More on Leadership

Sean Bloomfield
3 years ago
How Jeff Bezos wins meetings over

We've all been there: You propose a suggestion to your team at a meeting, and most people appear on board, but a handful or small minority aren't. How can we achieve collective buy-in when we need to go forward but don't know how to deal with some team members' perceived intransigence?
Steps:
Investigate the divergent opinions: Begin by sincerely attempting to comprehend the viewpoint of your disagreeing coworkers. Maybe it makes sense to switch horses in the middle of the race. Have you completely overlooked a blind spot, such as a political concern that could arise as an unexpected result of proceeding? This is crucial to ensure that the person or people feel heard as well as to advance the goals of the team. Sometimes all individuals need is a little affirmation before they fully accept your point of view.
It says a lot about you as a leader to be someone who always lets the perceived greatest idea win, regardless of the originating channel, if after studying and evaluating you see the necessity to align with the divergent position.
If, after investigation and assessment, you determine that you must adhere to the original strategy, we go to Step 2.
2. Disagree and Commit: Jeff Bezos, CEO of Amazon, has had this experience, and Julie Zhuo describes how he handles it in her book The Making of a Manager.
It's OK to disagree when the team is moving in the right direction, but it's not OK to accidentally or purposefully damage the team's efforts because you disagree. Let the team know your opinion, but then help them achieve company goals even if they disagree. Unknown. You could be wrong in today's ever-changing environment.
So next time you have a team member who seems to be dissenting and you've tried the previous tactics, you may ask the individual in the meeting I understand you but I don't want us to leave without you on board I need your permission to commit to this approach would you give us your commitment?

Jano le Roux
3 years ago
Quit worrying about Twitter: Elon moves quickly before refining
Elon's rides start rough, but then...

Elon Musk has never been so hated.
They don’t get Elon.
He began using PayPal in this manner.
He began with SpaceX in a similar manner.
He began with Tesla in this manner.
Disruptive.
Elon had rocky starts. His creativity requires it. Just like writing a first draft.
His fastest way to find the way is to avoid it.
PayPal's pricey launch
PayPal was a 1999 business flop.
They were considered insane.
Elon and his co-founders had big plans for PayPal. They adopted the popular philosophy of the time, exchanging short-term profit for growth, and pulled off a miracle just before the bubble burst.
PayPal was created as a dollar alternative. Original PayPal software allowed PalmPilot money transfers. Unfortunately, there weren't enough PalmPilot users.
Since everyone had email, the company emailed payments. Costs rose faster than sales.
The startup wanted to get a million subscribers by paying $10 to sign up and $10 for each referral. Elon thought the price was fair because PayPal made money by charging transaction fees. They needed to make money quickly.
A Wall Street Journal article valuing PayPal at $500 million attracted investors. The dot-com bubble burst soon after they rushed to get financing.
Musk and his partners sold PayPal to eBay for $1.5 billion in 2002. Musk's most successful company was PayPal.
SpaceX's start-up error
Elon and his friends bought a reconditioned ICBM in Russia in 2002.
He planned to invest much of his wealth in a stunt to promote NASA and space travel.
Many called Elon crazy.
The goal was to buy a cheap Russian rocket to launch mice or plants to Mars and return them. He thought SpaceX would revive global space interest. After a bad meeting in Moscow, Elon decided to build his own rockets to undercut launch contracts.
Then SpaceX was founded.
Elon’s plan was harder than expected.
Explosions followed explosions.
Millions lost on cargo.
Millions lost on the rockets.
Investors thought Elon was crazy, but he wasn't.
NASA's biggest competitor became SpaceX. NASA hired SpaceX to handle many of its missions.
Tesla's shaky beginning
Tesla began shakily.
Clients detested their roadster.
They continued to miss deadlines.
Lotus would handle the car while Tesla focused on the EV component, easing Tesla's entry. The business experienced elegance creep. Modifying specific parts kept the car from getting worse.
Cost overruns, delays, and other factors changed the Elise-like car's appearance. Only 7% of the Tesla Roadster's parts matched its Lotus twin.
Tesla was about to die.
Elon saved the mess as CEO.
He fired 25% of the workforce to reduce costs.
Elon Musk transformed Tesla into the world's most valuable automaker by running it like a startup.
Tesla hasn't spent a dime on advertising. They let the media do the talking by investing in innovation.
Elon sheds. Elon tries. Elon learns. Elon refines.
Twitter doesn't worry me.
The media is shocked. I’m not.
This is just Elon being Elon.
Elon makes lean.
Elon tries new things.
Elon listens to feedback.
Elon refines.
Besides Twitter will always be Twitter.

Joseph Mavericks
3 years ago
5 books my CEO read to make $30M
Offices without books are like bodies without souls.

After 10 years, my CEO sold his company for $30 million. I've shared many of his lessons on medium. You could ask him anything at his always-open office. He also said we could use his office for meetings while he was away. When I used his office for work, I was always struck by how many books he had.
Books are useful in almost every aspect of learning. Building a business, improving family relationships, learning a new language, a new skill... Books teach, guide, and structure. Whether fiction or nonfiction, books inspire, give ideas, and develop critical thinking skills.
My CEO prefers non-fiction and attends a Friday book club. This article discusses 5 books I found in his office that impacted my life/business. My CEO sold his company for $30 million, but I've built a steady business through blogging and video making.
I recall events and lessons I learned from my CEO and how they relate to each book, and I explain how I applied the book's lessons to my business and life.
Note: This post has no affiliate links.
1. The One Thing — Gary Keller

Gary Keller, a real estate agent, wanted more customers. So he and his team brainstormed ways to get more customers. They decided to write a bestseller about work and productivity. The more people who saw the book, the more customers they'd get.
Gary Keller focused on writing the best book on productivity, work, and efficiency for months. His business experience. Keller's business grew after the book's release.
The author summarizes the book in one question.
"What's the one thing that will make everything else easier or unnecessary?"
When I started my blog and business alongside my 9–5, I quickly identified my one thing: writing. My business relied on it, so it had to be great. Without writing, there was no content, traffic, or business.
My CEO focused on funding when he started his business. Even in his final years, he spent a lot of time on the phone with investors, either to get more money or to explain what he was doing with it. My CEO's top concern was money, and the other super important factors were handled by separate teams.
Product tech and design
Incredible customer support team
Excellent promotion team
Profitable sales team
My CEO didn't always focus on one thing and ignore the rest. He was on all of those teams when I started my job. He'd start his day in tech, have lunch with marketing, and then work in sales. He was in his office on the phone at night.
He eventually realized his errors. Investors told him he couldn't do everything for the company. If needed, he had to change internally. He learned to let go, mind his own business, and focus for the next four years. Then he sold for $30 million.
The bigger your project/company/idea, the more you'll need to delegate to stay laser-focused. I started something new every few months for 10 years before realizing this. So much to do makes it easy to avoid progress. Once you identify the most important aspect of your project and enlist others' help, you'll be successful.
2. Eat That Frog — Brian Tracy

The author quote sums up book's essence:
Mark Twain said that if you eat a live frog in the morning, it's probably the worst thing that will happen to you all day. Your "frog" is the biggest, most important task you're most likely to procrastinate on.
"Frog" and "One Thing" are both about focusing on what's most important. Eat That Frog recommends doing the most important task first thing in the morning.
I shared my CEO's calendar in an article 10 months ago. Like this:

CEO's average week (some information crossed out for confidentiality)
Notice anything about 8am-8:45am? Almost every day is the same (except Friday). My CEO started his day with a management check-in for 2 reasons:
Checking in with all managers is cognitively demanding, and my CEO is a morning person.
In a young startup where everyone is busy, the morning management check-in was crucial. After 10 am, you couldn't gather all managers.
When I started my blog, writing was my passion. I'm a morning person, so I woke up at 6 am and started writing by 6:30 am every day for a year. This allowed me to publish 3 articles a week for 52 weeks to build my blog and audience. After 2 years, I'm not stopping.
3. Deep Work — Cal Newport

Deep work is focusing on a cognitively demanding task without distractions (like a morning management meeting). It helps you master complex information quickly and produce better results faster. In a competitive world 10 or 20 years ago, focus wasn't a huge advantage. Smartphones, emails, and social media made focus a rare, valuable skill.
Most people can't focus anymore. Screens light up, notifications buzz, emails arrive, Instagram feeds... Many people don't realize they're interrupted because it's become part of their normal workflow.
Cal Newport mentions Bill Gates' "Think Weeks" in Deep Work.
Microsoft CEO Bill Gates would isolate himself (often in a lakeside cottage) twice a year to read and think big thoughts.
Inside Bill's Brain on Netflix shows Newport's lakeside cottage. I've always wanted a lakeside cabin to work in. My CEO bought a lakehouse after selling his company, but now he's retired.
As a company grows, you can focus less on it. In a previous section, I said investors told my CEO to get back to basics and stop micromanaging. My CEO's commitment and ability to get work done helped save the company. His deep work and new frameworks helped us survive the corona crisis (more on this later).
The ability to deep work will be a huge competitive advantage in the next century. Those who learn to work deeply will likely be successful while everyone else is glued to their screens, Bluetooth-synced to their watches, and playing Candy Crush on their tablets.
4. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People — Stephen R. Covey

It took me a while to start reading this book because it seemed like another shallow self-help bible. I kept finding this book when researching self-improvement. I tried it because it was everywhere.
Stephen Covey taught me 2 years ago to have a personal mission statement.
A 7 Habits mission statement describes the life you want to lead, the character traits you want to embody, and the impact you want to have on others. shortform.com
I've had many lunches with my CEO and talked about Vipassana meditation and Sunday forest runs, but I've never seen his mission statement. I'm sure his family is important, though. In the above calendar screenshot, you can see he always included family events (in green) so we could all see those time slots. We couldn't book him then. Although he never spent as much time with his family as he wanted, he always made sure to be on time for his kid's birthday rather than a conference call.
My CEO emphasized his company's mission. Your mission statement should answer 3 questions.
What does your company do?
How does it do it?
Why does your company do it?
As a graphic designer, I had to create mission-statement posters. My CEO hung posters in each office.
5. Measure What Matters — John Doerr

This book is about Andrew Grove's OKR strategy, developed in 1968. When he joined Google's early investors board, he introduced it to Larry Page and Sergey Brin. Google still uses OKR.
Objective Key Results
Objective: It explains your goals and desired outcome. When one goal is reached, another replaces it. OKR objectives aren't technical, measured, or numerical. They must be clear.
Key Result should be precise, technical, and measurable, unlike the Objective. It shows if the Goal is being worked on. Time-bound results are quarterly or yearly.
Our company almost sank several times. Sales goals were missed, management failed, and bad decisions were made. On a Monday, our CEO announced we'd implement OKR to revamp our processes.
This was a year before the pandemic, and I'm certain we wouldn't have sold millions or survived without this change. This book impacted the company the most, not just management but all levels. Organization and transparency improved. We reached realistic goals. Happy investors. We used the online tool Gtmhub to implement OKR across the organization.
My CEO's company went from near bankruptcy to being acquired for $30 million in 2 years after implementing OKR.
I hope you enjoyed this booklist. Here's a recap of the 5 books and the lessons I learned from each.
The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People — Stephen R. Covey
Have a mission statement that outlines your goals, character traits, and impact on others.
Deep Work — Cal Newport
Focus is a rare skill; master it. Deep workers will succeed in our hyper-connected, distracted world.
The One Thing — Gary Keller
What can you do that will make everything else easier or unnecessary? Once you've identified it, focus on it.
Eat That Frog — Brian Tracy
Identify your most important task the night before and do it first thing in the morning. You'll have a lighter day.
Measure What Matters — John Doerr
On a timeline, divide each long-term goal into chunks. Divide those slices into daily tasks (your goals). Time-bound results are quarterly or yearly. Objectives aren't measured or numbered.
Thanks for reading. Enjoy the ride!
You might also like
Wayne Duggan
3 years ago
What An Inverted Yield Curve Means For Investors
The yield spread between 10-year and 2-year US Treasury bonds has fallen below 0.2 percent, its lowest level since March 2020. A flattening or negative yield curve can be a bad sign for the economy.
What Is An Inverted Yield Curve?
In the yield curve, bonds of equal credit quality but different maturities are plotted. The most commonly used yield curve for US investors is a plot of 2-year and 10-year Treasury yields, which have yet to invert.
A typical yield curve has higher interest rates for future maturities. In a flat yield curve, short-term and long-term yields are similar. Inverted yield curves occur when short-term yields exceed long-term yields. Inversions of yield curves have historically occurred during recessions.
Inverted yield curves have preceded each of the past eight US recessions. The good news is they're far leading indicators, meaning a recession is likely not imminent.
Every US recession since 1955 has occurred between six and 24 months after an inversion of the two-year and 10-year Treasury yield curves, according to the San Francisco Fed. So, six months before COVID-19, the yield curve inverted in August 2019.
Looking Ahead
The spread between two-year and 10-year Treasury yields was 0.18 percent on Tuesday, the smallest since before the last US recession. If the graph above continues, a two-year/10-year yield curve inversion could occur within the next few months.
According to Bank of America analyst Stephen Suttmeier, the S&P 500 typically peaks six to seven months after the 2s-10s yield curve inverts, and the US economy enters recession six to seven months later.
Investors appear unconcerned about the flattening yield curve. This is in contrast to the iShares 20+ Year Treasury Bond ETF TLT +2.19% which was down 1% on Tuesday.
Inversion of the yield curve and rising interest rates have historically harmed stocks. Recessions in the US have historically coincided with or followed the end of a Federal Reserve rate hike cycle, not the start.

Max Chafkin
3 years ago
Elon Musk Bets $44 Billion on Free Speech's Future
Musk’s purchase of Twitter has sealed his bond with the American right—whether the platform’s left-leaning employees and users like it or not.
Elon Musk's pursuit of Twitter Inc. began earlier this month as a joke. It started slowly, then spiraled out of control, culminating on April 25 with the world's richest man agreeing to spend $44 billion on one of the most politically significant technology companies ever. There have been bigger financial acquisitions, but Twitter's significance has always outpaced its balance sheet. This is a unique Silicon Valley deal.
To recap: Musk announced in early April that he had bought a stake in Twitter, citing the company's alleged suppression of free speech. His complaints were vague, relying heavily on the dog whistles of the ultra-right. A week later, he announced he'd buy the company for $54.20 per share, four days after initially pledging to join Twitter's board. Twitter's directors noticed the 420 reference as well, and responded with a “shareholder rights” plan (i.e., a poison pill) that included a 420 joke.
Musk - Patrick Pleul/Getty Images
No one knew if the bid was genuine. Musk's Twitter plans seemed implausible or insincere. In a tweet, he referred to automated accounts that use his name to promote cryptocurrency. He enraged his prospective employees by suggesting that Twitter's San Francisco headquarters be turned into a homeless shelter, renaming the company Titter, and expressing solidarity with his growing conservative fan base. “The woke mind virus is making Netflix unwatchable,” he tweeted on April 19.
But Musk got funding, and after a frantic weekend of negotiations, Twitter said yes. Unlike most buyouts, Musk will personally fund the deal, putting up up to $21 billion in cash and borrowing another $12.5 billion against his Tesla stock.
Free Speech and Partisanship
Percentage of respondents who agree with the following
The deal is expected to replatform accounts that were banned by Twitter for harassing others, spreading misinformation, or inciting violence, such as former President Donald Trump's account. As a result, Musk is at odds with his own left-leaning employees, users, and advertisers, who would prefer more content moderation rather than less.
Dorsey - Photographer: Joe Raedle/Getty Images
Previously, the company's leadership had similar issues. Founder Jack Dorsey stepped down last year amid concerns about slowing growth and product development, as well as his dual role as CEO of payments processor Block Inc. Compared to Musk, a father of seven who already runs four companies (besides Tesla and SpaceX), Dorsey is laser-focused.
Musk's motivation to buy Twitter may be political. Affirming the American far right with $44 billion spent on “free speech” Right-wing activists have promoted a series of competing upstart Twitter competitors—Parler, Gettr, and Trump's own effort, Truth Social—since Trump was banned from major social media platforms for encouraging rioters at the US Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021. But Musk can give them a social network with lax content moderation and a real user base. Trump said he wouldn't return to Twitter after the deal was announced, but he wouldn't be the first to do so.
Trump - Eli Hiller/Bloomberg
Conservative activists and lawmakers are already ecstatic. “A great day for free speech in America,” said Missouri Republican Josh Hawley. The day the deal was announced, Tucker Carlson opened his nightly Fox show with a 10-minute laudatory monologue. “The single biggest political development since Donald Trump's election in 2016,” he gushed over Musk.
But Musk's supporters and detractors misunderstand how much his business interests influence his political ideology. He marketed Tesla's cars as carbon-saving machines that were faster and cooler than gas-powered luxury cars during George W. Bush's presidency. Musk gained a huge following among wealthy environmentalists who reserved hundreds of thousands of Tesla sedans years before they were made during Barack Obama's presidency. Musk in the Trump era advocated for a carbon tax, but he also fought local officials (and his own workers) over Covid rules that slowed the reopening of his Bay Area factory.
Teslas at the Las Vegas Convention Center Loop Central Station in April 2021. The Las Vegas Convention Center Loop was Musk's first commercial project. Ethan Miller/Getty Images
Musk's rightward shift matched the rise of the nationalist-populist right and the desire to serve a growing EV market. In 2019, he unveiled the Cybertruck, a Tesla pickup, and in 2018, he announced plans to manufacture it at a new plant outside Austin. In 2021, he decided to move Tesla's headquarters there, citing California's "land of over-regulation." After Ford and General Motors beat him to the electric truck market, Musk reframed Tesla as a company for pickup-driving dudes.
Similarly, his purchase of Twitter will be entwined with his other business interests. Tesla has a factory in China and is friendly with Beijing. This could be seen as a conflict of interest when Musk's Twitter decides how to treat Chinese-backed disinformation, as Amazon.com Inc. founder Jeff Bezos noted.
Musk has focused on Twitter's product and social impact, but the company's biggest challenges are financial: Either increase cash flow or cut costs to comfortably service his new debt. Even if Musk can't do that, he can still benefit from the deal. He has recently used the increased attention to promote other business interests: Boring has hyperloops and Neuralink brain implants on the way, Musk tweeted. Remember Tesla's long-promised robotaxis!
Musk may be comfortable saying he has no expectation of profit because it benefits his other businesses. At the TED conference on April 14, Musk insisted that his interest in Twitter was solely charitable. “I don't care about money.”
The rockets and weed jokes make it easy to see Musk as unique—and his crazy buyout will undoubtedly add to that narrative. However, he is a megabillionaire who is risking a small amount of money (approximately 13% of his net worth) to gain potentially enormous influence. Musk makes everything seem new, but this is a rehash of an old media story.

Joseph Mavericks
3 years ago
The world's 36th richest man uses a 5-step system to get what he wants.
Ray Dalio's super-effective roadmap

Ray Dalio's $22 billion net worth ranks him 36th globally. From 1975 to 2011, he built the world's most successful hedge fund, never losing more than 4% from 1991 to 2020. (and only doing so during 3 calendar years).
Dalio describes a 5-step process in his best-selling book Principles. It's the playbook he's used to build his hedge fund, beat the markets, and face personal challenges.
This 5-step system is so valuable and well-explained that I didn't edit or change anything; I only added my own insights in the parts I found most relevant and/or relatable as a young entrepreneur. The system's overview:
Have clear goals
Identify and don’t tolerate problems
Diagnose problems to get at their root causes
Design plans that will get you around those problems
Do what is necessary to push through the plans to get results
If you follow these 5 steps in a virtuous loop, you'll almost always see results. Repeat the process for each goal you have.
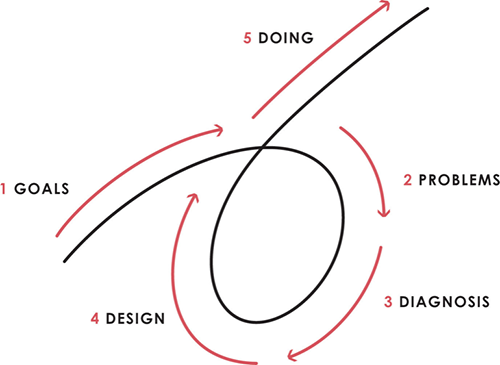
1. Have clear goals
a) Prioritize: You can have almost anything, but not everything.
I started and never launched dozens of projects for 10 years because I was scattered. I opened a t-shirt store, traded algorithms, sold art on Instagram, painted skateboards, and tinkered with electronics. I decided to try blogging for 6 months to see where it took me. Still going after 3 years.
b) Don’t confuse goals with desires.
A goal inspires you to act. Unreasonable desires prevent you from achieving your goals.
c) Reconcile your goals and desires to decide what you want.
d) Don't confuse success with its trappings.
e) Never dismiss a goal as unattainable.
Always one path is best. Your perception of what's possible depends on what you know now. I never thought I'd make money writing online so quickly, and now I see a whole new horizon of business opportunities I didn't know about before.
f) Expectations create abilities.
Don't limit your abilities. More you strive, the more you'll achieve.
g) Flexibility and self-accountability can almost guarantee success.
Flexible people accept what reality or others teach them. Self-accountability is the ability to recognize your mistakes and be more creative, flexible, and determined.
h) Handling setbacks well is as important as moving forward.
Learn when to minimize losses and when to let go and move on.
2. Don't ignore problems
a) See painful problems as improvement opportunities.
Every problem, painful situation, and challenge is an opportunity. Read The Art of Happiness for more.
b) Don't avoid problems because of harsh realities.
Recognizing your weaknesses isn't the same as giving in. It's the first step in overcoming them.
c) Specify your issues.
There is no "one-size-fits-all" solution.
d) Don’t mistake a cause of a problem with the real problem.
"I can't sleep" is a cause, not a problem. "I'm underperforming" could be a problem.
e) Separate big from small problems.
You have limited time and energy, so focus on the biggest problems.
f) Don't ignore a problem.
Identifying a problem and tolerating it is like not identifying it.
3. Identify problems' root causes
a) Decide "what to do" after assessing "what is."
"A good diagnosis takes 15 to 60 minutes, depending on its accuracy and complexity. [...] Like principles, root causes recur in different situations.
b) Separate proximate and root causes.
"You can only solve problems by removing their root causes, and to do that, you must distinguish symptoms from disease."
c) Knowing someone's (or your own) personality can help you predict their behavior.
4. Design plans that will get you around the problems
a) Retrace your steps.
Analyze your past to determine your future.
b) Consider your problem a machine's output.
Consider how to improve your machine. It's a game then.
c) There are many ways to reach your goals.
Find a solution.
d) Visualize who will do what in your plan like a movie script.
Consider your movie's actors and script's turning points, then act accordingly. The game continues.
e) Document your plan so others can judge your progress.
Accountability boosts success.
f) Know that a good plan doesn't take much time.
The execution is usually the hardest part, but most people either don't have a plan or keep changing it. Don't drive while building the car. Build it first, because it'll be bumpy.
5. Do what is necessary to push through the plans to get results
a) Great planners without execution fail.
Life is won with more than just planning. Similarly, practice without talent beats talent without practice.
b) Work ethic is undervalued.
Hyper-productivity is praised in corporate America, even if it leads nowhere. To get things done, use checklists, fewer emails, and more desk time.
c) Set clear metrics to ensure plan adherence.
I've written about the OKR strategy for organizations with multiple people here. If you're on your own, I recommend the Wheel of Life approach. Both systems start with goals and tasks to achieve them. Then start executing on a realistic timeline.
If you find solutions, weaknesses don't matter.
Everyone's weak. You, me, Gates, Dalio, even Musk. Nobody will be great at all 5 steps of the system because no one can think in all the ways required. Some are good at analyzing and diagnosing but bad at executing. Some are good planners but poor communicators. Others lack self-discipline.
Stay humble and ask for help when needed. Nobody has ever succeeded 100% on their own, without anyone else's help. That's the paradox of individual success: teamwork is the only way to get there.
Most people won't have the skills to execute even the best plan. You can get missing skills in two ways:
Self-taught (time-consuming)
Others' (requires humility) light
On knowing what to do with your life
“Some people have good mental maps and know what to do on their own. Maybe they learned them or were blessed with common sense. They have more answers than others. Others are more humble and open-minded. […] Open-mindedness and mental maps are most powerful.” — Ray Dalio
I've always known what I wanted to do, so I'm lucky. I'm almost 30 and have always had trouble executing. Good thing I never stopped experimenting, but I never committed to anything long-term. I jumped between projects. I decided 3 years ago to stick to one project for at least 6 months and haven't looked back.
Maybe you're good at staying focused and executing, but you don't know what to do. Maybe you have none of these because you haven't found your purpose. Always try new projects and talk to as many people as possible. It will give you inspiration and ideas and set you up for success.
There is almost always a way to achieve a crazy goal or idea.
Enjoy the journey, whichever path you take.
