 Ethereum for 12 seconds of transactions. This makes mistakes expensive and risky.
What Impact Does This Have On Energy Use?
Cryptocurrency is a natural calamity, sucking electricity and eating away at the earth one transaction at a time.
Many don't know the environmental impact of cryptocurrencies, yet it's tremendous.
A single Ethereum transaction used to use 200 kWh and leave a large carbon imprint. This update reduces global energy use by 0.2%.

Ethereum will submit a challenge to one validator, and that validator will forward it to randomly selected other validators who accept it.
This reduces the needed computing power.
They expect a 99.5% reduction, therefore a single transaction should cost 1 kWh.
Carbon footprint is 0.58 kgCO2, or 1,235 VISA transactions.
This is a big Ethereum blockchain update.
I love cryptocurrency and Mother Earth.
Isobel Asher Hamilton
3 years ago
$181 million in bitcoin buried in a dump. $11 million to get them back

James Howells lost 8,000 bitcoins. He has $11 million to get them back.
His life altered when he threw out an iPhone-sized hard drive.
Howells, from the city of Newport in southern Wales, had two identical laptop hard drives squirreled away in a drawer in 2013. One was blank; the other had 8,000 bitcoins, currently worth around $181 million.
He wanted to toss out the blank one, but the drive containing the Bitcoin went to the dump.
He's determined to reclaim his 2009 stash.
Howells, 36, wants to arrange a high-tech treasure hunt for bitcoins. He can't enter the landfill.

Newport's city council has rebuffed Howells' requests to dig for his hard drive for almost a decade, stating it would be expensive and environmentally destructive.
I got an early look at his $11 million idea to search 110,000 tons of trash. He expects submitting it to the council would convince it to let him recover the hard disk.
110,000 tons of trash, 1 hard drive
Finding a hard disk among heaps of trash may seem Herculean.
Former IT worker Howells claims it's possible with human sorters, robot dogs, and an AI-powered computer taught to find hard drives on a conveyor belt.
His idea has two versions, depending on how much of the landfill he can search.
His most elaborate solution would take three years and cost $11 million to sort 100,000 metric tons of waste. Scaled-down version costs $6 million and takes 18 months.
He's created a team of eight professionals in AI-powered sorting, landfill excavation, garbage management, and data extraction, including one who recovered Columbia's black box data.
The specialists and their companies would be paid a bonus if they successfully recovered the bitcoin stash.
Howells: "We're trying to commercialize this project."
Howells claimed rubbish would be dug up by machines and sorted near the landfill.
Human pickers and a Max-AI machine would sort it. The machine resembles a scanner on a conveyor belt.
Remi Le Grand of Max-AI told us it will train AI to recognize Howells-like hard drives. A robot arm would select candidates.
Howells has added security charges to his scheme because he fears people would steal the hard drive.
He's budgeted for 24-hour CCTV cameras and two robotic "Spot" canines from Boston Dynamics that would patrol at night and look for his hard drive by day.
Howells said his crew met in May at the Celtic Manor Resort outside Newport for a pitch rehearsal.
Richard Hammond's narrative swings from banal to epic.
Richard Hammond filmed the meeting and created a YouTube documentary on Howells.
Hammond said of Howells' squad, "They're committed and believe in him and the idea."
Hammond: "It goes from banal to gigantic." "If I were in his position, I wouldn't have the strength to answer the door."
Howells said trash would be cleaned and repurposed after excavation. Reburying the rest.
"We won't pollute," he declared. "We aim to make everything better."

After the project is finished, he hopes to develop a solar or wind farm on the dump site. The council is unlikely to accept his vision soon.
A council representative told us, "Mr. Howells can't convince us of anything." "His suggestions constitute a significant ecological danger, which we can't tolerate and are forbidden by our permit."
Will the recovered hard drive work?
The "platter" is a glass or metal disc that holds the hard drive's data. Howells estimates 80% to 90% of the data will be recoverable if the platter isn't damaged.
Phil Bridge, a data-recovery expert who consulted Howells, confirmed these numbers.

If the platter is broken, Bridge adds, data recovery is unlikely.
Bridge says he was intrigued by the proposal. "It's an intriguing case," he added. Helping him get it back and proving everyone incorrect would be a great success story.
Who'd pay?
Swiss and German venture investors Hanspeter Jaberg and Karl Wendeborn told us they would fund the project if Howells received council permission.
Jaberg: "It's a needle in a haystack and a high-risk investment."
Howells said he had no contract with potential backers but had discussed the proposal in Zoom meetings. "Until Newport City Council gives me something in writing, I can't commit," he added.
Suppose he finds the bitcoins.
Howells said he would keep 30% of the data, worth $54 million, if he could retrieve it.
A third would go to the recovery team, 30% to investors, and the remainder to local purposes, including gifting £50 ($61) in bitcoin to each of Newport's 150,000 citizens.
Howells said he opted to spend extra money on "professional firms" to help convince the council.
What if the council doesn't approve?
If Howells can't win the council's support, he'll sue, claiming its actions constitute a "illegal embargo" on the hard drive. "I've avoided that path because I didn't want to cause complications," he stated. I wanted to cooperate with Newport's council.
Howells never met with the council face-to-face. He mentioned he had a 20-minute Zoom meeting in May 2021 but thought his new business strategy would help.
He met with Jessica Morden on June 24. Morden's office confirmed meeting.
After telling the council about his proposal, he can only wait. "I've never been happier," he said. This is our most professional operation, with the best employees.
The "crypto proponent" buys bitcoin every month and sells it for cash.
Howells tries not to think about what he'd do with his part of the money if the hard disk is found functional. "Otherwise, you'll go mad," he added.
This post is a summary. Read the full article here.
You might also like
Sam Hickmann
3 years ago
What is this Fed interest rate everybody is talking about that makes or breaks the stock market?
The Federal Funds Rate (FFR) is the target interest rate set by the Federal Reserve System (Fed)'s policy-making body (FOMC). This target is the rate at which the Fed suggests commercial banks borrow and lend their excess reserves overnight to each other.
The FOMC meets 8 times a year to set the target FFR. This is supposed to promote economic growth. The overnight lending market sets the actual rate based on commercial banks' short-term reserves. If the market strays too far, the Fed intervenes.
Banks must keep a certain percentage of their deposits in a Federal Reserve account. A bank's reserve requirement is a percentage of its total deposits. End-of-day bank account balances averaged over two-week reserve maintenance periods are used to determine reserve requirements.
If a bank expects to have end-of-day balances above what's needed, it can lend the excess to another institution.
The FOMC adjusts interest rates based on economic indicators that show inflation, recession, or other issues that affect economic growth. Core inflation and durable goods orders are indicators.
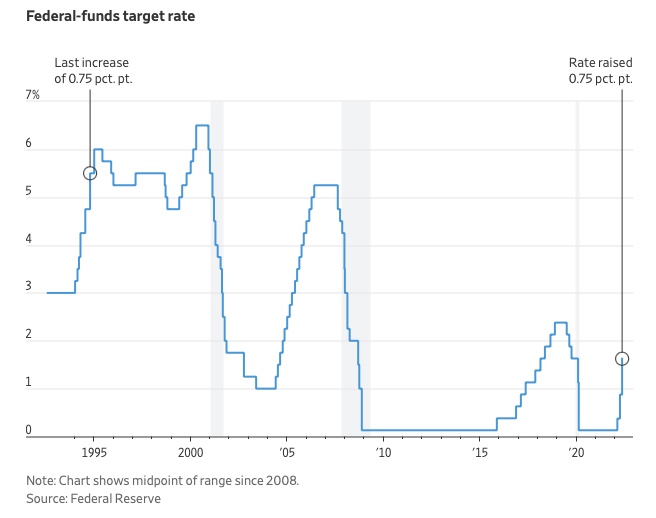
In response to economic conditions, the FFR target has changed over time. In the early 1980s, inflation pushed it to 20%. During the Great Recession of 2007-2009, the rate was slashed to 0.15 percent to encourage growth.
Inflation picked up in May 2022 despite earlier rate hikes, prompting today's 0.75 percent point increase. The largest increase since 1994. It might rise to around 3.375% this year and 3.1% by the end of 2024.

Entreprogrammer
3 years ago
The Steve Jobs Formula: A Guide to Everything
A must-read for everyone

Jobs is well-known. You probably know the tall, thin guy who wore the same clothing every day. His influence is unavoidable. In fewer than 40 years, Jobs' innovations have impacted computers, movies, cellphones, music, and communication.
Steve Jobs may be more imaginative than the typical person, but if we can use some of his ingenuity, ambition, and good traits, we'll be successful. This essay explains how to follow his guidance and success secrets.
1. Repetition is necessary for success.
Be patient and diligent to master something. Practice makes perfect. This is why older workers are often more skilled.
When should you repeat a task? When you're confident and excited to share your product. It's when to stop tweaking and repeating.
Jobs stated he'd make the crowd sh** their pants with an iChat demo.
Use this in your daily life.
Start with the end in mind. You can put it in writing and be as detailed as you like with your plan's schedule and metrics. For instance, you have a goal of selling three coffee makers in a week.
Break it down, break the goal down into particular tasks you must complete, and then repeat those tasks. To sell your coffee maker, you might need to make 50 phone calls.
Be mindful of the amount of work necessary to produce the desired results. Continue doing this until you are happy with your product.
2. Acquire the ability to add and subtract.
How did Picasso invent cubism? Pablo Picasso was influenced by stylised, non-naturalistic African masks that depict a human figure.
Artists create. Constantly seeking inspiration. They think creatively about random objects. Jobs said creativity is linking things. Creative people feel terrible when asked how they achieved something unique because they didn't do it all. They saw innovation. They had mastered connecting and synthesizing experiences.
Use this in your daily life.
On your phone, there is a note-taking app. Ideas for what you desire to learn should be written down. It may be learning a new language, calligraphy, or anything else that inspires or intrigues you.
Note any ideas you have, quotations, or any information that strikes you as important.
Spend time with smart individuals, that is the most important thing. Jim Rohn, a well-known motivational speaker, has observed that we are the average of the five people with whom we spend the most time.
Learning alone won't get you very far. You need to put what you've learnt into practice. If you don't use your knowledge and skills, they are useless.
3. Develop the ability to refuse.
Steve Jobs deleted thousands of items when he created Apple's design ethic. Saying no to distractions meant upsetting customers and partners.
John Sculley, the former CEO of Apple, said something like this. According to Sculley, Steve’s methodology differs from others as he always believed that the most critical decisions are things you choose not to do.
Use this in your daily life.
Never be afraid to say "no," "I won't," or "I don't want to." Keep it simple. This method works well in some situations.
Give a different option. For instance, X might be interested even if I won't be able to achieve it.
Control your top priority. Before saying yes to anything, make sure your work schedule and priority list are up to date.
4. Follow your passion
“Follow your passion” is the worst advice people can give you. Steve Jobs didn't start Apple because he suddenly loved computers. He wanted to help others attain their maximum potential.
Great things take a lot of work, so quitting makes sense if you're not passionate. Jobs learned from history that successful people were passionate about their work and persisted through challenges.
Use this in your daily life.
Stay away from your passion. Allow it to develop daily. Keep working at your 9-5-hour job while carefully gauging your level of desire and endurance. Less risk exists.
The truth is that if you decide to work on a project by yourself rather than in a group, it will take you years to complete it instead of a week. Instead, network with others who have interests in common.
Prepare a fallback strategy in case things go wrong.
Success, this small two-syllable word eventually gives your life meaning, a perspective. What is success? For most, it's achieving their ambitions. However, there's a catch. Successful people aren't always happy.
Furthermore, where do people’s goals and achievements end? It’s a never-ending process. Success is a journey, not a destination. We wish you not to lose your way on this journey.

Jussi Luukkonen, MBA
3 years ago
Is Apple Secretly Building A Disruptive Tsunami?
A TECHNICAL THOUGHT
The IT giant is seeding the digital Great Renaissance.

Recently, technology has been dull.
We're still fascinated by processing speeds. Wearables are no longer an engineer's dream.
Apple has been quiet and avoided huge announcements. Slowness speaks something. Everything in the spaceship HQ seems to be turning slowly, unlike competitors around buzzwords.
Is this a sign of the impending storm?
Metas stock has fallen while Google milks dumb people. Microsoft steals money from corporations and annexes platforms like Linkedin.
Just surface bubbles?
Is Apple, one of the technology continents, pushing against all others to create a paradigm shift?
The fundamental human right to privacy
Apple's unusual remarks emphasize privacy. They incorporate it into their business models and judgments.
Apple believes privacy is a human right. There are no compromises.
This makes it hard for other participants to gain Apple's ecosystem's efficiencies.
Other players without hardware platforms lose.
Apple delivers new kidneys without rejection, unlike other software vendors. Nothing compromises your privacy.
Corporate citizenship will become more popular.
Apples have full coffers. They've started using that flow to better communities, which is great.
Apple's $2.5B home investment is one example. Google and Facebook are building or proposing to build workforce housing.
Apple's funding helps marginalized populations in more than 25 California counties, not just Apple employees.
Is this a trend, and does Apple keep giving back? Hope so.
I'm not cynical enough to suspect these investments have malicious motives.
The last frontier is the environment.
Climate change is a battle-to-win.
Long-term winners will be companies that protect the environment, turning climate change dystopia into sustainable growth.
Apple has been quietly changing its supply chain to be carbon-neutral by 2030.
“Apple is dedicated to protecting the planet we all share with solutions that are supporting the communities where we work.” Lisa Jackson, Apple’s vice president of environment.
Apple's $4.7 billion Green Bond investment will produce 1.2 gigawatts of green energy for the corporation and US communities. Apple invests $2.2 billion in Europe's green energy. In the Philippines, Thailand, Nigeria, Vietnam, Colombia, Israel, and South Africa, solar installations are helping communities obtain sustainable energy.
Apple is already carbon neutral today for its global corporate operations, and this new commitment means that by 2030, every Apple device sold will have net zero climate impact. -Apple.
Apple invests in green energy and forests to reduce its paper footprint in China and the US. Apple and the Conservation Fund are safeguarding 36,000 acres of US working forest, according to GreenBiz.
Apple's packaging paper is recycled or from sustainably managed forests.
What matters is the scale.
$1 billion is a rounding error for Apple.
These small investments originate from a tree with deep, spreading roots.
Apple's genes are anchored in building the finest products possible to improve consumers' lives.
I felt it when I switched to my iPhone while waiting for a train and had to pack my Macbook. iOS 16 dictation makes writing more enjoyable. Small change boosts productivity. Smooth transition from laptop to small screen and dictation.
Apples' tiny, well-planned steps have great growth potential for all consumers in everything they do.
There is clearly disruption, but it doesn't have to be violent
Digital channels, methods, and technologies have globalized human consciousness. One person's responsibility affects many.
Apple gives us tools to be privately connected. These technologies foster creativity, innovation, fulfillment, and safety.
Apple has invented a mountain of technologies, services, and channels to assist us adapt to the good future or combat evil forces who cynically aim to control us and ruin the environment and communities. Apple has quietly disrupted sectors for decades.
Google, Microsoft, and Meta, among others, should ride this wave. It's a tsunami, but it doesn't have to be devastating if we care, share, and cooperate with political decision-makers and community leaders worldwide.
A fresh Renaissance
Renaissance geniuses Michelangelo and Da Vinci. Different but seeing something no one else could yet see. Both were talented in many areas and could discover art in science and science in art.
These geniuses exemplified a period that changed humanity for the better. They created, used, and applied new, valuable things. It lives on.
Apple is a digital genius orchard. Wozniak and Jobs offered us fertile ground for the digital renaissance. We'll build on their legacy.
We may put our seeds there and see them bloom despite corporate greed and political ignorance.
I think the coming tsunami will illuminate our planet like the Renaissance.
