The latest “bubble indicator” readings.
As you know, I like to turn my intuition into decision rules (principles) that can be back-tested and automated to create a portfolio of alpha bets. I use one for bubbles. Having seen many bubbles in my 50+ years of investing, I described what makes a bubble and how to identify them in markets—not just stocks.
A bubble market has a high degree of the following:
- High prices compared to traditional values (e.g., by taking the present value of their cash flows for the duration of the asset and comparing it with their interest rates).
- Conditons incompatible with long-term growth (e.g., extrapolating past revenue and earnings growth rates late in the cycle).
- Many new and inexperienced buyers were drawn in by the perceived hot market.
- Broad bullish sentiment.
- Debt financing a large portion of purchases.
- Lots of forward and speculative purchases to profit from price rises (e.g., inventories that are more than needed, contracted forward purchases, etc.).
I use these criteria to assess all markets for bubbles. I have periodically shown you these for stocks and the stock market.
What Was Shown in January Versus Now
I will first describe the picture in words, then show it in charts, and compare it to the last update in January.
As of January, the bubble indicator showed that a) the US equity market was in a moderate bubble, but not an extreme one (ie., 70 percent of way toward the highest bubble, which occurred in the late 1990s and late 1920s), and b) the emerging tech companies (ie. As well, the unprecedented flood of liquidity post-COVID financed other bubbly behavior (e.g. SPACs, IPO boom, big pickup in options activity), making things bubbly. I showed which stocks were in bubbles and created an index of those stocks, which I call “bubble stocks.”
Those bubble stocks have popped. They fell by a third last year, while the S&P 500 remained flat. In light of these and other market developments, it is not necessarily true that now is a good time to buy emerging tech stocks.
The fact that they aren't at a bubble extreme doesn't mean they are safe or that it's a good time to get long. Our metrics still show that US stocks are overvalued. Once popped, bubbles tend to overcorrect to the downside rather than settle at “normal” prices.
The following charts paint the picture. The first shows the US equity market bubble gauge/indicator going back to 1900, currently at the 40% percentile. The charts also zoom in on the gauge in recent years, as well as the late 1920s and late 1990s bubbles (during both of these cases the gauge reached 100 percent ).
The chart below depicts the average bubble gauge for the most bubbly companies in 2020. Those readings are down significantly.
The charts below compare the performance of a basket of emerging tech bubble stocks to the S&P 500. Prices have fallen noticeably, giving up most of their post-COVID gains.
The following charts show the price action of the bubble slice today and in the 1920s and 1990s. These charts show the same market dynamics and two key indicators. These are just two examples of how a lot of debt financing stock ownership coupled with a tightening typically leads to a bubble popping.
Everything driving the bubbles in this market segment is classic—the same drivers that drove the 1920s bubble and the 1990s bubble. For instance, in the last couple months, it was how tightening can act to prick the bubble. Review this case study of the 1920s stock bubble (starting on page 49) from my book Principles for Navigating Big Debt Crises to grasp these dynamics.
The following charts show the components of the US stock market bubble gauge. Since this is a proprietary indicator, I will only show you some of the sub-aggregate readings and some indicators.
Each of these six influences is measured using a number of stats. This is how I approach the stock market. These gauges are combined into aggregate indices by security and then for the market as a whole. The table below shows the current readings of these US equity market indicators. It compares current conditions for US equities to historical conditions. These readings suggest that we’re out of a bubble.
1. How High Are Prices Relatively?
This price gauge for US equities is currently around the 50th percentile.
2. Is price reduction unsustainable?
This measure calculates the earnings growth rate required to outperform bonds. This is calculated by adding up the readings of individual securities. This indicator is currently near the 60th percentile for the overall market, higher than some of our other readings. Profit growth discounted in stocks remains high.
Even more so in the US software sector. Analysts' earnings growth expectations for this sector have slowed, but remain high historically. P/Es have reversed COVID gains but remain high historical.
3. How many new buyers (i.e., non-existing buyers) entered the market?
Expansion of new entrants is often indicative of a bubble. According to historical accounts, this was true in the 1990s equity bubble and the 1929 bubble (though our data for this and other gauges doesn't go back that far). A flood of new retail investors into popular stocks, which by other measures appeared to be in a bubble, pushed this gauge above the 90% mark in 2020. The pace of retail activity in the markets has recently slowed to pre-COVID levels.
4. How Broadly Bullish Is Sentiment?
The more people who have invested, the less resources they have to keep investing, and the more likely they are to sell. Market sentiment is now significantly negative.
5. Are Purchases Being Financed by High Leverage?
Leveraged purchases weaken the buying foundation and expose it to forced selling in a downturn. The leverage gauge, which considers option positions as a form of leverage, is now around the 50% mark.
6. To What Extent Have Buyers Made Exceptionally Extended Forward Purchases?
Looking at future purchases can help assess whether expectations have become overly optimistic. This indicator is particularly useful in commodity and real estate markets, where forward purchases are most obvious. In the equity markets, I look at indicators like capital expenditure, or how much businesses (and governments) invest in infrastructure, factories, etc. It reflects whether businesses are projecting future demand growth. Like other gauges, this one is at the 40th percentile.
What one does with it is a tactical choice. While the reversal has been significant, future earnings discounting remains high historically. In either case, bubbles tend to overcorrect (sell off more than the fundamentals suggest) rather than simply deflate. But I wanted to share these updated readings with you in light of recent market activity.
More on Economics & Investing
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Adam Hayes
3 years ago
Bernard Lawrence "Bernie" Madoff, the largest Ponzi scheme in history
Madoff who?
Bernie Madoff ran the largest Ponzi scheme in history, defrauding thousands of investors over at least 17 years, and possibly longer. He pioneered electronic trading and chaired Nasdaq in the 1990s. On April 14, 2021, he died while serving a 150-year sentence for money laundering, securities fraud, and other crimes.
Understanding Madoff
Madoff claimed to generate large, steady returns through a trading strategy called split-strike conversion, but he simply deposited client funds into a single bank account and paid out existing clients. He funded redemptions by attracting new investors and their capital, but the market crashed in late 2008. He confessed to his sons, who worked at his firm, on Dec. 10, 2008. Next day, they turned him in. The fund reported $64.8 billion in client assets.
Madoff pleaded guilty to 11 federal felony counts, including securities fraud, wire fraud, mail fraud, perjury, and money laundering. Ponzi scheme became a symbol of Wall Street's greed and dishonesty before the financial crisis. Madoff was sentenced to 150 years in prison and ordered to forfeit $170 billion, but no other Wall Street figures faced legal ramifications.
Bernie Madoff's Brief Biography
Bernie Madoff was born in Queens, New York, on April 29, 1938. He began dating Ruth (née Alpern) when they were teenagers. Madoff told a journalist by phone from prison that his father's sporting goods store went bankrupt during the Korean War: "You watch your father, who you idolize, build a big business and then lose everything." Madoff was determined to achieve "lasting success" like his father "whatever it took," but his career had ups and downs.
Early Madoff investments
At 22, he started Bernard L. Madoff Investment Securities LLC. First, he traded penny stocks with $5,000 he earned installing sprinklers and as a lifeguard. Family and friends soon invested with him. Madoff's bets soured after the "Kennedy Slide" in 1962, and his father-in-law had to bail him out.
Madoff felt he wasn't part of the Wall Street in-crowd. "We weren't NYSE members," he told Fishman. "It's obvious." According to Madoff, he was a scrappy market maker. "I was happy to take the crumbs," he told Fishman, citing a client who wanted to sell eight bonds; a bigger firm would turn it down.
Recognition
Success came when he and his brother Peter built electronic trading capabilities, or "artificial intelligence," that attracted massive order flow and provided market insights. "I had all these major banks coming down, entertaining me," Madoff told Fishman. "It was mind-bending."
By the late 1980s, he and four other Wall Street mainstays processed half of the NYSE's order flow. Controversially, he paid for much of it, and by the late 1980s, Madoff was making in the vicinity of $100 million a year. He was Nasdaq chairman from 1990 to 1993.
Madoff's Ponzi scheme
It is not certain exactly when Madoff's Ponzi scheme began. He testified in court that it began in 1991, but his account manager, Frank DiPascali, had been at the firm since 1975.
Why Madoff did the scheme is unclear. "I had enough money to support my family's lifestyle. "I don't know why," he told Fishman." Madoff could have won Wall Street's respect as a market maker and electronic trading pioneer.
Madoff told Fishman he wasn't solely responsible for the fraud. "I let myself be talked into something, and that's my fault," he said, without saying who convinced him. "I thought I could escape eventually. I thought it'd be quick, but I couldn't."
Carl Shapiro, Jeffry Picower, Stanley Chais, and Norm Levy have been linked to Bernard L. Madoff Investment Securities LLC for years. Madoff's scheme made these men hundreds of millions of dollars in the 1960s and 1970s.
Madoff told Fishman, "Everyone was greedy, everyone wanted to go on." He says the Big Four and others who pumped client funds to him, outsourcing their asset management, must have suspected his returns or should have. "How can you make 15%-18% when everyone else is making less?" said Madoff.
How Madoff Got Away with It for So Long
Madoff's high returns made clients look the other way. He deposited their money in a Chase Manhattan Bank account, which merged to become JPMorgan Chase & Co. in 2000. The bank may have made $483 million from those deposits, so it didn't investigate.
When clients redeemed their investments, Madoff funded the payouts with new capital he attracted by promising unbelievable returns and earning his victims' trust. Madoff created an image of exclusivity by turning away clients. This model let half of Madoff's investors profit. These investors must pay into a victims' fund for defrauded investors.
Madoff wooed investors with his philanthropy. He defrauded nonprofits, including the Elie Wiesel Foundation for Peace and Hadassah. He approached congregants through his friendship with J. Ezra Merkin, a synagogue officer. Madoff allegedly stole $1 billion to $2 billion from his investors.
Investors believed Madoff for several reasons:
- His public portfolio seemed to be blue-chip stocks.
- His returns were high (10-20%) but consistent and not outlandish. In a 1992 interview with Madoff, the Wall Street Journal reported: "[Madoff] insists the returns were nothing special, given that the S&P 500-stock index returned 16.3% annually from 1982 to 1992. 'I'd be surprised if anyone thought matching the S&P over 10 years was remarkable,' he says.
- "He said he was using a split-strike collar strategy. A collar protects underlying shares by purchasing an out-of-the-money put option.
SEC inquiry
The Securities and Exchange Commission had been investigating Madoff and his securities firm since 1999, which frustrated many after he was prosecuted because they felt the biggest damage could have been prevented if the initial investigations had been rigorous enough.
Harry Markopolos was a whistleblower. In 1999, he figured Madoff must be lying in an afternoon. The SEC ignored his first Madoff complaint in 2000.
Markopolos wrote to the SEC in 2005: "The largest Ponzi scheme is Madoff Securities. This case has no SEC reward, so I'm turning it in because it's the right thing to do."
Many believed the SEC's initial investigations could have prevented Madoff's worst damage.
Markopolos found irregularities using a "Mosaic Method." Madoff's firm claimed to be profitable even when the S&P fell, which made no mathematical sense given what he was investing in. Markopolos said Madoff Securities' "undisclosed commissions" were the biggest red flag (1 percent of the total plus 20 percent of the profits).
Markopolos concluded that "investors don't know Bernie Madoff manages their money." Markopolos learned Madoff was applying for large loans from European banks (seemingly unnecessary if Madoff's returns were high).
The regulator asked Madoff for trading account documentation in 2005, after he nearly went bankrupt due to redemptions. The SEC drafted letters to two of the firms on his six-page list but didn't send them. Diana Henriques, author of "The Wizard of Lies: Bernie Madoff and the Death of Trust," documents the episode.
In 2008, the SEC was criticized for its slow response to Madoff's fraud.
Confession, sentencing of Bernie Madoff
Bernard L. Madoff Investment Securities LLC reported 5.6% year-to-date returns in November 2008; the S&P 500 fell 39%. As the selling continued, Madoff couldn't keep up with redemption requests, and on Dec. 10, he confessed to his sons Mark and Andy, who worked at his firm. "After I told them, they left, went to a lawyer, who told them to turn in their father, and I never saw them again. 2008-12-11: Bernie Madoff arrested.
Madoff insists he acted alone, but several of his colleagues were jailed. Mark Madoff died two years after his father's fraud was exposed. Madoff's investors committed suicide. Andy Madoff died of cancer in 2014.
2009 saw Madoff's 150-year prison sentence and $170 billion forfeiture. Marshals sold his three homes and yacht. Prisoner 61727-054 at Butner Federal Correctional Institution in North Carolina.
Madoff's lawyers requested early release on February 5, 2020, claiming he has a terminal kidney disease that may kill him in 18 months. Ten years have passed since Madoff's sentencing.
Bernie Madoff's Ponzi scheme aftermath
The paper trail of victims' claims shows Madoff's complexity and size. Documents show Madoff's scam began in the 1960s. His final account statements show $47 billion in "profit" from fake trades and shady accounting.
Thousands of investors lost their life savings, and multiple stories detail their harrowing loss.
Irving Picard, a New York lawyer overseeing Madoff's bankruptcy, has helped investors. By December 2018, Picard had recovered $13.3 billion from Ponzi scheme profiteers.
A Madoff Victim Fund (MVF) was created in 2013 to help compensate Madoff's victims, but the DOJ didn't start paying out the $4 billion until late 2017. Richard Breeden, a former SEC chair who oversees the fund, said thousands of claims were from "indirect investors"
Breeden and his team had to reject many claims because they weren't direct victims. Breeden said he based most of his decisions on one simple rule: Did the person invest more than they withdrew? Breeden estimated 11,000 "feeder" investors.
Breeden wrote in a November 2018 update for the Madoff Victim Fund, "We've paid over 27,300 victims 56.65% of their losses, with thousands more to come." In December 2018, 37,011 Madoff victims in the U.S. and around the world received over $2.7 billion. Breeden said the fund expected to make "at least one more significant distribution in 2019"
This post is a summary. Read full article here
Sam Hickmann
3 years ago
What is this Fed interest rate everybody is talking about that makes or breaks the stock market?
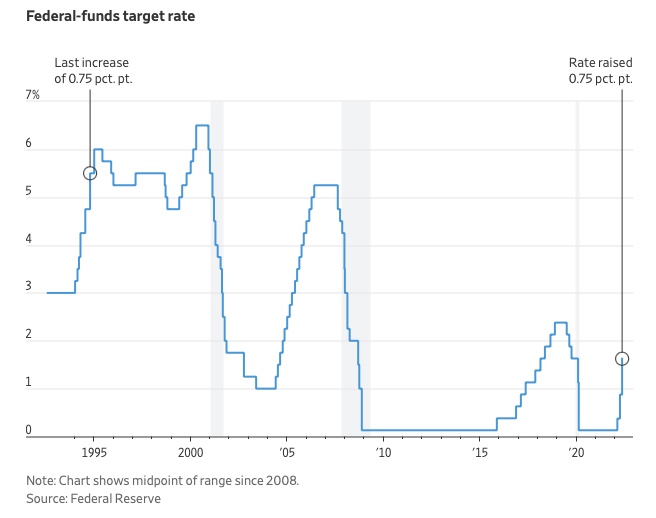
The Federal Funds Rate (FFR) is the target interest rate set by the Federal Reserve System (Fed)'s policy-making body (FOMC). This target is the rate at which the Fed suggests commercial banks borrow and lend their excess reserves overnight to each other.
The FOMC meets 8 times a year to set the target FFR. This is supposed to promote economic growth. The overnight lending market sets the actual rate based on commercial banks' short-term reserves. If the market strays too far, the Fed intervenes.
Banks must keep a certain percentage of their deposits in a Federal Reserve account. A bank's reserve requirement is a percentage of its total deposits. End-of-day bank account balances averaged over two-week reserve maintenance periods are used to determine reserve requirements.
If a bank expects to have end-of-day balances above what's needed, it can lend the excess to another institution.
The FOMC adjusts interest rates based on economic indicators that show inflation, recession, or other issues that affect economic growth. Core inflation and durable goods orders are indicators.
In response to economic conditions, the FFR target has changed over time. In the early 1980s, inflation pushed it to 20%. During the Great Recession of 2007-2009, the rate was slashed to 0.15 percent to encourage growth.
Inflation picked up in May 2022 despite earlier rate hikes, prompting today's 0.75 percent point increase. The largest increase since 1994. It might rise to around 3.375% this year and 3.1% by the end of 2024.

Ben Carlson
3 years ago
Bear market duration and how to invest during one

Bear markets don't last forever, but that's hard to remember. Jamie Cullen's illustration
A bear market is a 20% decline from peak to trough in stock prices.
The S&P 500 was down 24% from its January highs at its low point this year. Bear market.
The U.S. stock market has had 13 bear markets since WWII (including the current one). Previous 12 bear markets averaged –32.7% losses. From peak to trough, the stock market averaged 12 months. The average time from bottom to peak was 21 months.
In the past seven decades, a bear market roundtrip to breakeven has averaged less than three years.
Long-term averages can vary widely, as with all historical market data. Investors can learn from past market crashes.
Historical bear markets offer lessons.
Bear market duration
A bear market can cost investors money and time. Most of the pain comes from stock market declines, but bear markets can be long.
Here are the longest U.S. stock bear markets since World war 2:
Stock market crashes can make it difficult to break even. After the 2008 financial crisis, the stock market took 4.5 years to recover. After the dotcom bubble burst, it took seven years to break even.
The longer you're underwater in the market, the more suffering you'll experience, according to research. Suffering can lead to selling at the wrong time.
Bear markets require patience because stocks can take a long time to recover.
Stock crash recovery
Bear markets can end quickly. The Corona Crash in early 2020 is an example.
The S&P 500 fell 34% in 23 trading sessions, the fastest bear market from a high in 90 years. The entire crash lasted one month. Stocks broke even six months after bottoming. Stocks rose 100% from those lows in 15 months.
Seven bear markets have lasted two years or less since 1945.
The 2020 recovery was an outlier, but four other bear markets have made investors whole within 18 months.
During a bear market, you don't know if it will end quickly or feel like death by a thousand cuts.
Recessions vs. bear markets
Many people believe the U.S. economy is in or heading for a recession.
I agree. Four-decade high inflation. Since 1945, inflation has exceeded 5% nine times. Each inflationary spike caused a recession. Only slowing economic demand seems to stop price spikes.
This could happen again. Stocks seem to be pricing in a recession.
Recessions almost always cause a bear market, but a bear market doesn't always equal a recession. In 1946, the stock market fell 27% without a recession in sight. Without an economic slowdown, the stock market fell 22% in 1966. Black Monday in 1987 was the most famous stock market crash without a recession. Stocks fell 30% in less than a week. Many believed the stock market signaled a depression. The crash caused no slowdown.
Economic cycles are hard to predict. Even Wall Street makes mistakes.
Bears vs. bulls
Bear markets for U.S. stocks always end. Every stock market crash in U.S. history has been followed by new all-time highs.
How should investors view the recession? Investing risk is subjective.
You don't have as long to wait out a bear market if you're retired or nearing retirement. Diversification and liquidity help investors with limited time or income. Cash and short-term bonds drag down long-term returns but can ensure short-term spending.
Young people with years or decades ahead of them should view this bear market as an opportunity. Stock market crashes are good for net savers in the future. They let you buy cheap stocks with high dividend yields.
You need discipline, patience, and planning to buy stocks when it doesn't feel right.
Bear markets aren't fun because no one likes seeing their portfolio fall. But stock market downturns are a feature, not a bug. If stocks never crashed, they wouldn't offer such great long-term returns.
You might also like

Hudson Rennie
3 years ago
My Work at a $1.2 Billion Startup That Failed
Sometimes doing everything correctly isn't enough.

In 2020, I could fix my life.
After failing to start a business, I owed $40,000 and had no work.
A $1.2 billion startup on the cusp of going public pulled me up.
Ironically, it was getting ready for an epic fall — with the world watching.
Life sometimes helps. Without a base, even the strongest fall. A corporation that did everything right failed 3 months after going public.
First-row view.
Apple is the creator of Adore.
Out of respect, I've altered the company and employees' names in this account, despite their failure.
Although being a publicly traded company, it may become obvious.
We’ll call it “Adore” — a revolutionary concept in retail shopping.
Two Apple execs established Adore in 2014 with a focus on people-first purchasing.
Jon and Tim:
The concept for the stylish Apple retail locations you see today was developed by retail expert Jon Swanson, who collaborated closely with Steve Jobs.
Tim Cruiter is a graphic designer who produced the recognizable bouncing lamp video that appears at the start of every Pixar film.
The dynamic duo realized their vision.
“What if you could combine the convenience of online shopping with the confidence of the conventional brick-and-mortar store experience.”
Adore's mobile store concept combined traditional retail with online shopping.
Adore brought joy to 70+ cities and 4 countries over 7 years, including the US, Canada, and the UK.
Being employed on the ground floor, with world dominance and IPO on the horizon, was exciting.
I started as an Adore Expert.
I delivered cell phones, helped consumers set them up, and sold add-ons.
As the company grew, I became a Virtual Learning Facilitator and trained new employees across North America using Zoom.
In this capacity, I gained corporate insider knowledge. I worked with the creative team and Jon and Tim.

It's where I saw company foundation fissures. Despite appearances, investors were concerned.
The business strategy was ground-breaking.
Even after seeing my employee stocks fall from a home down payment to $0 (when Adore filed for bankruptcy), it's hard to pinpoint what went wrong.
Solid business model, well-executed.
Jon and Tim's chase for public funding ended in glory.
Here’s the business model in a nutshell:
Buying cell phones is cumbersome. You have two choices:
Online purchase: not knowing what plan you require or how to operate your device.
Enter a store, which can be troublesome and stressful.
Apple, AT&T, and Rogers offered Adore as a free delivery add-on. Customers could:
Have their phone delivered by UPS or Canada Post in 1-2 weeks.
Alternately, arrange for a person to visit them the same day (or sometimes even the same hour) to assist them set up their phone and demonstrate how to use it (transferring contacts, switching the SIM card, etc.).
Each Adore Expert brought a van with extra devices and accessories to customers.
Happy customers.
Here’s how Adore and its partners made money:
Adores partners appreciated sending Experts to consumers' homes since they improved customer satisfaction, average sale, and gadget returns.
**Telecom enterprises have low customer satisfaction. The average NPS is 30/100. Adore's global NPS was 80.
Adore made money by:
a set cost for each delivery
commission on sold warranties and extras
Consumer product applications seemed infinite.
A proprietary scheduling system (“The Adore App”), allowed for same-day, even same-hour deliveries.
It differentiates Adore.
They treated staff generously by:
Options on stock
health advantages
sales enticements
high rates per hour
Four-day workweeks were set by experts.
Being hired early felt like joining Uber, Netflix, or Tesla. We hoped the company's stocks would rise.
Exciting times.
I smiled as I greeted more than 1,000 new staff.
I spent a decade in retail before joining Adore. I needed a change.
After a leap of faith, I needed a lifeline. So, I applied for retail sales jobs in the spring of 2019.
The universe typically offers you what you want after you accept what you need. I needed a job to settle my debt and reach $0 again.
And the universe listened.
After being hired as an Adore Expert, I became a Virtual Learning Facilitator. Enough said.
After weeks of economic damage from the pandemic.
This employment let me work from home during the pandemic. It taught me excellent business skills.
I was active in brainstorming, onboarding new personnel, and expanding communication as we grew.
This job gave me vital skills and a regular paycheck during the pandemic.
It wasn’t until January of 2022 that I left on my own accord to try to work for myself again — this time, it’s going much better.
Adore was perfect. We valued:
Connection
Discovery
Empathy
Everything we did centered on compassion, and we held frequent Justice Calls to discuss diversity and work culture.
The last day of onboarding typically ended in tears as employees felt like they'd found a home, as I had.
Like all nice things, the wonderful vibes ended.
First indication of distress
My first day at the workplace was great.
Fun, intuitive, and they wanted creative individuals, not salesman.
While sales were important, the company's vision was more important.
“To deliver joy through life-changing mobile retail experiences.”
Thorough, forward-thinking training. We had a module on intuition. It gave us role ownership.
We were flown cross-country for training, gave feedback, and felt like we made a difference. Multiple contacts responded immediately and enthusiastically.
The atmosphere was genuine.
Making money was secondary, though. Incredible service was a priority.
Jon and Tim answered new hires' questions during Zoom calls during onboarding. CEOs seldom meet new hires this way, but they seemed to enjoy it.
All appeared well.
But in late 2021, things started changing.
Adore's leadership changed after its IPO. From basic values to sales maximization. We lost communication and were forced to fend for ourselves.
Removed the training wheels.
It got tougher to gain instructions from those above me, and new employees told me their roles weren't as advertised.
External money-focused managers were hired.
Instead of creative types, we hired salespeople.
With a new focus on numbers, Adore's uniqueness began to crumble.
Via Zoom, hundreds of workers were let go.
So.
Early in 2022, mass Zoom firings were trending. A CEO firing 900 workers over Zoom went viral.
Adore was special to me, but it became a headline.
30 June 2022, Vice Motherboard published Watch as Adore's CEO Fires Hundreds.
It described a leaked video of Jon Swanson laying off all staff in Canada and the UK.
They called it a “notice of redundancy”.
The corporation couldn't pay its employees.
I loved Adore's underlying ideals, among other things. We called clients Adorers and sold solutions, not add-ons.
But, like anything, a company is only as strong as its weakest link. And obviously, the people-first focus wasn’t making enough money.
There were signs. The expansion was presumably a race against time and money.
Adore finally declared bankruptcy.
Adore declared bankruptcy 3 months after going public. It happened in waves, like any large-scale fall.
Initial key players to leave were
Then, communication deteriorated.
Lastly, the corporate culture disintegrated.
6 months after leaving Adore, I received a letter in the mail from a Law firm — it was about my stocks.
Adore filed Chapter 11. I had to sue to collect my worthless investments.
I hoped those stocks will be valuable someday. Nope. Nope.
Sad, I sighed.
$1.2 billion firm gone.
I left the workplace 3 months before starting a writing business. Despite being mediocre, I'm doing fine.
I got up as Adore fell.
Finally, can we scale kindness?
I trust my gut. Changes at Adore made me leave before it sank.
Adores' unceremonious slide from a top startup to bankruptcy is astonishing to me.
The company did everything perfectly, in my opinion.
first to market,
provided excellent service
paid their staff handsomely.
was responsible and attentive to criticism
The company wasn't led by an egotistical eccentric. The crew had centuries of cumulative space experience.
I'm optimistic about the future of work culture, but is compassion scalable?

Alexander Nguyen
3 years ago
A Comparison of Amazon, Microsoft, and Google's Compensation
Learn or earn

In 2020, I started software engineering. My base wage has progressed as follows:
Amazon (2020): $112,000
Microsoft (2021): $123,000
Google (2022): $169,000
I didn't major in math, but those jumps appear more than a 7% wage increase. Here's a deeper look at the three.
The Three Categories of Compensation
Most software engineering compensation packages at IT organizations follow this format.
Minimum Salary
Base salary is pre-tax income. Most organizations give a base pay. This is paid biweekly, twice monthly, or monthly.
Recruiting Bonus
Sign-On incentives are one-time rewards to new hires. Companies need an incentive to switch. If you leave early, you must pay back the whole cost or a pro-rated amount.
Equity
Equity is complex and requires its own post. A company will promise to give you a certain amount of company stock but when you get it depends on your offer. 25% per year for 4 years, then it's gone.
If a company gives you $100,000 and distributes 25% every year for 4 years, expect $25,000 worth of company stock in your stock brokerage on your 1 year work anniversary.
Performance Bonus
Tech offers may include yearly performance bonuses. Depends on performance and funding. I've only seen 0-20%.
Engineers' overall compensation usually includes:
Base Salary + Sign-On + (Total Equity)/4 + Average Performance Bonus
Amazon: (TC: 150k)

Base Pay System
Amazon pays Seattle employees monthly on the first work day. I'd rather have my money sooner than later, even if it saves processing and pay statements.
The company upped its base pay cap from $160,000 to $350,000 to compete with other tech companies.
Performance Bonus
Amazon has no performance bonus, so you can work as little or as much as you like and get paid the same. Amazon is savvy to avoid promising benefits it can't deliver.
Sign-On Bonus
Amazon gives two two-year sign-up bonuses. First-year workers could receive $20,000 and second-year workers $15,000. It's probably to make up for the company's strange equity structure.
If you leave during the first year, you'll owe the entire money and a prorated amount for the second year bonus.
Equity
Most organizations prefer a 25%, 25%, 25%, 25% equity structure. Amazon takes a different approach with end-heavy equity:
the first year, 5%
15% after one year.
20% then every six months
We thought it was constructed this way to keep staff longer.
Microsoft (TC: 185k)

Base Pay System
Microsoft paid biweekly.
Gainful Performance
My offer letter suggested a 0%-20% performance bonus. Everyone will be satisfied with a 10% raise at year's end.
But misleading press where the budget for the bonus is doubled can upset some employees because they won't earn double their expected bonus. Still barely 10% for 2022 average.
Sign-On Bonus
Microsoft's sign-on bonus is a one-time payout. The contract can require 2-year employment. You must negotiate 1 year. It's pro-rated, so that's fair.
Equity
Microsoft is one of those companies that has standard 25% equity structure. Except if you’re a new graduate.
In that case it’ll be
25% six months later
25% each year following that
New grads will acquire equity in 3.5 years, not 4. I'm guessing it's to keep new grads around longer.
Google (TC: 300k)

Base Pay Structure
Google pays biweekly.
Performance Bonus
Google's offer letter specifies a 15% bonus. It's wonderful there's no cap, but I might still get 0%. A little more than Microsoft’s 10% and a lot more than Amazon’s 0%.
Sign-On Bonus
Google gave a 1-year sign-up incentive. If the contract is only 1 year, I can move without any extra obligations.
Not as fantastic as Amazon's sign-up bonuses, but the remainder of the package might compensate.
Equity
We covered Amazon's tail-heavy compensation structure, so Google's front-heavy equity structure may surprise you.
Annual structure breakdown
33% Year 1
33% Year 2
22% Year 3
12% Year 4
The goal is to get them to Google and keep them there.
Final Thoughts
This post hopefully helped you understand the 3 firms' compensation arrangements.
There's always more to discuss, such as refreshers, 401k benefits, and business discounts, but I hope this shows a distinction between these 3 firms.

The Secret Developer
3 years ago
What Elon Musk's Take on Bitcoin Teaches Us

Tesla Q2 earnings revealed unethical dealings.
As of end of Q2, we have converted approximately 75% of our Bitcoin purchases into fiat currency
That’s OK then, isn’t it?
Elon Musk, Tesla's CEO, is now untrustworthy.
It’s not about infidelity, it’s about doing the right thing
And what can we learn?
The Opening Remark
Musk tweets on his (and Tesla's) future goals.
Don’t worry, I’m not expecting you to read it.
What's crucial?
Tesla will not be selling any Bitcoin
The Situation as It Develops
2021 Tesla spent $1.5 billion on Bitcoin. In 2022, they sold 75% of the ownership for $946 million.
That’s a little bit of a waste of money, right?
Musk predicted the reverse would happen.
What gives? Why would someone say one thing, then do the polar opposite?
The Justification For Change
Tesla's public. They must follow regulations. When a corporation trades, they must record what happens.
At least this keeps Musk some way in line.
We now understand Musk and Tesla's actions.
Musk claimed that Tesla sold bitcoins to maximize cash given the unpredictability of COVID lockdowns in China.
Tesla may buy Bitcoin in the future, he said.
That’s fine then. He’s not knocking the NFT at least.
Tesla has moved investments into cash due to China lockdowns.
That doesn’t explain the 180° though
Musk's Tweet isn't company policy. Therefore, the CEO's change of heart reflects the organization. Look.
That's okay, since
Leaders alter their positions when circumstances change.
Leaders must adapt to their surroundings. This isn't embarrassing; it's a leadership prerequisite.
Yet
The Man
Someone stated if you're not in the office full-time, you need to explain yourself. He doesn't treat his employees like adults.
This is the individual mentioned in the quote.
If Elon was not happy, you knew it. Things could get nasty
also, He fired his helper for requesting a raise.
This public persona isn't good. Without mentioning his disastrous performances on Twitter (pedo dude) or Joe Rogan. This image sums up the odd Podcast appearance:

Which describes the man.
I wouldn’t trust this guy to feed a cat
What we can discover
When Musk's company bet on Bitcoin, what happened?
Exactly what we would expect
The company's position altered without the CEO's awareness. He seems uncaring.
This article is about how something happened, not what happened. Change of thinking requires contrition.
This situation is about a lack of respect- although you might argue that followers on Twitter don’t deserve any
Tesla fans call the sale a great move.
It's absurd.
As you were, then.
Conclusion
Good luck if you gamble.
When they pay off, congrats!
When wrong, admit it.
You must take chances if you want to succeed.
Risks don't always pay off.
Mr. Musk lacks insight and charisma to combine these two attributes.
I don’t like him, if you hadn’t figured.
It’s probably all of the cheating.
